虽然官方文档(man capabilities)和《Linux 内核安全模块深入剖析》书的第六章对"能力"有很全面详细的描述,但是我之前遇到了两个和能力有关的案例,从文档中看不出来原因,只好猜测原因并从源码中确认结论。
本文记录这两个特殊案例,加深自己对"能力"概念的理解,也希望能对linux安全有兴趣的读者有点帮助。
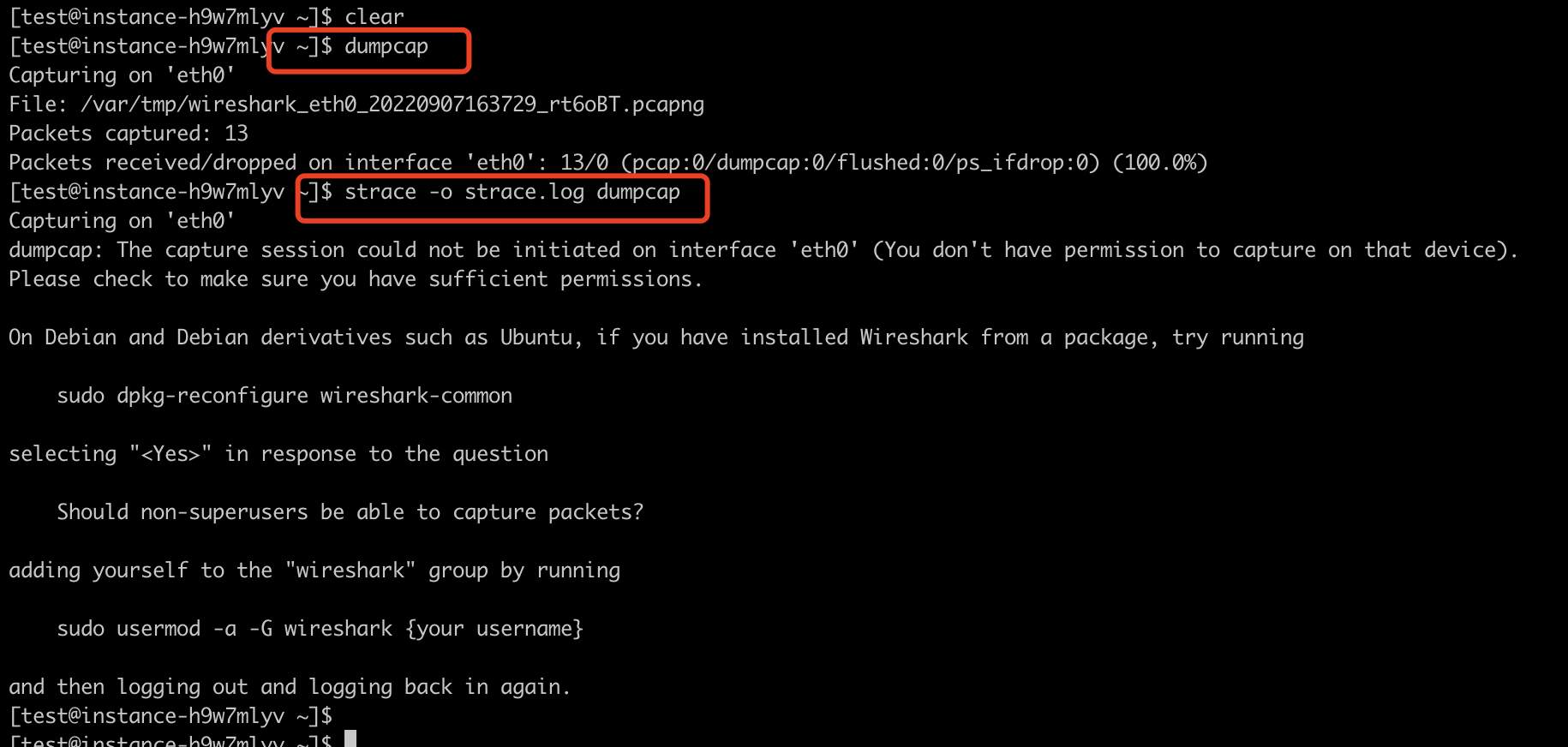
第一个案例是普通用户执行dumpcap时可以按照预期运行,而strace dumpcap时提示权限不足。如下

更详细的问题背景可以见正文,或者看我提的issue: https://github.com/strace/strace/issues/221
第二个案例是我好奇root用户执行su - test变成非root用户后会有哪些能力?
先来看第一个案例。
研究这个问题的起因
在 基于netfilter的后门 文章中,我最早是用dumpcap -i nflog:2333代替tcpdump -i nflog:2333抓包的。
我在安装dumpcap命令、添加x权限后,发现非root用户也可以用dumpcap抓整个主机上的包。如下
[[email protected] ~]# yum install wireshark -y // 安装dumpcap命令
[[email protected] ~]# chmod +x /usr/bin/dumpcap // 添加执行权限
[[email protected] ~]$ dumpcap -i eth0 // 抓eth0网卡的包
Capturing on 'eth0'
File: /var/tmp/wireshark_eth0_20220907165305_9Quu6X.pcapng
Packets captured: 17
Packets received/dropped on interface 'eth0': 17/0 (pcap:0/dumpcap:0/flushed:0/ps_ifdrop:0) (100.0%)一个普通用户能够获取主机上的所有流量,听着就很不安全,所以我就想看看为什么非root用户可以用dumpcap命令监听网卡流量。
[[email protected] ~]$ getcap /usr/bin/dumpcap
/usr/bin/dumpcap = cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw+ep如上,可以看到dumpcap有cap_net_raw文件能力。或许你知道只要线程有cap_net_raw能力,就可以用socket(AF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL))创建socket来抓包。
所以可以猜测dumpcap也是用AF_PACKET socket抓包的,于是我想执行strace dumpcap看一下系统调用中是否有创建AF_PACKET socket。然后发现普通用户执行strace dumpcap时提示报错,如下
[[email protected] ~]$ strace -o strace.log dumpcap
Capturing on 'eth0'
dumpcap: The capture session could not be initiated on interface 'eth0' (You don't have permission to capture on that device).
Please check to make sure you have sufficient permissions.
...这里就让我感觉很奇怪:为什么普通用户执行dumpcap时可以按照预期运行,而strace dumpcap时提示权限不足?
还有类似的现象:普通用户
strace ping www.baidu.com也会提示权限不足
为什么普通用户执行strace dumpcap时提示权限不足?
man execve看到下面一段文档
The aforementioned transformations of the effective IDs are not performed (i.e., the set-user-ID and set-group-ID bits are ignored) if any of the following is true:
* the no_new_privs attribute is set for the calling thread (see prctl(2));
* the underlying filesystem is mounted nosuid (the MS_NOSUID flag for mount(2)); or
* the calling process is being ptraced. // 进程正在被ptrace
The capabilities of the program file (see capabilities(7)) are also ignored if any of the above are true.man capabilities看到下面一段文档
Note: the capability transitions described above may not be performed (i.e., file capabilities may be ignored) for the same reasons that the set-user-ID and set-group-ID bits are ignored; see
execve(2).从文档得出结论:只要进程被ptrace,那么execve时就会忽略文件能力和set-uid/set-gid等。因为strace底层就是ptrace,所以似乎这个结论可以解释我遇到的现象。
但是当用root用户给strace文件添加能力后,普通用户运行strace dumpcap又可以正常工作,上面的结论就解释不通了。如下
[[email protected] ~]# setcap cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw+ep /usr/bin/strace // 给strace文件添加能力
[[email protected] ~]#
[[email protected] ~]# su - test // 切换到普通用户
...
[[email protected] ~]$ getcap /usr/bin/strace
/usr/bin/strace = cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw+ep
[[email protected] ~]$ getcap /usr/bin/dumpcap
/usr/bin/dumpcap = cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw+ep
[[email protected] ~]$ strace -o strace.log dumpcap // strace dumpcap现在可以抓包
Capturing on 'eth0'
File: /var/tmp/wireshark_eth0_20220908182215_A7Uikl.pcapng
Packets captured: 11
Packets received/dropped on interface 'eth0': 11/0 (pcap:0/dumpcap:0/flushed:0/ps_ifdrop:0) (100.0%)所以看起来,普通用户执行strace dumpcap后dumpcap进程的有效能力集是strace文件能力和dumpcap文件能力交集。
那到底是不是这样呢?
是不是交集?
strace dumpcap时,从用户态看strace原理大概如下
// fork后,strace子进程能力集和strace进程是相同的
pid_t pid = fork();
// 子进程
if (pid == 0) {
ptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME,0,NULL,NULL);
// 加载被调试的程序
execve("/usr/bin/dumpcap", NULL, NULL);
}内核在执行execve时,会执行到cap_bprm_set_creds函数,函数栈如下
[[email protected] ~]# bpftrace -e 'kprobe:cap_bprm_set_creds {printf("%s\n",kstack)}'
Attaching 1 probe...
cap_bprm_set_creds+1
security_bprm_set_creds+34
prepare_binprm+299
do_execveat_common.isra.37+1274
__x64_sys_execve+50 // execve系统调用入口
do_syscall_64+91
entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe+101代码位置在:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.18/source/security/commoncap.c#L854
可以看到cap_bprm_set_creds函数会对能力做交集
int cap_bprm_set_creds(struct linux_binprm *bprm)
{
const struct cred *old = current_cred();
struct cred *new = bprm->cred;
...
ret = get_file_caps(bprm, &effective, &has_fcap); // 会从文件扩展属性中找到能力集合,赋值给brpm->cred相应字段
...
if ((is_setid || __cap_gained(permitted, new, old)) &&
((bprm->unsafe & ~LSM_UNSAFE_PTRACE) ||
!ptracer_capable(current, new->user_ns))) {
/* downgrade; they get no more than they had, and maybe less */
if (!ns_capable(new->user_ns, CAP_SETUID) ||
(bprm->unsafe & LSM_UNSAFE_NO_NEW_PRIVS)) {
new->euid = new->uid;
new->egid = new->gid;
}
new->cap_permitted = cap_intersect(new->cap_permitted, // new->cap_permitted是execve后的进程允许能力集,当前的值是dumpcap文件的允许能力集
old->cap_permitted); // old->cap_permitted是当前进程的允许能力集,也就是strace fork后子进程的能力集
}
...
}那strace进程的能力集是怎么来的呢?
strace进程的能力集是怎么来的呢?
strace进程能力是根据bash进程能力和strace文件能力,按照计算规则得来的,如下

那普通用户的bash进程能力集又是啥呢?它是怎么计算出来的呢? 这就是我的第二个疑问
如下,可以看到普通用户的bash进程除了限制能力集其他能力集都是0
[[email protected] ~]# su - test
[[email protected] ~]$ ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
18042 pts/4 00:00:00 bash
[[email protected] ~]$ cat /proc/18042/status|grep -i cap
CapInh: 0000000000000000
CapPrm: 0000000000000000
CapEff: 0000000000000000
CapBnd: 000001ffffffffff
CapAmb: 0000000000000000test用户是
useradd test创建的普通用户
对比可以发现: root用户切换test用户后,能力变少了。
[[email protected] ~]# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
52739 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
[[email protected] ~]# cat /proc/52739/status|grep -i cap
CapInh: 0000000000000000
CapPrm: 000001ffffffffff
CapEff: 000001ffffffffff
CapBnd: 000001ffffffffff
CapAmb: 0000000000000000root用户通过su - test切换新用户后,为什么能力会变少呢?
为什么root用户切换到新用户后能力变少?
《Linux 内核安全模块深入剖析》6.4.2节中提到capset、capget、prctl三个系统调用都能改变进程的能力集,但是从下面可以看出来,su并没有用这三个系统调用
[[email protected] ~]# strace -f su - test 2>&1|grep -i cap
[[email protected] ~]# strace -f su - test 2>&1|grep -i -E '\bprctl'在《Linux系统编程手册》39.6节中提到这种情况
为了与用户 ID 在 0 与非 0 之间切换的传统含义保持兼容,在改变进程的用户 ID(使用 setuid()等)时,内核会完成下列操作。
1. 如果真实用户ID、有效用户ID或saved set-user-ID之前的值为0,那么修改了用户 ID 之后,所有这三个 ID 的值都会变成非 0,并且进程的许可和有效能力集会被清除 (即所有的能力都被永久地删除了)。
2. 如果有效用户 ID 从 0 变成了非 0,那么有效能力集会被清除(即有效能力被删除了,但那些位于许可集中的能力会被再次提升)。也就是说,当用户调用setuid系统调用从特权用户变成非特权用户时,允许能力集和有效能力集会被清除。
下面来验证一下,看看su程序是不是用到了setuid系统调用、setuid系统调用是不是真的可能清空能力集。
验证setuid和能力的关系
通过strace可以观察到su程序确实调用了setuid
[[email protected] ~]# strace -f su - test 2>&1|grep setuid
[pid 23628] setuid(1000 <unfinished ...>
[pid 23628] <... setuid resumed>) = 0阅读内核代码后,也可以看到在cap_emulate_setxuid函数中内核清除了进程的能力集。
代码位置在:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.18/source/security/commoncap.c#L1005
static inline void cap_emulate_setxuid(struct cred *new, const struct cred *old)
{
...
cap_clear(new->cap_permitted);
cap_clear(new->cap_effective);
...
cap_clear(new->cap_ambient);
}
...
}cap_emulate_setxuid函数因为inline被内敛优化,所以没有办法被bpftrace观察到,但我们可以观察它的调用者cap_task_fix_setuid函数。
在su - test时,可以观察到执行了cap_task_fix_setuid函数,并且有效能力集从0x1ffffffffff变成0。如下
[[email protected] ~]# bpftrace -e 'kfunc:cap_task_fix_setuid /comm=="su"/ {printf("%x,%x\n", ((struct cred*)args->new)->cap_effective.cap[0], ((struct cred*)args->new)->cap_effective.cap[1]);}'
...
ffffffff,1ff
[[email protected] ~]# bpftrace -e 'kretfunc:cap_task_fix_setuid /comm=="su"/ {printf("%x,%x\n", ((struct cred*)args->new)->cap_effective.cap[0], ((struct cred*)args->new)->cap_effective.cap[1]);}'
...
0,0从setuid到cap_task_fix_setuid,函数调用栈如下
[[email protected] ~]# bpftrace -e 'kprobe:cap_task_fix_setuid /comm=="su"/ {printf("%s\n", kstack)}'
Attaching 1 probe...
cap_task_fix_setuid+1
security_task_fix_setuid+48
__sys_setuid+151 // setuid系统调用入口
do_syscall_64+91
entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe+101
所以,setuid时root用户变成非root用户时,允许能力集和有效能力集会被清零。
能力的计算机制感觉很复杂。
普通用户在执行strace xxx后,xxx进程的有效能力集可以认为是strace文件和xxx文件的允许能力集的交集。
调用setuid系统调用从特权用户变成非特权用户时,允许能力集和有效能力集会被清除。
通过阅读代码和bpftrace工具,可以定位到内核中处理能力的代码位置,进一步验证结论。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh