关于Aced
Aced是一款针对活动目录的安全检测与分析工具,该工具可以帮助广大研究人员解析单个目标活动目录的DACL。Aced可以针对目标帐户识别可疑的入站访问权限,解析入站权限的SID,并将该数据呈现给研究人员。除此之外,Aced还整合了pyldapsearch工具的日志记录功能,可以在本地记录目标主体的LDAP属性,而pyldapsearch的配套工具BOFHound可以对这些属性进行解析,随后我们可以将收集到的数据导入到BloodHound中进行后续操作。
使用场景
我们之所以会开发Aced,是因为我们需要一种更有针对性的方法来查询ACL。虽然Bloodhound的功能已经很强大了,但它收集到的数据太过复杂。而Aced只会收集研究人员所需要的目标数据,并提供了针对目标数据的更多控制机制。对于LDAP,我们只需要查询我们想要知道的数据,而无需执行很多复杂且量大的LDAP查询操作,这样就可以尽可能地降低被检测到的概率。Aced可以选择使用LDAPS,而不是LDAP。通过与BloodHound集成,我们可以将收集到的数据以我们熟悉的格式进行存储,也可以跟团队共享。
工具下载
由于该工具基于Python开发,因此我们首先需要在本地设备上安装并配置好Python环境。接下来,使用下列命令将该项目源码克隆至本地:
git clone https://github.com/garrettfoster13/aced.git
工具使用
└─# python3 aced.py -h_____|A . | _____| /.\ ||A ^ | _____|(_._)|| / \ ||A _ | _____| | || \ / || ( ) ||A_ _ ||____V|| . ||(_'_)||( v )||____V|| | || \ / ||____V|| . ||____V|v1.0Parse and log a target principal's DACL.@garrfosterusage: aced.py [-h] [-ldaps] [-dc-ip DC_IP] [-k] [-no-pass] [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] [-aes hex key] [-debug] [-no-smb] targetTool to enumerate a single target's DACL in Active Directoryoptional arguments:-h, --help show this help message and exitAuthentication:target [[domain/username[:password]@]<address>-ldaps Use LDAPS isntead of LDAPOptional Flags:-dc-ip DC_IP IP address or FQDN of domain controller-k, --kerberos Use Kerberos authentication. Grabs credentials from ccache file (KRB5CCNAME) based on target parameters. If validcredentials cannot be found, it will use the ones specified in the command line-no-pass don't ask for password (useful for -k)-hashes LMHASH:NTHASHLM and NT hashes, format is LMHASH:NTHASH-aes hex key AES key to use for Kerberos Authentication (128 or 256 bits)-debug Enable verbose logging.-no-smb Do not resolve DC hostname through SMB. Requires a FQDN with -dc-ip.
(向右滑动、查看更多)参数解释
-h, --help:显示工具帮助信息和退出;target:[[domain/username[:password]@]<address>-ldaps:使用LDAPS;-dc-ip DC_IP:域控制器的IP地址或FQDN-k, --kerberos:使用Kerberos认证,根据目标参数从ccache文件获取凭证。如果没有找到有效凭证,工具将使用命令行参数指定的凭证;-no-pass:不询问密码;-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH:LM和NT哈希,格式为LMHASH:NTHASH;-aes hex key:Kerberos 认证所使用的AES密钥(128或256位);-debug:启用Verbose模式;-no-smb:不通过SMB解析DC主机名,需要FQDN(向右滑动、查看更多)
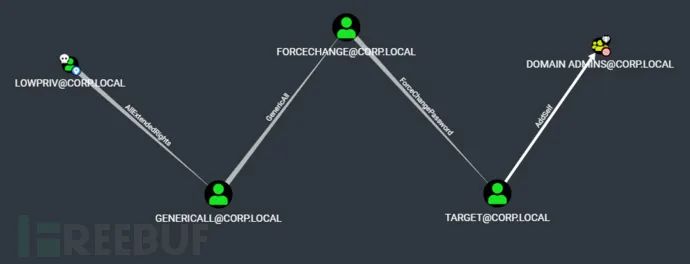
工具演示
在下面的工具演示样例中,我们使用了corp.local\lowpriv账号的凭证信息。首先,我们枚举了域管理员,并通过分析有价值的目标来识别潜在的提权路径:
项目地址
参考资料:
https://github.com/fortalice/pyldapsearch https://github.com/fortalice/bofhound http://directoryadmin.blogspot.com/2019/10/hunting-bad-ldap-queries-on-your-dc.html
精彩推荐
文章来源: http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MjM5NjA0NjgyMA==&mid=2651193092&idx=4&sn=c70c0268f708096bd989fd9b00678c0e&chksm=bd1e6d8f8a69e4991d62a2109284a19c6bcd409b584117caa719b275e770794e255de666af6a#rd
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh