2019-08-04
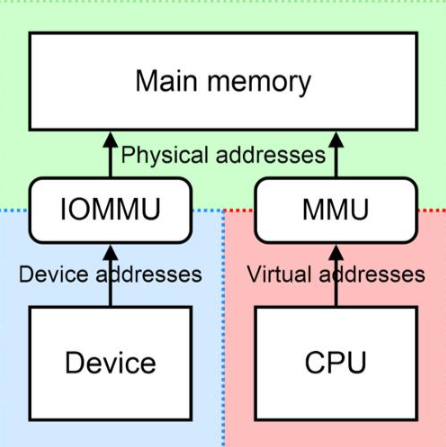
MMU is used by CPU to translate a virtual address to physical address. The virtual address of MMU is in CPU’s view. The IOMMU in contrast is used by device to translate another virtual address called IOVA(IO virtual address) to physical address. Following show the basic idea of IOMMU.
IOMMU is very useful for device assignment in virtual machine platform. Device assignment directly assign the physical IO device to VMs. In device assignment the driver for an assigned IO device runs in the VM to which it is assigned and is allowed to interact directly with the device hardware with minimal or no VMM involvement. Device assignment has very high performance compared with the software-based device emulation and virtio-based device emulation.
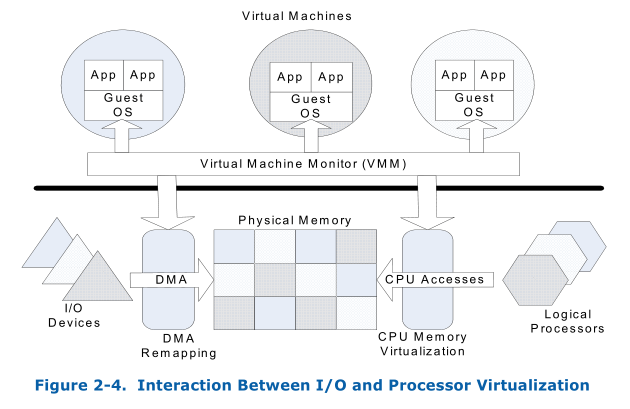
Device assignment introduces an issue just like how the virtual machine accesses the VM’s physical memory. In virtual machine environment, the OS in VM uses the virtual address to access data, this guest virtual address(GVA) is translated to guest physical address(GPA). However we still need to access the host physical address as it stores data. This is done by EPT in VT-x hardware. For device assignment, the driver in guest OS specify the guest physical address for DMA, however the physical IO device need the host physical adress to access. The device need something like EPT to translate the DMA address(GPA) specify by device driver in guest OS to host physical address. This is the mainly purpose of IOMMU. IOMMU has the ability to isolate and restrict device accesses to the resources(the physical memory allcated to the VM for example) owned by the virtual machine. Following figure depicts how system software interacts with hardware support for both VT-x and VT-d.
Intel IOMMU(also called VT-d) has the following capabilities:
- DMA remapping: this supports address translations for DMA from device.
- Interrupt remapping: this supports isolation and routing of interrupts from devices and external interrupt controllers to appropriate VMs.
- Interrupt posting: this supports direct delivery of virtual interrupts from devfices and excternal interrupt controllers to virtual processors.
qemu/kvm virtual machine now uses VFIO to do device assignment. VFIO utilizes IOMMU’s DMA remapping to do DMA in VM, but it doesn’t use interrupt remapping as it is not efficient compared with the irqfd in kernel IMO.
The basic idea of IOMMU DMA remapping is the same as the MMU for address translation. When the physical IO device do DMA, the address for DMA is called IOVA, the IOMMU first using the device’s address(PCI BDF address) to find a page table then using the the IOVA to walk this page table and finally get the host physical address. This is very like that how the MMU work to translate a virtual address to a physical address. Following figure show the basic idea of DMA remapping, this is the legacy mode, there is also a scalable mode, though the detail differs, the idea is the same.
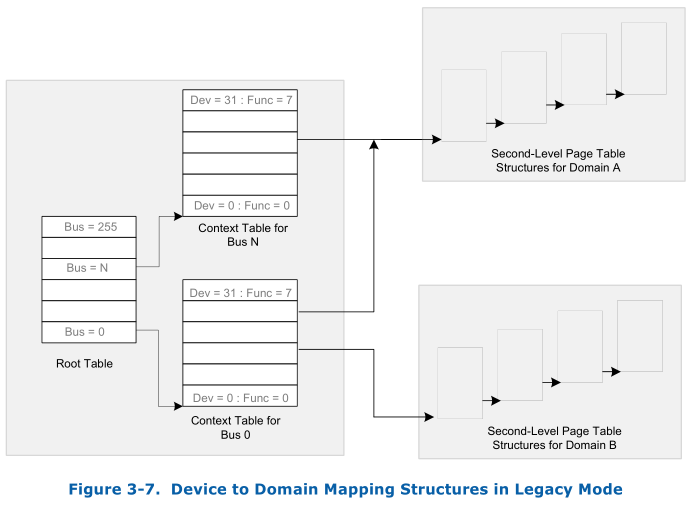
The device’s bus is useds to index in Root Table, the root table is 4-KByte in size and contains 256 root-entries. The root-table-entry contains the context-table pointer which references the context-table for all the devices on the bus identified by the root-entry.
A context-entry maps a specific I/O device on a bus to the domain to which it is assigned, and, in turn, to the address translation structures for the domain. Each context-table contains 256 entries, with each entry corresponding to a PCI device function on the bus. For a PCI device, the device and function numbers (lower 8-bits) are used to index into the context-table.
The root-table and context table is setup by the IOMMU driver, the page table is usually setup by the VMM. Of course, any process can do setup this page table. The IOVA is used as the input for the IOMMU translation, this address is device’s view address. The IOVA can be any address that is meaningfor for the guest or process. For example, the qemu/kvm uses the GPA as the IOVA and also you can uses another address as the IOVA. The VFIO uses IOMMU to do the translation from GPA to HPA.
Next I will write the code analysis of the intel IOMMU driver. Also I will write a post for the iommu hardware’s implementation as qemu implements the amd and intel iommu.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh